Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5829 - Evaluating APRI as a Fibrosis Marker in Diabetic MASH: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- OW
Owais ahmad Wani, MBBS
Government Medical College and Hospital
Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
Presenting Author(s)
Owais ahmad. Wani, MBBS1, Masood ahmad. Tanveer, MD1, Zhahid ahmad. Beigh, DM1, Khubaib ahmad. Murtafa, MBBS1, Waseem Nabi, MD2, Muzamil Khan, MBBS3, Daaniya Tariq, MBBS4
1Government Medical College and Hospital, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; 2Wyckoff Heights Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3George Washington University, Niles, IL; 4University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Introduction: Non-invasive biomarkers are commonly used to evaluate liver fibrosis and steatosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASH), especially in those with type 2 diabetes. The AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) is a simple and accessible marker, but its concordance with imaging-based parameters such as liver stiffness measurement (LSM), controlled attenuation parameter (CAP), and ultrasound-based fatty liver grading remains uncertain. This study assessed the relationship between APRI and both imaging-based and biochemical fibrosis measures, particularly the FIB-4 score, in diabetic individuals.
Methods:This cross-sectional study included 400 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who underwent liver fibrosis assessment. APRI and FIB-4 scores were calculated using routine laboratory parameters. FibroScan® was used to obtain LSM and CAP values, while fatty liver was graded by ultrasound. Associations between APRI and categorical fibrosis or steatosis grades were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U tests, and statistical significance was tested with the Chi-square test (χ²). Correlations between APRI and continuous variables (LSM, CAP, and FIB-4) were evaluated using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (ρ), with thresholds defined as strong (ρ ≥ 0.70), moderate (ρ = 0.40–0.69), weak (ρ = 0.10–0.39), or none (ρ < 0.10). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
1Government Medical College and Hospital, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India; 2Wyckoff Heights Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3George Washington University, Niles, IL; 4University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Introduction: Non-invasive biomarkers are commonly used to evaluate liver fibrosis and steatosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASH), especially in those with type 2 diabetes. The AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) is a simple and accessible marker, but its concordance with imaging-based parameters such as liver stiffness measurement (LSM), controlled attenuation parameter (CAP), and ultrasound-based fatty liver grading remains uncertain. This study assessed the relationship between APRI and both imaging-based and biochemical fibrosis measures, particularly the FIB-4 score, in diabetic individuals.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included 400 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who underwent liver fibrosis assessment. APRI and FIB-4 scores were calculated using routine laboratory parameters. FibroScan® was used to obtain LSM and CAP values, while fatty liver was graded by ultrasound. Associations between APRI and categorical fibrosis or steatosis grades were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U tests, and statistical significance was tested with the Chi-square test (χ²). Correlations between APRI and continuous variables (LSM, CAP, and FIB-4) were evaluated using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (ρ), with thresholds defined as strong (ρ ≥ 0.70), moderate (ρ = 0.40–0.69), weak (ρ = 0.10–0.39), or none (ρ < 0.10). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: No significant association was found between APRI and imaging-based fibrosis (χ² = 0.764, p = 0.858) or ultrasound-based steatosis grades (χ² = 1.351, p = 0.717). APRI showed weak, non-significant correlations with both LSM (ρ = 0.02, p = 0.629) and CAP (ρ = 0.03, p = 0.525). In contrast, APRI demonstrated a strong and statistically significant correlation with the FIB-4 score (ρ = 0.88, p < 0.001). Patients with FIB-4 >2.67 had significantly higher APRI values compared to those with intermediate FIB-4 scores (1.07 vs. 0.52, p < 0.001).
Discussion: APRI strongly correlates with the FIB-4 score, however it shows no meaningful association with elastographic or sonographic indicators of liver fibrosis or steatosis in diabetic patients. These findings suggest that APRI may be reliable as a biochemical marker but has limited utility in reflecting imaging-based liver pathology.
