Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5835 - Trends and Disparities in Liver Disease and Renal Failure-Related Mortality in Adults ≥ 65 Years From 1999 to 2023 in the United States
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Khizar Hayat, MBBS, MD, BSc (he/him/his)
Waheed Khanzada Medical Center
Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Khizar Hayat, MBBS, MD, BSc1, Muhammad Ali, MBBS2, Sadia Ghafur, MBBS3, Komal Khalid, MD, MBBS, BSc4, Anas Nasir, MBBS5, Dania Hussain, MBBS3, Saif Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Shaikh Muhammad Daniyal, MBBS7, Shireen Asifa, MBBS7, Haider Imran, MBBS8
1Waheed Khanzada Medical Center, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Dow University of Health Sciences, Sugar Land, TX; 3united medical and dental college, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Hameed Latif Hospital, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Shaikh Zayed Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6bacha khan, Mardan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 7Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Foundation University Medical College, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Liver disease (LD) and renal failure (RF) are interrelated, as their concurrence is associated with dire outcomes and accelerated mortality. Cirrhosis can precipitate RF, as in hepatorenal syndrome, while RF may also exacerbate hepatic dysfunction. Research on LD and RF-related mortality trends stratified by demographic and regional factors in the United States remains limited. This study analyzes national LD and RF-related mortality trends among adults ≥ 65 years from 1999 to 2023.
Methods: The CDC WONDER Multiple-Cause-of-Death dataset (1999–2023) was used to assess mortality trends among adults ≥ 65 years using ICD-10 codes for LD (K70-K76) and RF (N17-N19). Data were stratified by year, demographic, and geographic classifications. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) were calculated per 100,000 persons by standardizing crude mortality rates (CMR) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI). Average annual percent change (AAPC) was calculated via the Joinpoint regression model, with statistical significance defined as P < 0.05.
Results: A total of 185,827 LD and RF-related deaths occurred from 1999 to 2023. Overall, AAMR rose from 15.2 in 1999 to 23.3 in 2023 (AAPC: 1.9; 95%CI: 1.1 to 2.6). Men, in comparison to women, had higher average AAMR, while women had a higher rate of increase (AAPC: 2.1679; 95%CI: 1.4 to 3.0). In terms of age groups, adults aged 75-84 years had the highest average CMR, while adults ≥ 85 years had the highest rate of increase (AAPC: 2.1; 95%CI: 1.2 to 3.0). Racially, non-Hispanic (NH) American Indian/Alaska Natives had the highest average AAMR, but had stable rates along with Hispanic/Latinos. NH Whites and NH Black/African Americans had increasing rates, while NH Asian/Pacific Islanders experienced decreasing rates (AAPC NH White: 1.9; 95%CI: 1.3 to 2.6, NH Black/African American: 1.3; 95%CI: 0.7 to 1.9, NH Asian/Pacific Islander: -1.2; 95%CI: -2.3 to -0.1). Regionally, the West had the highest average AAMR, along with the highest rate of increase (AAPC: 2.0; 95%CI: 1.1 to 2.8). From 1999 to 2020, rural areas, in comparison to urban areas, had higher average AAMR, but both had stable rates.
Discussion: LD and RF-related mortality among adults ≥65 years increased significantly from 1999 to 2023, with marked disparities across demographic and geographic groups. These disparities underscore the urgency for targeted interventions and policy reforms to decrease mortality rates in high-risk demographics.
