Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P5771 - Evaluating the Impact of BMI and Diabetes on Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores in MASLD Patients: A Retrospective Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Abdelrhman Refaey, MD
Division of Gastroenterology and Liver Disease, Department of Medicine, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Teaneck, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Abdelrhman Refaey, MD1, Ahmed Ebeid, MD2, Ahmed Attia, MD2, Susie Park, MD3, Omar Saadi, BS4, Ishan Abdullah, BS4, Nakul Ganju, MD5, Zeina Bani Hani, MBBS3, Sabrina Hsiao, BA4, Matthew Walker, BA6, Abdelrahman Moharam, BS7, Sean M. Lee, PhD8, Ameer Abutaleb, MD9
1Division of Gastroenterology and Liver Disease, Department of Medicine, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 2Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Science, Washington, DC; 3Department of Medicine, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 4The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 5Department of Medicine, Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 6The George Washington University School Of Medicine And Health Science, Washington, DC; 7The George Washington University School of Engineering, Washington, DC; 8Office of Clinical Research, The George Washington University Medical Faculty Associates, Washington, DC; 9The George Washington Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, The George Washington University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) affects over 100 million U.S. adults and is closely linked to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Liver fibrosis, the strongest predictor of liver-related outcomes in MASLD, is routinely assessed using non-invasive markers such as the NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS), FIB-4 Index, and AST Platelet Ratio Index (APRI). However, the performance of these tools may be confounded by metabolic factors such as BMI and diabetes, which are central to MASLD pathogenesis. We aim to evaluate the association between BMI, diabetes status, and non-invasive fibrosis scores in a retrospective cohort of MASLD patients.
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective study of patients with a diagnosis code of MASLD from January 1, 2022, until December 31, 2023. Patients were grouped into BMI categories per CDC guidelines (normal: 18.5–24.9; overweight: 25–29.9; obese: ≥30) and by diabetes status. Patients with missing labs were excluded. We compared NFS, FIB-4, and APRI scores across these groups using Kruskal-Wallis tests. We used two-sided hypothesis tests and a 5% alpha.
Results: We reviewed 4644 patients with a diagnosis code of MASLD. 3416 had labs available to calculate the fibrosis scores. Of them, 2233 had imaging-based steatosis while 1183 had no evidence of steatosis. 48% were males, 46.9% were African American, while 27.25% were white. The mean age was 54.7 years, while the mean BMI was 31.5. The number of subjects with advanced fibrosis was 174, 165, and 80 using FIB-4, NFS, and APRI, respectively. With stratification by BMI and DM, using NFS, obese and diabetic subjects respectively had the highest percentage of advanced fibrosis, whereas using FIB-4 and APRI, normal BMI and non-diabetic subjects respectively had the highest percentage of advanced fibrosis even after adjusting for age and platelet count.
Discussion: Our findings suggest that elevated BMI and diabetes are associated with increased likelihood of high-risk NFS scores. However, paradoxically, normal BMI and non-diabetic patients exhibited higher FIB-4 and APRI scores, even after adjustment for age and platelet count, which may suggest potential unexplained confounders. These results highlight the complexity of interpreting fibrosis risk in MASLD and underscore the need to refine non-invasive assessment tools in metabolically diverse populations.
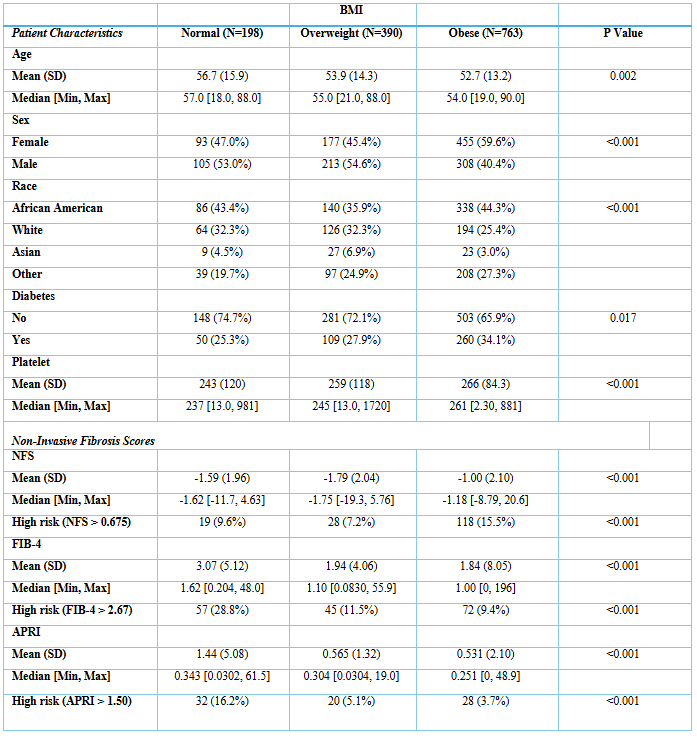
Figure: Table 1. Non-invasive fibrosis scores and patient characteristics stratified by body mass index (BMI).
