Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5780 - Patterns of Care in Hepatic Encephalopathy: What Are We Missing?
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Suria Devarapalli, DO
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Little Rock, AR
Presenting Author(s)
Suria Devarapalli, DO1, Adalberto Guzman, MD2, Mauricio Garcia, MD1, Ragesh Thandassery, MD3
1University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR; 2University of Arkansas, Little Rock, AR; 3Dept of Solid Organ Transplantation, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a frequent and profoundly incapacitating complication of chronic liver disease. Although its pathophysiology is complex and not fully understood, ammonia is a major contributor to HE development. Lactulose, a nonabsorbable disaccharide, is commonly used as the first-line treatment due to its ability to lower colonic pH and act as an osmotic diuretic. In addition, rifaximin is traditionally introduced if a recurrent episode occurs, as it has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of HE recurrence. We conducted a retrospective analysis to assess treatment approaches and survival outcomes in patients with cirrhosis and HE.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study utilizing TriNetX, a global health research network database, to evaluate treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with cirrhosis and HE. The cohort consisted of 44,588 patients identified using ICD codes for cirrhosis and HE. Patients with prescriptions for lactulose and rifaximin were stratified into three groups: lactulose only, both lactulose and rifaximin, and rifaximin only. Time intervals from cirrhosis and HE diagnoses to treatment initiation, duration of therapy, survival, and end-of-record duration were analyzed. Descriptive statistics and survival analysis was conducted for each treatment group.
Results: Of the 44,588 patients included, the mean age was 62.8 ± 12.9 years, with a mean age at cirrhosis and HE diagnoses of 58.7 ± 12.6 years. The cohort comprised 56.28% males and 39.14% females. Treatment patterns with lactulose only was 53.5% with a median survival of 60 days, compared to just rifaximin was 16.8% with a median survival of 119 days. The combination of lactulose and rifaximin was 29.7% of patients with median survival of 708 days .
Discussion: In this cohort of patients with cirrhosis and HE, less than half were receiving optimal combination therapy with lactulose and rifaximin. Patients treated with both medications exhibited the longest median survival (708 days), while rifaximin alone was associated with the shortest median survival (119 days). The findings underscore a significant gap in evidence-based management of HE and highlight the potential survival benefit of combination therapy. Further studies are warranted to identify barriers to optimal treatment and strategies to improve outcomes in this population.
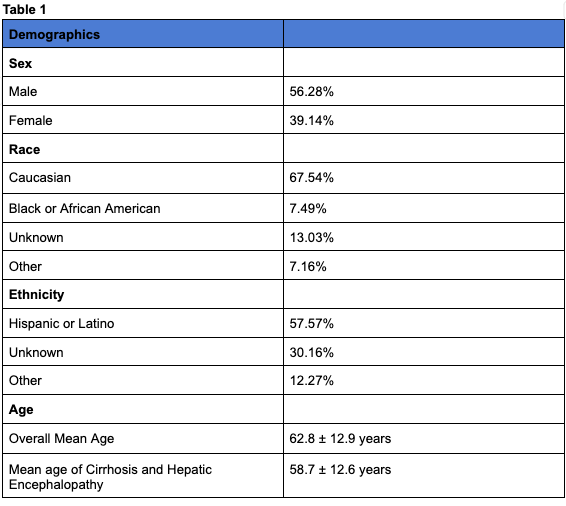
Figure: Demographics
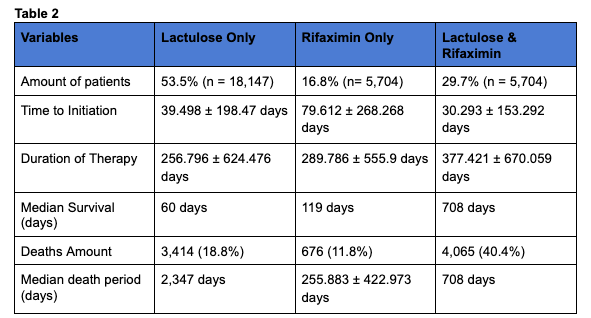
Figure: Treatment Patterns per Group
Disclosures:
Suria Devarapalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adalberto Guzman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ragesh Thandassery indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suria Devarapalli, DO1, Adalberto Guzman, MD2, Mauricio Garcia, MD1, Ragesh Thandassery, MD3. P5780 - Patterns of Care in Hepatic Encephalopathy: What Are We Missing?, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR; 2University of Arkansas, Little Rock, AR; 3Dept of Solid Organ Transplantation, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a frequent and profoundly incapacitating complication of chronic liver disease. Although its pathophysiology is complex and not fully understood, ammonia is a major contributor to HE development. Lactulose, a nonabsorbable disaccharide, is commonly used as the first-line treatment due to its ability to lower colonic pH and act as an osmotic diuretic. In addition, rifaximin is traditionally introduced if a recurrent episode occurs, as it has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of HE recurrence. We conducted a retrospective analysis to assess treatment approaches and survival outcomes in patients with cirrhosis and HE.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study utilizing TriNetX, a global health research network database, to evaluate treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with cirrhosis and HE. The cohort consisted of 44,588 patients identified using ICD codes for cirrhosis and HE. Patients with prescriptions for lactulose and rifaximin were stratified into three groups: lactulose only, both lactulose and rifaximin, and rifaximin only. Time intervals from cirrhosis and HE diagnoses to treatment initiation, duration of therapy, survival, and end-of-record duration were analyzed. Descriptive statistics and survival analysis was conducted for each treatment group.
Results: Of the 44,588 patients included, the mean age was 62.8 ± 12.9 years, with a mean age at cirrhosis and HE diagnoses of 58.7 ± 12.6 years. The cohort comprised 56.28% males and 39.14% females. Treatment patterns with lactulose only was 53.5% with a median survival of 60 days, compared to just rifaximin was 16.8% with a median survival of 119 days. The combination of lactulose and rifaximin was 29.7% of patients with median survival of 708 days .
Discussion: In this cohort of patients with cirrhosis and HE, less than half were receiving optimal combination therapy with lactulose and rifaximin. Patients treated with both medications exhibited the longest median survival (708 days), while rifaximin alone was associated with the shortest median survival (119 days). The findings underscore a significant gap in evidence-based management of HE and highlight the potential survival benefit of combination therapy. Further studies are warranted to identify barriers to optimal treatment and strategies to improve outcomes in this population.

Figure: Demographics

Figure: Treatment Patterns per Group
Disclosures:
Suria Devarapalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adalberto Guzman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ragesh Thandassery indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suria Devarapalli, DO1, Adalberto Guzman, MD2, Mauricio Garcia, MD1, Ragesh Thandassery, MD3. P5780 - Patterns of Care in Hepatic Encephalopathy: What Are We Missing?, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

