Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P5685 - Shifting Treatment Patterns in Achalasia: The Surge in POEM Adoption
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Carson Creamer, DO
University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME
Gainesville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Carson Creamer, DO1, Mohammad Abu Assi, MD2, Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD2, Yaseen Perbtani, DO2, Tony Brar, MD2
1University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Gainesville, FL; 2University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder that requires effective treatment strategies to manage symptoms and improve patient outcomes. This study investigates the incidence and prevalence trends of key achalasia treatments, Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM), Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections, across diverse demographic groups from 2016 to 2024.
Methods: Data were collected on March 1, 2025, from the TriNetX Network, which includes electronic medical records from over 145 million patients seen at 130 healthcare organizations across 23 countries. Annual incidence and prevalence rates per 100,000 population were analyzed for each treatment. Stratified analyses by age, sex, race, and ethnicity were performed to identify demographic variations.
Results: POEM procedures showed a sharp rise in incidence and prevalence beginning in 2022, coinciding with the introduction of a dedicated procedure code. Incidence increased from 2.56 per 100,000 in 2021 to 29.04 in 2024, while prevalence rose from 2.56 to 60.5 per 100,000. POEM was more frequently performed in younger adults, males, and American Indian/Alaska Native populations. Heller Myotomy incidence remained stable (8.4 to 11.9 per 100,000), with prevalence increasing from 36.2 in 2016 to 74.4 in 2024. This treatment was more common among older adults and White populations. Botox injections showed consistent growth, with incidence rising from 4.4 to 13.3 per 100,000 and prevalence from 13.7 to 70.3. Botox was used most frequently in older adults, males, and White patients, with Hispanic/Latino populations showing marked increases post-2022. All treatments experienced a decline in 2019–2020, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Discussion: The rapid increase in POEM after 2022 suggests that improved coding and reimbursement, rather than clinical shifts alone, drove adoption. Its