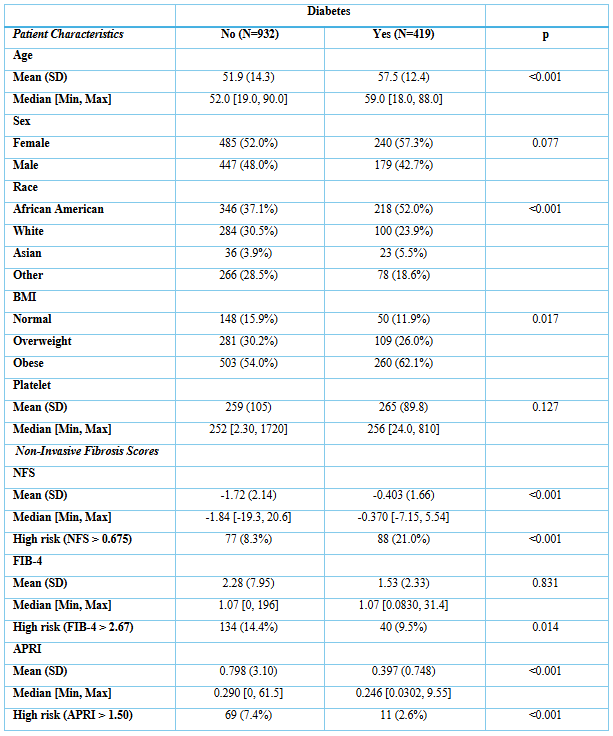
Figure: Table 2. Non-invasive fibrosis scores and patient characteristics stratified by history of diabetes.
Disclosures:
Abdelrhman Refaey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ebeid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Attia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Susie Park indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Saadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishan Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nakul Ganju indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeina Bani Hani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sabrina Hsiao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Walker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Moharam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ameer Abutaleb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrhman Refaey, MD1, Ahmed Ebeid, MD2, Ahmed Attia, MD2, Susie Park, MD3, Omar Saadi, BS4, Ishan Abdullah, BS4, Nakul Ganju, MD5, Zeina Bani Hani, MBBS3, Sabrina Hsiao, BA4, Matthew Walker, BA6, Abdelrahman Moharam, BS7, Sean M. Lee, PhD8, Ameer Abutaleb, MD9. P5771 - Evaluating the Impact of BMI and Diabetes on Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores in MASLD Patients: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Division of Gastroenterology and Liver Disease, Department of Medicine, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 2Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Science, Washington, DC; 3Department of Medicine, George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 4The George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC; 5Department of Medicine, Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 6The George Washington University School Of Medicine And Health Science, Washington, DC; 7The George Washington University School of Engineering, Washington, DC; 8Office of Clinical Research, The George Washington University Medical Faculty Associates, Washington, DC; 9The George Washington Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery, The George Washington University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) affects over 100 million U.S. adults and is closely linked to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Liver fibrosis, the strongest predictor of liver-related outcomes in MASLD, is routinely assessed using non-invasive markers such as the NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS), FIB-4 Index, and AST Platelet Ratio Index (APRI). However, the performance of these tools may be confounded by metabolic factors such as BMI and diabetes, which are central to MASLD pathogenesis. We aim to evaluate the association between BMI, diabetes status, and non-invasive fibrosis scores in a retrospective cohort of MASLD patients.
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective study of patients with a diagnosis code of MASLD from January 1, 2022, until December 31, 2023. Patients were grouped into BMI categories per CDC guidelines (normal: 18.5–24.9; overweight: 25–29.9; obese: ≥30) and by diabetes status. Patients with missing labs were excluded. We compared NFS, FIB-4, and APRI scores across these groups using Kruskal-Wallis tests. We used two-sided hypothesis tests and a 5% alpha.
Results: We reviewed 4644 patients with a diagnosis code of MASLD. 3416 had labs available to calculate the fibrosis scores. Of them, 2233 had imaging-based steatosis while 1183 had no evidence of steatosis. 48% were males, 46.9% were African American, while 27.25% were white. The mean age was 54.7 years, while the mean BMI was 31.5. The number of subjects with advanced fibrosis was 174, 165, and 80 using FIB-4, NFS, and APRI, respectively. With stratification by BMI and DM, using NFS, obese and diabetic subjects respectively had the highest percentage of advanced fibrosis, whereas using FIB-4 and APRI, normal BMI and non-diabetic subjects respectively had the highest percentage of advanced fibrosis even after adjusting for age and platelet count.
Discussion: Our findings suggest that elevated BMI and diabetes are associated with increased likelihood of high-risk NFS scores. However, paradoxically, normal BMI and non-diabetic patients exhibited higher FIB-4 and APRI scores, even after adjustment for age and platelet count, which may suggest potential unexplained confounders. These results highlight the complexity of interpreting fibrosis risk in MASLD and underscore the need to refine non-invasive assessment tools in metabolically diverse populations.

Figure: Table 1. Non-invasive fibrosis scores and patient characteristics stratified by body mass index (BMI).

Figure: Table 2. Non-invasive fibrosis scores and patient characteristics stratified by history of diabetes.
Disclosures:
Abdelrhman Refaey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ebeid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Attia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Susie Park indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Saadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishan Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nakul Ganju indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeina Bani Hani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sabrina Hsiao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Walker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Moharam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ameer Abutaleb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrhman Refaey, MD1, Ahmed Ebeid, MD2, Ahmed Attia, MD2, Susie Park, MD3, Omar Saadi, BS4, Ishan Abdullah, BS4, Nakul Ganju, MD5, Zeina Bani Hani, MBBS3, Sabrina Hsiao, BA4, Matthew Walker, BA6, Abdelrahman Moharam, BS7, Sean M. Lee, PhD8, Ameer Abutaleb, MD9. P5771 - Evaluating the Impact of BMI and Diabetes on Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores in MASLD Patients: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