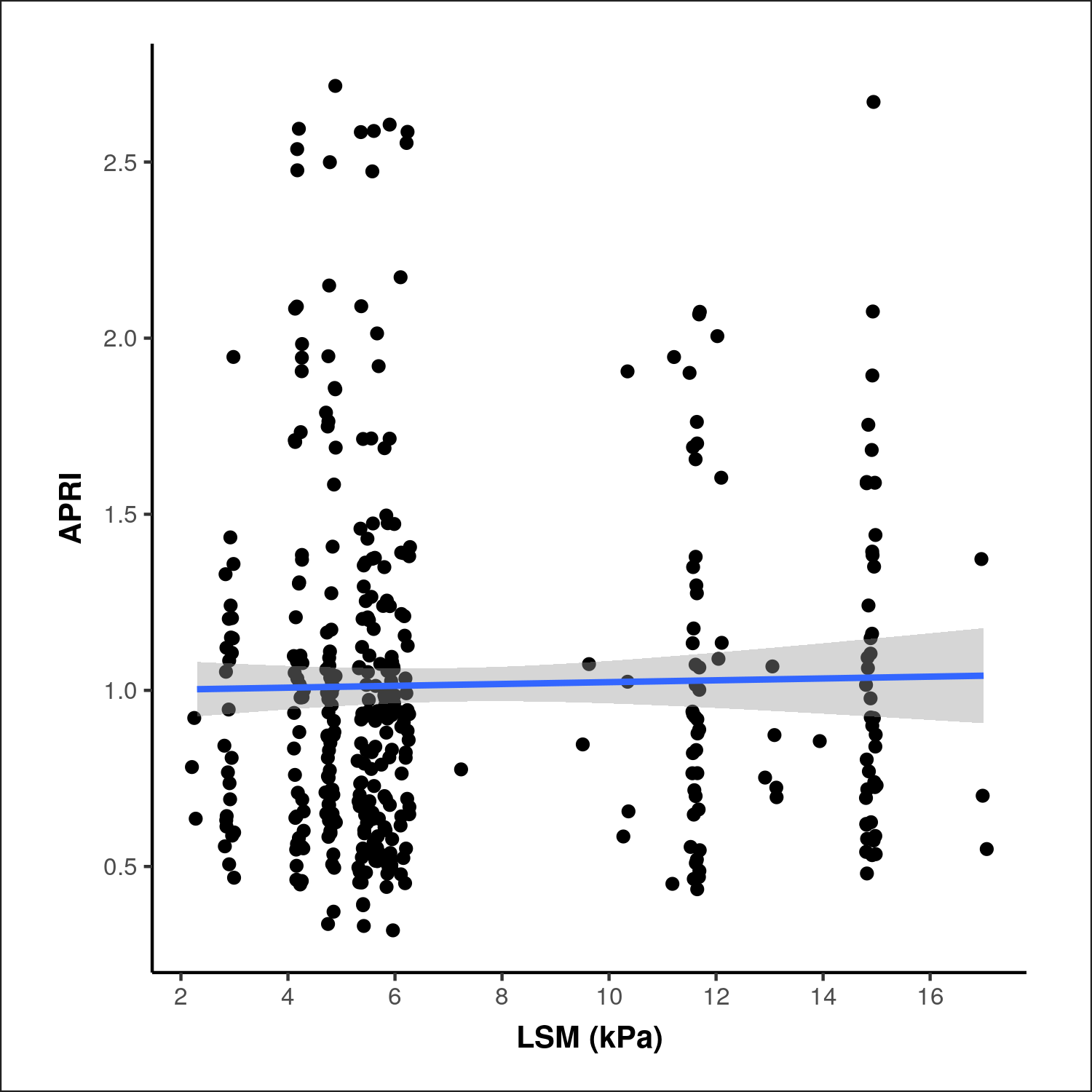
Figure: Figure X. Scatter plot demonstrating a significant positive linear correlation between the AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) and the FIB-4 Score. Each dot represents an individual data point, with the fitted regression line and 95% confidence interval shaded in blue. The strong association highlights the concordance between these two non-invasive markers of hepatic fibrosis.
