Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5872 - The Impact of Ischemic Hepatitis on Outcomes and Healthcare Resources Utilization in Patients With Sepsis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Khaled Al Smadi, MD
University of California Riverside School of Medicine
Rancho Cucamonga, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Khaled Al Smadi, MD1, Muhammad Shikaib. Shabbir, MD2, Ashujot Dang, MD3, Miguel Salazar, MD4, Donghyun Ko, MD5, Do Han Kim, MD, MSc6, Gianina Flocco, MD7, Zeid Kayali, MD4, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD8
1University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Rancho Cucamonga, CA; 2University of California Riverside School of Medicine, San Bernardino, CA; 3University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Redlands, CA; 4University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Rialto, CA; 5Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 6Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 7Cleveland Clinic, Fairview Park, OH; 8Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Sepsis is a clinical syndrome characterized by a dysregulated systemic immune response to infection, leading to end-organ dysfunction. Sepsis remains to be a leading cause of in-hospital mortality worldwide, relaying a significant burden on the healthcare system. Liver hypoperfusion in the setting of sepsis leads to Ischemic hepatitis. Accordingly, we are evaluating IH as a potential predictor of sepsis outcomes.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016 to 2020 was retrospectively queried using ICD-10CM/PCS codes to identify patients discharged with a diagnosis of sepsis and concomitant ischemic hepatitis (IH). The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Secondary outcomes included rate of post-procedural complications such as acute kidney injury (AKI), shock, encephalopathy, and sepsis. Length of stay (LOS), total hospital charges and hospital cost were calculated. Moreover, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to adjust for potential confounders.
Results: A total of 2,790,624 patients who were discharged after hospitalization for sepsis were included in the analysis. Patients were categorized into two groups based on the presence of IH. Among these patients, 1,240 (0.0004%) were identified to have IH. These patients were less likely to be White (62.4% Vs. 55.7%; p=0.02). Mean age of diagnosis was lower among those with ischemic hepatitis (55.9 Vs. 62.9; p< 0.01) which explains the predominance of Medicare insurance in both groups (45.6% and 58.0%; p< 0.01). Patients with ischemic hepatitis had higher rate of severe malnutrition (22.9% Vs 9.9%; p< 0.01), CKD stage V (14.1% Vs 10.2%; p= 0.05) and cirrhosis, both compensated (5.6% Vs 2.4%; p< 0.01) and decompensated (10.9% Vs 1.9%; p< 0.01).
Among patients with IH, predictors of mortality were SIRS (HR 12.93; p< 0.01), decompensated cirrhosis (HR 1.97; p< 0.01), AKI (HR 2.10; p< 0.01) and age over 65 years (HR 3.81; p< 0.01).
On multivariate analysis, there was increased in-hospital mortality (aOR 3.44; p<0.01) or in the length of stay (15.99 days; p< 0.01) and healthcare cost (578,646 US$; p< 0.01). IH had higher odds of ICU admissions (aOR 4.66; p< 0.01), shock (aOR 2.34; p<0.01), AKI (aOR 2.43; p<0.01) and pleural effusion (aOR 3.24; p< 0.01).
Discussion: Sepsis with concomitant IH is associated with significantly higher in-hospital mortality, complications, length of stay and healthcare cost. Patients with IH have higher rates of comorbidities including liver cirrhosis.
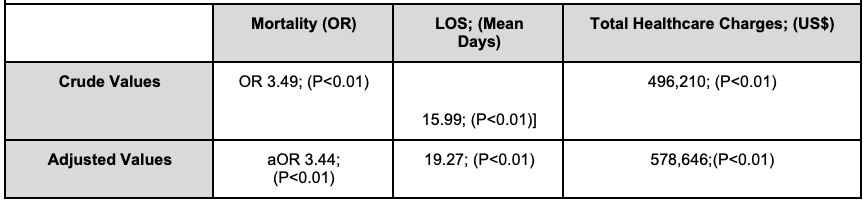
Figure: Table 1. Primary endpoint and healthcare burden for sepsis with ischemic hepatitis
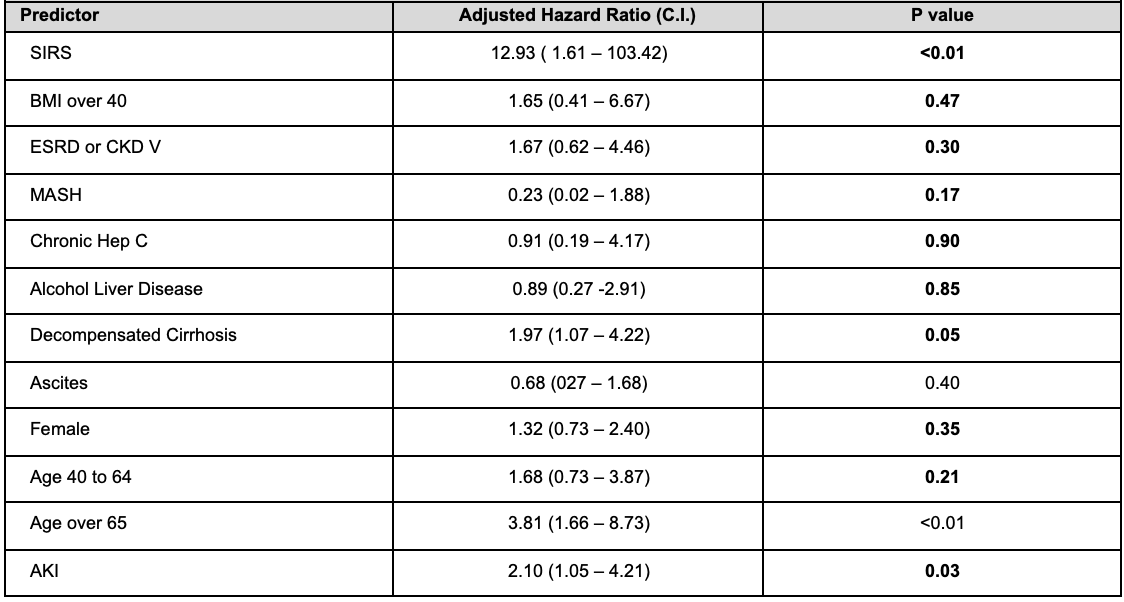
Figure: Table 2. Adjusted Predictors of In-hospital Mortality
Disclosures:
