Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P5689 - Efficacy of Intra-Gastric Balloon versus Intra-Gastric Balloon and Anti-Obesity Medications for Weight Loss: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- ZG
Zane Gouda, MD
Weill Cornell Medicine
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Usman Baig, MBBS1, Zane Gouda, MD2, Ali Lahooti, MD2, Kate E. Johnson, BA2, Sean Rangwani, MD2, Hakan Gelincik, MD3, Mohannad Bisher Zuhair Al-Bakain, MBBS4, Sanad Tarick Haddad, MBBS5, Zuhair Osamah Zuhair Al-Bakaeen, MBBS4, Chino Aneke-Nash, MD2, Carolyn Newberry, MD6, Mark Hanscom, MD2, Kartik Sampath, MD2, SriHari Mahadev, MD2, David Carr-Locke, MD, FACG2, Shelby Sullivan, MD, FACG7, Reem Z.. Sharaiha, MD, MSc1
1Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY; 2Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 3NYC Health + Hospitals/Woodhull, Brooklyn, NY; 4Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 5University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6NewYork-Presbyterian / Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 7Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH
Introduction: Intra-gastric balloons (IGB) are synthetic balloons placed in the stomach to help patients with obesity to achieve weight loss. While multiple studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of IGBs alone, the potential benefits of combining IGBs with anti-obesity medications (AOM) remain understudied. We aimed to conduct a systematic review and a meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of IGB versus IGB + anti-obesity medications (AOM) on weight loss.
Methods: Bibliographic databases (PubMed, Medline, Embase) were systematically searched for studies assessing the impact of IGB versus IGB + AOM on weight loss. All randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies comparing these interventions were included and analyzed using the Inverse variance method and Random-effects model.
Results: 4 studies containing 309 patients were included (2 observational studies and 2 RCTs). Patients in both groups were instructed about lifestyle modifications. The follow-up period was 6 months for most studies, except Farina et al. (2012) which followed patients for 12 months. The primary outcome was the weight loss difference between the IGB + AOM group versus the IGB group which was measured as Mean Difference (MD).
IGB + AOM resulted in significantly greater weight loss, with a mean difference of 4.05 kg (95% CI [1.52, 6.57], P= 0.002) compared to IGB alone (Figure 1). Subgroup analysis by age showed consistent results favoring IGB + AOM: patients < 35 years achieved an additional weight loss of 5.93 kg (95% CI [1.63, 10.22], P= 0.007), while patients >35 years achieved an additional weight loss of 1.80 kg (95% CI [1.20, 2.39], P< 0.00001) (Figure 2).
Discussion: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, adding anti-obesity medications to IGB treatment resulted in significantly greater weight loss compared to IGB alone.
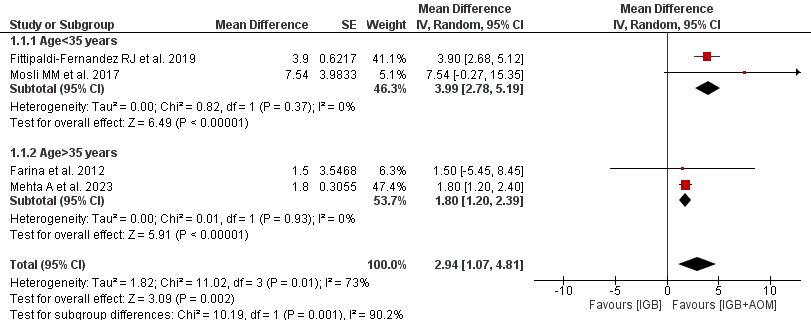
Figure: Figure 1. IGB + anti-obesity medication (AOM) vs IGB effect on weight loss.
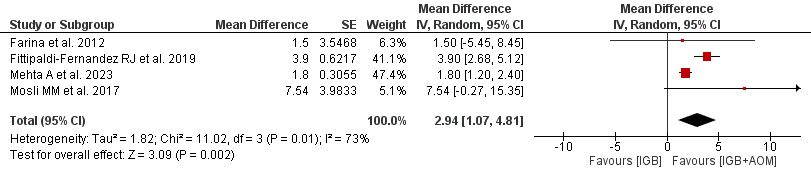
Figure: Figure 2. Subgroup analysis of IGB + AOM vs IGB on age 35.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Usman Baig indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zane Gouda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Lahooti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kate Johnson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Rangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakan Gelincik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohannad Bisher Zuhair Al-Bakain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanad Tarick Haddad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zuhair Osamah Zuhair Al-Bakaeen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chino Aneke-Nash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carolyn Newberry: Eli Lilly & Co – Consultant.
