Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5896 - Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Hypovolemic Phlebotomy in Patients With Liver Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Khadija Mohib, MD (she/her/hers)
Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Khadija Mohib, MD1, Haseeb Javed Khan, MBBS2, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD4, Marium Khan, MBBS5, Muhammad Abdullah Ali, MBBS6, Muhammad Mukhlis. Hussain, MBBS7, Umama Alam, 8, Muhammad Fawad Tahir, MBBS9, Sania Aimen, MBBS10, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD11
1Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 5Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, Pakistan, Peshawar, Northern Areas, Pakistan; 7Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 8Khyber medical college, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9H.B.S Medical and Dental College, Islamabad, Pakistan, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 10Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 11Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Significant blood loss is common in major liver surgery, heightening the need for transfusions and increasing postoperative risks. Hypovolemic phlebotomy (HP) has surfaced as an effective method to reduce bleeding by decreasing central venous pressure, all without the need for volume replacement. This meta-analysis examines the safety and effectiveness of HP in reducing blood loss during liver resection.
Methods: From inception until March 2025, a comprehensive literature review was performed using PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect. Risk ratios (RR) and weighted mean differences (WMD) for both categorical and continuous outcomes were aggregated utilizing the random effects model in Review Manager software version 5.4.1. A sensitivity analysis, which excluded one study at a time, was executed to evaluate heterogeneity. The assessment of quality was conducted using the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
Results: This meta-analysis includes eight studies with a total of 1,901 patients. In the HP group, blood loss is significantly lower compared to the placebo group (MD: -440.13 mL; 95% CI: [-756.20, -124.07]; p = 0.006). The HP arm also sees a notable decrease in hospital stay length (MD = -15.98 days; 95% CI: [-21.36, -10.60]; p < 0.01). Other measures, including red blood cell transfusion (RR=0.60; 95% CI:[0.35, 1.04]; p=0.07), major complications (RR=1.40; 95% CI: [0.93, 2.13]; p=0.11), and overall complications (RR = 1.15; 95% CI: [0.86, 1.53]; p = 0.35), show comparable results between both groups.