Khaled Al Smadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shabbir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashujot Dang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Salazar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donghyun Ko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Do Han Kim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gianina Flocco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeid Kayali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Palacios Argueta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Al Smadi, MD1, Muhammad Shikaib. Shabbir, MD2, Ashujot Dang, MD3, Miguel Salazar, MD4, Donghyun Ko, MD5, Do Han Kim, MD, MSc6, Gianina Flocco, MD7, Zeid Kayali, MD4, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD8. P5872 - The Impact of Ischemic Hepatitis on Outcomes and Healthcare Resources Utilization in Patients With Sepsis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Rancho Cucamonga, CA; 2University of California Riverside School of Medicine, San Bernardino, CA; 3University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Redlands, CA; 4University of California Riverside School of Medicine, Rialto, CA; 5Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 6Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 7Cleveland Clinic, Fairview Park, OH; 8Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Sepsis is a clinical syndrome characterized by a dysregulated systemic immune response to infection, leading to end-organ dysfunction. Sepsis remains to be a leading cause of in-hospital mortality worldwide, relaying a significant burden on the healthcare system. Liver hypoperfusion in the setting of sepsis leads to Ischemic hepatitis. Accordingly, we are evaluating IH as a potential predictor of sepsis outcomes.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016 to 2020 was retrospectively queried using ICD-10CM/PCS codes to identify patients discharged with a diagnosis of sepsis and concomitant ischemic hepatitis (IH). The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Secondary outcomes included rate of post-procedural complications such as acute kidney injury (AKI), shock, encephalopathy, and sepsis. Length of stay (LOS), total hospital charges and hospital cost were calculated. Moreover, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to adjust for potential confounders.
Results: A total of 2,790,624 patients who were discharged after hospitalization for sepsis were included in the analysis. Patients were categorized into two groups based on the presence of IH. Among these patients, 1,240 (0.0004%) were identified to have IH. These patients were less likely to be White (62.4% Vs. 55.7%; p=0.02). Mean age of diagnosis was lower among those with ischemic hepatitis (55.9 Vs. 62.9; p< 0.01) which explains the predominance of Medicare insurance in both groups (45.6% and 58.0%; p< 0.01). Patients with ischemic hepatitis had higher rate of severe malnutrition (22.9% Vs 9.9%; p< 0.01), CKD stage V (14.1% Vs 10.2%; p= 0.05) and cirrhosis, both compensated (5.6% Vs 2.4%; p< 0.01) and decompensated (10.9% Vs 1.9%; p< 0.01).
Among patients with IH, predictors of mortality were SIRS (HR 12.93; p< 0.01), decompensated cirrhosis (HR 1.97; p< 0.01), AKI (HR 2.10; p< 0.01) and age over 65 years (HR 3.81; p< 0.01).
On multivariate analysis, there was increased in-hospital mortality (aOR 3.44; p<0.01) or in the length of stay (15.99 days; p< 0.01) and healthcare cost (578,646 US$; p< 0.01). IH had higher odds of ICU admissions (aOR 4.66; p< 0.01), shock (aOR 2.34; p<0.01), AKI (aOR 2.43; p<0.01) and pleural effusion (aOR 3.24; p< 0.01).
Discussion: Sepsis with concomitant IH is associated with significantly higher in-hospital mortality, complications, length of stay and healthcare cost. Patients with IH have higher rates of comorbidities including liver cirrhosis.

Figure: Table 1. Primary endpoint and healthcare burden for sepsis with ischemic hepatitis

Figure: Table 2. Adjusted Predictors of In-hospital Mortality
Disclosures:
Khaled Al Smadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shabbir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashujot Dang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Salazar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donghyun Ko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Do Han Kim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gianina Flocco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeid Kayali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Palacios Argueta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Al Smadi, MD1, Muhammad Shikaib. Shabbir, MD2, Ashujot Dang, MD3, Miguel Salazar, MD4, Donghyun Ko, MD5, Do Han Kim, MD, MSc6, Gianina Flocco, MD7, Zeid Kayali, MD4, Pedro Palacios Argueta, MD8. P5872 - The Impact of Ischemic Hepatitis on Outcomes and Healthcare Resources Utilization in Patients With Sepsis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