Mark Hanscom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kartik Sampath: CONMED – Consultant.
SriHari Mahadev: Boston scientific – Consultant. Conmed – Consultant.
David Carr-Locke: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Steris Corporation – Royalties.
Shelby Sullivan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reem Sharaiha: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Surgical Intuitive – Consultant.
Muhammad Usman Baig, MBBS1, Zane Gouda, MD2, Ali Lahooti, MD2, Kate E. Johnson, BA2, Sean Rangwani, MD2, Hakan Gelincik, MD3, Mohannad Bisher Zuhair Al-Bakain, MBBS4, Sanad Tarick Haddad, MBBS5, Zuhair Osamah Zuhair Al-Bakaeen, MBBS4, Chino Aneke-Nash, MD2, Carolyn Newberry, MD6, Mark Hanscom, MD2, Kartik Sampath, MD2, SriHari Mahadev, MD2, David Carr-Locke, MD, FACG2, Shelby Sullivan, MD, FACG7, Reem Z.. Sharaiha, MD, MSc1. P5689 - Efficacy of Intra-Gastric Balloon versus Intra-Gastric Balloon and Anti-Obesity Medications for Weight Loss: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY; 2Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 3NYC Health + Hospitals/Woodhull, Brooklyn, NY; 4Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 5University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 6NewYork-Presbyterian / Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 7Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH
Introduction: Intra-gastric balloons (IGB) are synthetic balloons placed in the stomach to help patients with obesity to achieve weight loss. While multiple studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of IGBs alone, the potential benefits of combining IGBs with anti-obesity medications (AOM) remain understudied. We aimed to conduct a systematic review and a meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of IGB versus IGB + anti-obesity medications (AOM) on weight loss.
Methods: Bibliographic databases (PubMed, Medline, Embase) were systematically searched for studies assessing the impact of IGB versus IGB + AOM on weight loss. All randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies comparing these interventions were included and analyzed using the Inverse variance method and Random-effects model.
Results: 4 studies containing 309 patients were included (2 observational studies and 2 RCTs). Patients in both groups were instructed about lifestyle modifications. The follow-up period was 6 months for most studies, except Farina et al. (2012) which followed patients for 12 months. The primary outcome was the weight loss difference between the IGB + AOM group versus the IGB group which was measured as Mean Difference (MD).
IGB + AOM resulted in significantly greater weight loss, with a mean difference of 4.05 kg (95% CI [1.52, 6.57], P= 0.002) compared to IGB alone (Figure 1). Subgroup analysis by age showed consistent results favoring IGB + AOM: patients < 35 years achieved an additional weight loss of 5.93 kg (95% CI [1.63, 10.22], P= 0.007), while patients >35 years achieved an additional weight loss of 1.80 kg (95% CI [1.20, 2.39], P< 0.00001) (Figure 2).
Discussion: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, adding anti-obesity medications to IGB treatment resulted in significantly greater weight loss compared to IGB alone.

Figure: Figure 1. IGB + anti-obesity medication (AOM) vs IGB effect on weight loss.

Figure: Figure 2. Subgroup analysis of IGB + AOM vs IGB on age 35.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Usman Baig indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zane Gouda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Lahooti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kate Johnson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Rangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakan Gelincik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohannad Bisher Zuhair Al-Bakain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanad Tarick Haddad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zuhair Osamah Zuhair Al-Bakaeen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chino Aneke-Nash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carolyn Newberry: Eli Lilly & Co – Consultant.
Mark Hanscom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kartik Sampath: CONMED – Consultant.
SriHari Mahadev: Boston scientific – Consultant. Conmed – Consultant.
David Carr-Locke: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Steris Corporation – Royalties.
Shelby Sullivan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reem Sharaiha: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Surgical Intuitive – Consultant.
Muhammad Usman Baig, MBBS1, Zane Gouda, MD2, Ali Lahooti, MD2, Kate E. Johnson, BA2, Sean Rangwani, MD2, Hakan Gelincik, MD3, Mohannad Bisher Zuhair Al-Bakain, MBBS4, Sanad Tarick Haddad, MBBS5, Zuhair Osamah Zuhair Al-Bakaeen, MBBS4, Chino Aneke-Nash, MD2, Carolyn Newberry, MD6, Mark Hanscom, MD2, Kartik Sampath, MD2, SriHari Mahadev, MD2, David Carr-Locke, MD, FACG2, Shelby Sullivan, MD, FACG7, Reem Z.. Sharaiha, MD, MSc1. P5689 - Efficacy of Intra-Gastric Balloon versus Intra-Gastric Balloon and Anti-Obesity Medications for Weight Loss: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