Discussion: HP greatly minimizes blood loss during liver resection surgery and shortens hospital stays for patients while avoiding an increase in transfusion requirements or complications, demonstrating its safety and efficacy. Additional research could further enhance its implementation in clinical settings.
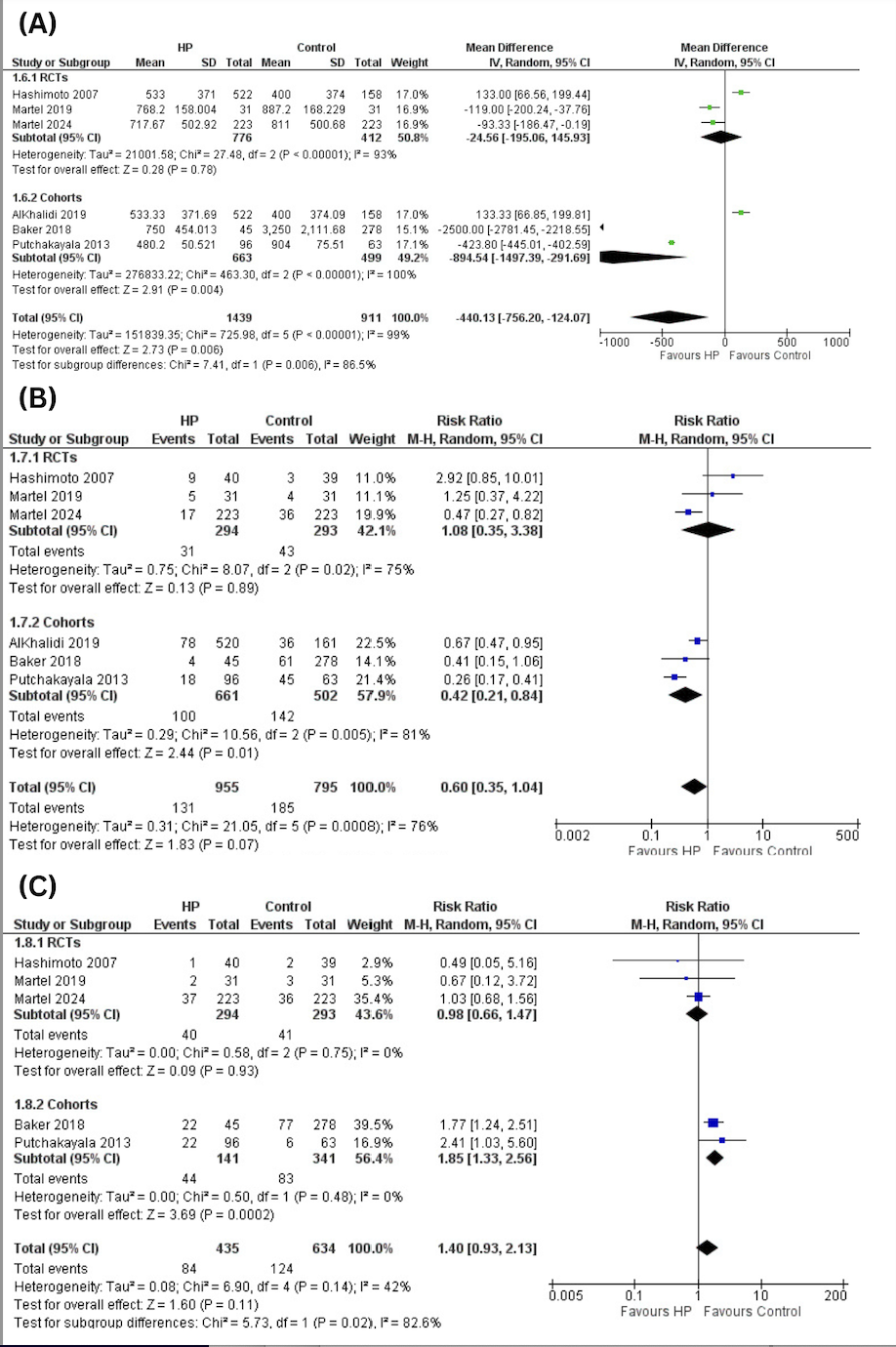
Figure: Figure 1: (A) Blood Loss (B) Red Blood Cell Transfusion (C) Major Complications
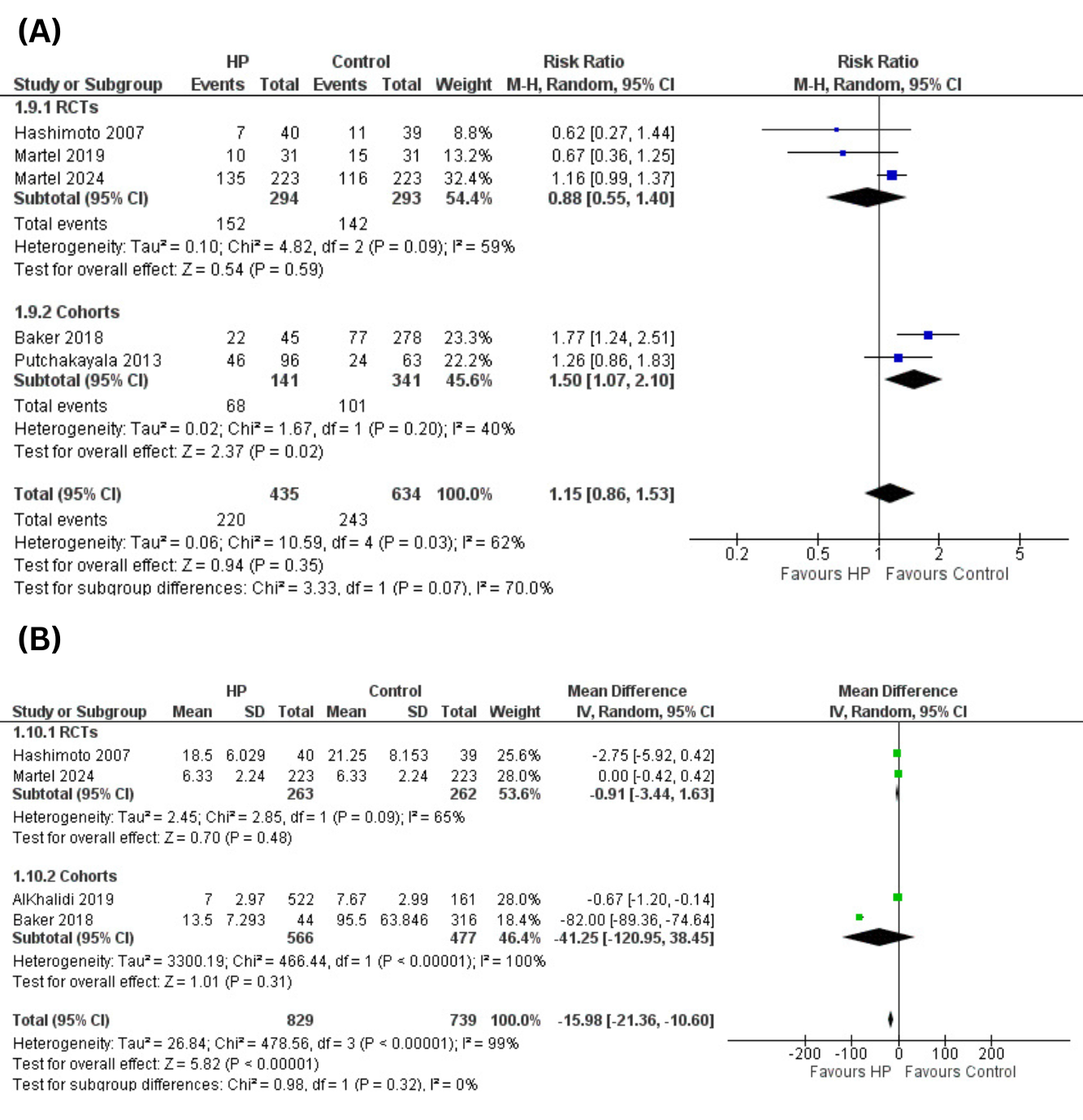
Figure: Figure 2: (A) Overall Complications (B) Length of hospital stay
Disclosures:
Khadija Mohib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Javed Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marium Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Abdullah Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umama Alam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Fawad Tahir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Khadija Mohib, MD1, Haseeb Javed Khan, MBBS2, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD4, Marium Khan, MBBS5, Muhammad Abdullah Ali, MBBS6, Muhammad Mukhlis. Hussain, MBBS7, Umama Alam, 8, Muhammad Fawad Tahir, MBBS9, Sania Aimen, MBBS10, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD11. P5896 - Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Hypovolemic Phlebotomy in Patients With Liver Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 5Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 6Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, Pakistan, Peshawar, Northern Areas, Pakistan; 7Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 8Khyber medical college, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9H.B.S Medical and Dental College, Islamabad, Pakistan, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan; 10Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 11Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Significant blood loss is common in major liver surgery, heightening the need for transfusions and increasing postoperative risks. Hypovolemic phlebotomy (HP) has surfaced as an effective method to reduce bleeding by decreasing central venous pressure, all without the need for volume replacement. This meta-analysis examines the safety and effectiveness of HP in reducing blood loss during liver resection.