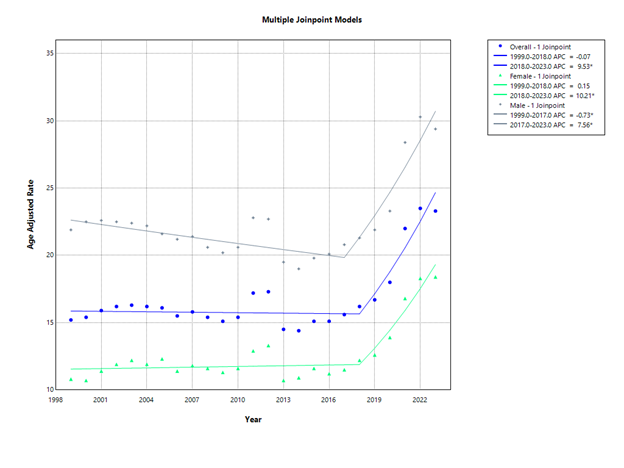
Figure: Multiple Joinpoint Models
Disclosures:
Khizar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sadia Ghafur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Komal Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Nasir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dania Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saif Ur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaikh Muhammad Daniyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shireen Asifa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haider Imran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khizar Hayat, MBBS, MD, BSc1, Muhammad Ali, MBBS2, Sadia Ghafur, MBBS3, Komal Khalid, MD, MBBS, BSc4, Anas Nasir, MBBS5, Dania Hussain, MBBS3, Saif Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Shaikh Muhammad Daniyal, MBBS7, Shireen Asifa, MBBS7, Haider Imran, MBBS8. P5835 - Trends and Disparities in Liver Disease and Renal Failure-Related Mortality in Adults ≥ 65 Years From 1999 to 2023 in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Waheed Khanzada Medical Center, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Dow University of Health Sciences, Sugar Land, TX; 3united medical and dental college, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Hameed Latif Hospital, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Shaikh Zayed Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6bacha khan, Mardan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 7Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Foundation University Medical College, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Liver disease (LD) and renal failure (RF) are interrelated, as their concurrence is associated with dire outcomes and accelerated mortality. Cirrhosis can precipitate RF, as in hepatorenal syndrome, while RF may also exacerbate hepatic dysfunction. Research on LD and RF-related mortality trends stratified by demographic and regional factors in the United States remains limited. This study analyzes national LD and RF-related mortality trends among adults ≥ 65 years from 1999 to 2023.
Methods: The CDC WONDER Multiple-Cause-of-Death dataset (1999–2023) was used to assess mortality trends among adults ≥ 65 years using ICD-10 codes for LD (K70-K76) and RF (N17-N19). Data were stratified by year, demographic, and geographic classifications. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) were calculated per 100,000 persons by standardizing crude mortality rates (CMR) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI). Average annual percent change (AAPC) was calculated via the Joinpoint regression model, with statistical significance defined as P < 0.05.
Results: A total of 185,827 LD and RF-related deaths occurred from 1999 to 2023. Overall, AAMR rose from 15.2 in 1999 to 23.3 in 2023 (AAPC: 1.9; 95%CI: 1.1 to 2.6). Men, in comparison to women, had higher average AAMR, while women had a higher rate of increase (AAPC: 2.1679; 95%CI: 1.4 to 3.0). In terms of age groups, adults aged 75-84 years had the highest average CMR, while adults ≥ 85 years had the highest rate of increase (AAPC: 2.1; 95%CI: 1.2 to 3.0). Racially, non-Hispanic (NH) American Indian/Alaska Natives had the highest average AAMR, but had stable rates along with Hispanic/Latinos. NH Whites and NH Black/African Americans had increasing rates, while NH Asian/Pacific Islanders experienced decreasing rates (AAPC NH White: 1.9; 95%CI: 1.3 to 2.6, NH Black/African American: 1.3; 95%CI: 0.7 to 1.9, NH Asian/Pacific Islander: -1.2; 95%CI: -2.3 to -0.1). Regionally, the West had the highest average AAMR, along with the highest rate of increase (AAPC: 2.0; 95%CI: 1.1 to 2.8). From 1999 to 2020, rural areas, in comparison to urban areas, had higher average AAMR, but both had stable rates.
Discussion: LD and RF-related mortality among adults ≥65 years increased significantly from 1999 to 2023, with marked disparities across demographic and geographic groups. These disparities underscore the urgency for targeted interventions and policy reforms to decrease mortality rates in high-risk demographics.

Figure: Multiple Joinpoint Models
Disclosures:
Khizar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sadia Ghafur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Komal Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Nasir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dania Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saif Ur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaikh Muhammad Daniyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shireen Asifa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haider Imran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khizar Hayat, MBBS, MD, BSc1, Muhammad Ali, MBBS2, Sadia Ghafur, MBBS3, Komal Khalid, MD, MBBS, BSc4, Anas Nasir, MBBS5, Dania Hussain, MBBS3, Saif Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Shaikh Muhammad Daniyal, MBBS7, Shireen Asifa, MBBS7, Haider Imran, MBBS8. P5835 - Trends and Disparities in Liver Disease and Renal Failure-Related Mortality in Adults ≥ 65 Years From 1999 to 2023 in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