popularity among younger adults and American Indian/Alaska Native populations reflects a broader trend toward minimally invasive therapies. Heller Myotomy’s stability points to its continued relevance, especially for older adults seeking a well-established procedure. Botox’s steady rise, particularly among Hispanic/Latino populations, highlights demographic differences in treatment selection. These findings underscore evolving treatment patterns in achalasia, the influence of policy and coding, and the importance of equitable access and long-term outcome research.
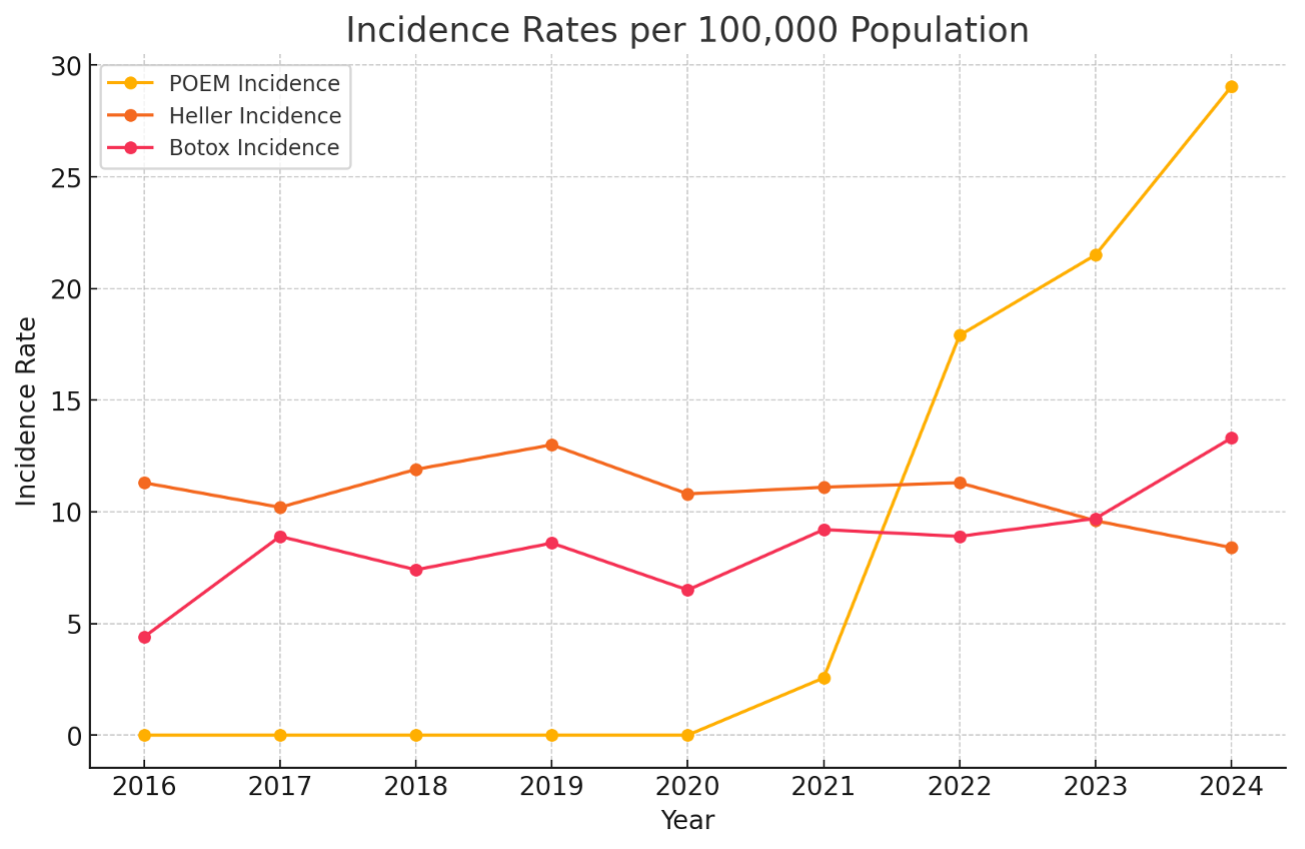
Figure: Annual incidence rates per 100,000 population for POEM, Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections from 2016 to 2024.
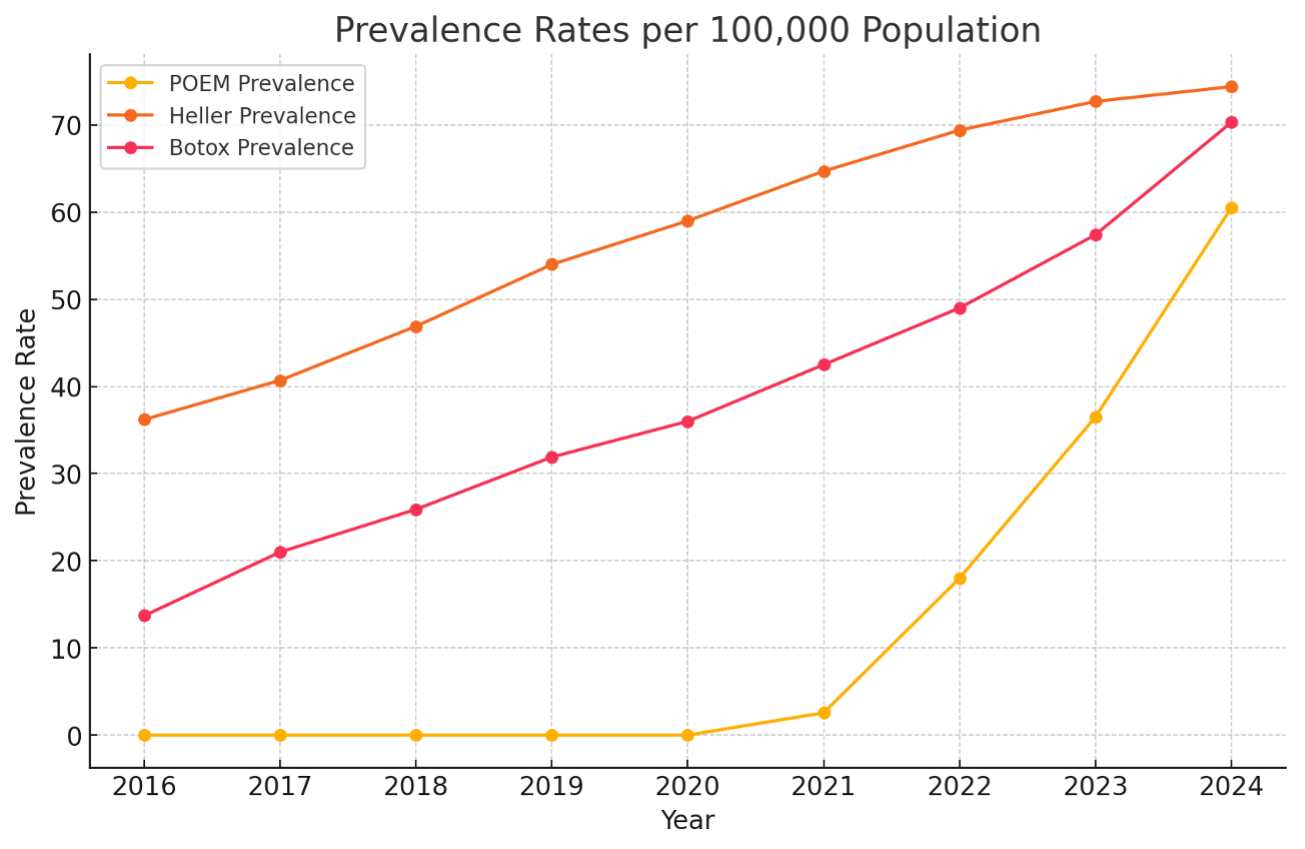
Figure: Annual prevalence rates per 100,000 population for POEM, Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections from 2016 to 2024.
Disclosures:
Carson Creamer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Abu Assi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsimran Kalsi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Perbtani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tony Brar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carson Creamer, DO1, Mohammad Abu Assi, MD2, Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD2, Yaseen Perbtani, DO2, Tony Brar, MD2. P5685 - Shifting Treatment Patterns in Achalasia: The Surge in POEM Adoption, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Gainesville, FL; 2University of Central Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder that requires effective treatment strategies to manage symptoms and improve patient outcomes. This study investigates the incidence and prevalence trends of key achalasia treatments, Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM), Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections, across diverse demographic groups from 2016 to 2024.
Methods: Data were collected on March 1, 2025, from the TriNetX Network, which includes electronic medical records from over 145 million patients seen at 130 healthcare organizations across 23 countries. Annual incidence and prevalence rates per 100,000 population were analyzed for each treatment. Stratified analyses by age, sex, race, and ethnicity were performed to identify demographic variations.