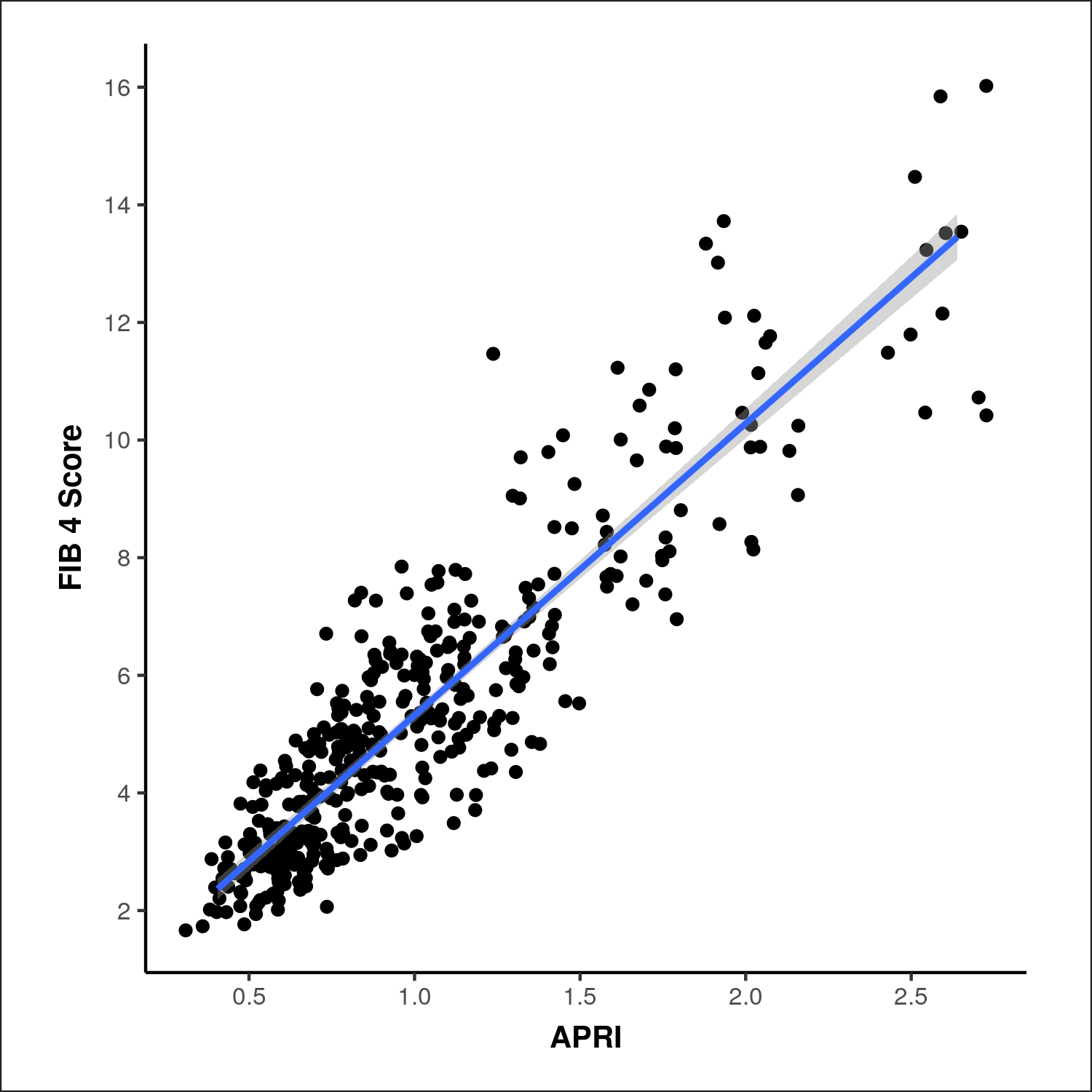
Figure: Figure. Scatter plot showing the relationship between the AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM, in kPa) obtained via transient elastography. The plot demonstrates a weak or absent linear correlation, as indicated by the near-horizontal regression line and wide confidence interval. This suggests limited concordance between APRI and LSM as markers of liver fibrosis in this cohort.
Disclosures:
Owais Wani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Masood Tanveer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zhahid Beigh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khubaib Murtafa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waseem Nabi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muzamil Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daaniya Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Owais ahmad. Wani, MBBS1, Masood ahmad. Tanveer, MD1, Zhahid ahmad. Beigh, DM1, Khubaib ahmad. Murtafa, MBBS1, Waseem Nabi, MD2, Muzamil Khan, MBBS3, Daaniya Tariq, MBBS4. P5829 - Evaluating APRI as a Fibrosis Marker in Diabetic MASH: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

Figure: Figure X. Scatter plot demonstrating a significant positive linear correlation between the AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) and the FIB-4 Score. Each dot represents an individual data point, with the fitted regression line and 95% confidence interval shaded in blue. The strong association highlights the concordance between these two non-invasive markers of hepatic fibrosis.

Figure: Figure. Scatter plot showing the relationship between the AST to Platelet Ratio Index (APRI) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM, in kPa) obtained via transient elastography. The plot demonstrates a weak or absent linear correlation, as indicated by the near-horizontal regression line and wide confidence interval. This suggests limited concordance between APRI and LSM as markers of liver fibrosis in this cohort.
Disclosures:
Owais Wani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Masood Tanveer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zhahid Beigh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khubaib Murtafa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waseem Nabi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muzamil Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daaniya Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Owais ahmad. Wani, MBBS1, Masood ahmad. Tanveer, MD1, Zhahid ahmad. Beigh, DM1, Khubaib ahmad. Murtafa, MBBS1, Waseem Nabi, MD2, Muzamil Khan, MBBS3, Daaniya Tariq, MBBS4. P5829 - Evaluating APRI as a Fibrosis Marker in Diabetic MASH: A Cross-Sectional Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