Methods: From inception until March 2025, a comprehensive literature review was performed using PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect. Risk ratios (RR) and weighted mean differences (WMD) for both categorical and continuous outcomes were aggregated utilizing the random effects model in Review Manager software version 5.4.1. A sensitivity analysis, which excluded one study at a time, was executed to evaluate heterogeneity. The assessment of quality was conducted using the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
Results: This meta-analysis includes eight studies with a total of 1,901 patients. In the HP group, blood loss is significantly lower compared to the placebo group (MD: -440.13 mL; 95% CI: [-756.20, -124.07]; p = 0.006). The HP arm also sees a notable decrease in hospital stay length (MD = -15.98 days; 95% CI: [-21.36, -10.60]; p < 0.01). Other measures, including red blood cell transfusion (RR=0.60; 95% CI:[0.35, 1.04]; p=0.07), major complications (RR=1.40; 95% CI: [0.93, 2.13]; p=0.11), and overall complications (RR = 1.15; 95% CI: [0.86, 1.53]; p = 0.35), show comparable results between both groups.
Discussion: HP greatly minimizes blood loss during liver resection surgery and shortens hospital stays for patients while avoiding an increase in transfusion requirements or complications, demonstrating its safety and efficacy. Additional research could further enhance its implementation in clinical settings.

Figure: Figure 1: (A) Blood Loss (B) Red Blood Cell Transfusion (C) Major Complications

Figure: Figure 2: (A) Overall Complications (B) Length of hospital stay
Disclosures:
Khadija Mohib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Javed Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marium Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Abdullah Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umama Alam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Fawad Tahir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Khadija Mohib, MD1, Haseeb Javed Khan, MBBS2, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD4, Marium Khan, MBBS5, Muhammad Abdullah Ali, MBBS6, Muhammad Mukhlis. Hussain, MBBS7, Umama Alam, 8, Muhammad Fawad Tahir, MBBS9, Sania Aimen, MBBS10, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD11. P5896 - Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Hypovolemic Phlebotomy in Patients With Liver Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