Results: POEM procedures showed a sharp rise in incidence and prevalence beginning in 2022, coinciding with the introduction of a dedicated procedure code. Incidence increased from 2.56 per 100,000 in 2021 to 29.04 in 2024, while prevalence rose from 2.56 to 60.5 per 100,000. POEM was more frequently performed in younger adults, males, and American Indian/Alaska Native populations. Heller Myotomy incidence remained stable (8.4 to 11.9 per 100,000), with prevalence increasing from 36.2 in 2016 to 74.4 in 2024. This treatment was more common among older adults and White populations. Botox injections showed consistent growth, with incidence rising from 4.4 to 13.3 per 100,000 and prevalence from 13.7 to 70.3. Botox was used most frequently in older adults, males, and White patients, with Hispanic/Latino populations showing marked increases post-2022. All treatments experienced a decline in 2019–2020, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Discussion: The rapid increase in POEM after 2022 suggests that improved coding and reimbursement, rather than clinical shifts alone, drove adoption. Its popularity among younger adults and American Indian/Alaska Native populations reflects a broader trend toward minimally invasive therapies. Heller Myotomy’s stability points to its continued relevance, especially for older adults seeking a well-established procedure. Botox’s steady rise, particularly among Hispanic/Latino populations, highlights demographic differences in treatment selection. These findings underscore evolving treatment patterns in achalasia, the influence of policy and coding, and the importance of equitable access and long-term outcome research.

Figure: Annual incidence rates per 100,000 population for POEM, Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections from 2016 to 2024.

Figure: Annual prevalence rates per 100,000 population for POEM, Heller Myotomy, and Botox injections from 2016 to 2024.
Disclosures:
Carson Creamer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Abu Assi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harsimran Kalsi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Perbtani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tony Brar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carson Creamer, DO1, Mohammad Abu Assi, MD2, Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD2, Harsimran Kalsi, MD2, Yaseen Perbtani, DO2, Tony Brar, MD2. P5685 - Shifting Treatment Patterns in Achalasia: The Surge in POEM Adoption, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
