Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P5648 - Two-Year Outcomes Following Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (E-POEM) for Non-Achalasia Esophageal Motility Disorders
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- RA
Rawia Aburumman, MD
Louisiana State University
Spring, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Rawia Aburumman, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Lena Kawji, MD3, Mohammad Alfrad Nobel Bhuiyan, MD3, Qiang Cai, MD, PhD, MACG4
1Louisiana State University, Spring, TX; 2LSU Health Shreveport, Shreveport, LA; 3Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 4LSU Health Sciences Center - SHREVEPORT, LA, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Non-achalasia esophageal motility disorders (NAEMDs) including esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO), distal esophageal spasm (DES), hypercontractile esophagus, and ineffective esophageal motility can cause debilitating symptoms. The Eckardt score (range 0-12), is a validated composite of dysphagia, chest pain, regurgitation, and weight loss, that is commonly used to quantify symptom severity. Esophageal peroral endoscopic myotomy (E-POEM) is a minimally invasive technique targeting the circular muscle layer of the esophagus, offering a possible therapeutic option for NAEMDs.
Methods: Fourteen patients diagnosed with NAEMDs underwent E-POEM between July 2021 and December 2022 (mean age 56.3 years; 64% female). Eckardt scores were assessed pre-procedure, 1-3 months post-procedure, and at 2-year follow-up. Paired t-test was used to compare scores at each interval. Mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results: Initial mean baseline Eckardt score was 7.5. At 1–3 months post-procedure, the mean score improved by 5.64 points (95% CI: 4.22-7.07; p = 0.00000107). At 2 years, the mean improvement from baseline was 4.07 points (95% CI: 2.05–6.09; p = 0.0008). A statistically significant increase in symptoms was observed between the early post-procedure and 2-year follow-up scores (mean difference = -1.57; 95% CI: -2.89 to -0.26; p = 0.0228), though overall improvement remained clinically and statistically significant.
Discussion: E-POEM provides significant short-term and long-term symptom relief in patients with NAEMDs, as measured by sustained improvement in Eckardt scores over two years. While a modest increase in symptom burden was noted over time, most patients continued to benefit from the procedure. These findings support E-POEM as an effective treatment for selected NAEMD patients. Further long term follow up and large-scale studies are warranted.
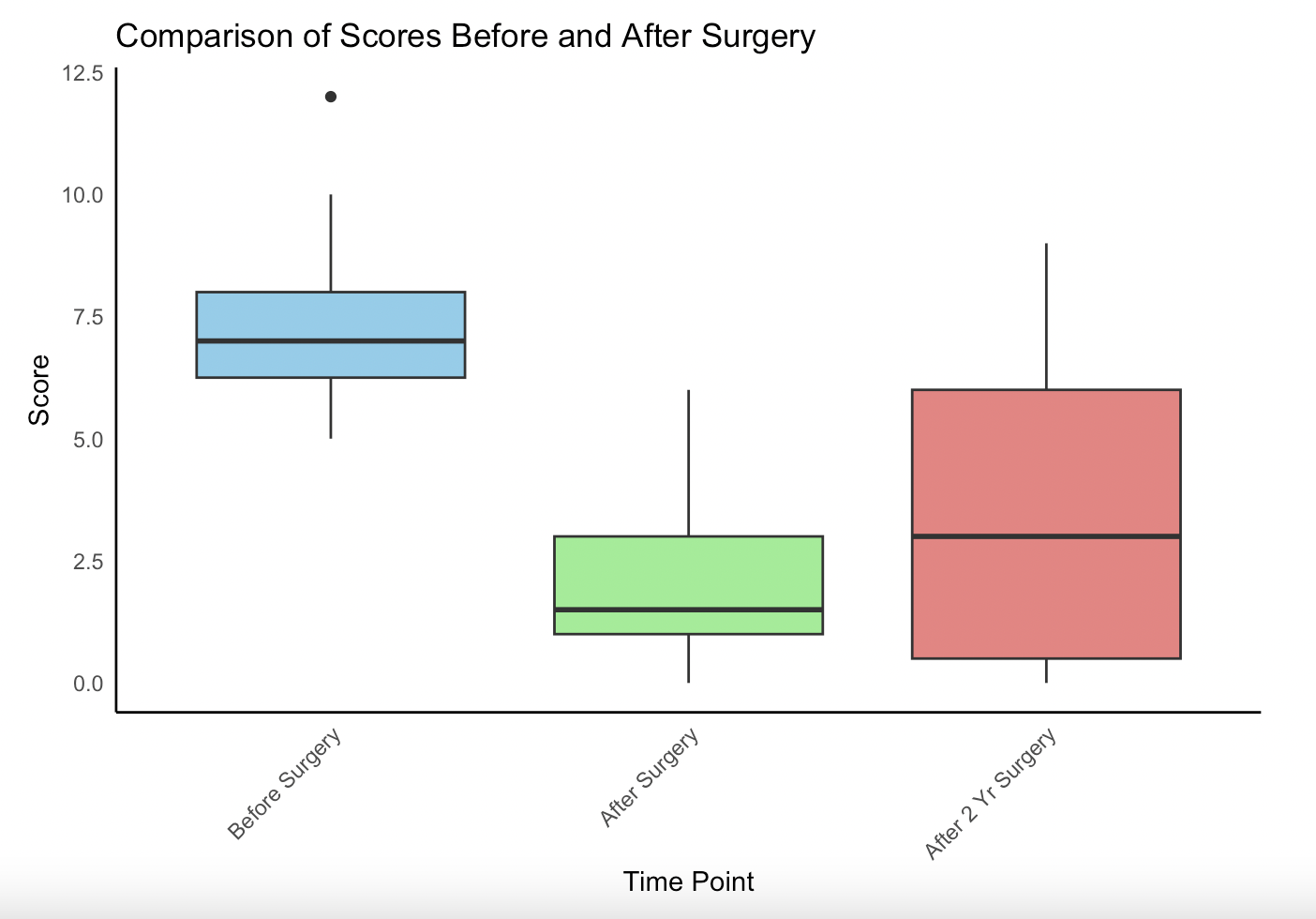
Figure:
Disclosures:
Rawia Aburumman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Okuampa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lena Kawji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Alfrad Nobel Bhuiyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qiang Cai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rawia Aburumman, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Lena Kawji, MD3, Mohammad Alfrad Nobel Bhuiyan, MD3, Qiang Cai, MD, PhD, MACG4. P5648 - Two-Year Outcomes Following Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (E-POEM) for Non-Achalasia Esophageal Motility Disorders, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Louisiana State University, Spring, TX; 2LSU Health Shreveport, Shreveport, LA; 3Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 4LSU Health Sciences Center - SHREVEPORT, LA, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Non-achalasia esophageal motility disorders (NAEMDs) including esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO), distal esophageal spasm (DES), hypercontractile esophagus, and ineffective esophageal motility can cause debilitating symptoms. The Eckardt score (range 0-12), is a validated composite of dysphagia, chest pain, regurgitation, and weight loss, that is commonly used to quantify symptom severity. Esophageal peroral endoscopic myotomy (E-POEM) is a minimally invasive technique targeting the circular muscle layer of the esophagus, offering a possible therapeutic option for NAEMDs.
Methods: Fourteen patients diagnosed with NAEMDs underwent E-POEM between July 2021 and December 2022 (mean age 56.3 years; 64% female). Eckardt scores were assessed pre-procedure, 1-3 months post-procedure, and at 2-year follow-up. Paired t-test was used to compare scores at each interval. Mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results: Initial mean baseline Eckardt score was 7.5. At 1–3 months post-procedure, the mean score improved by 5.64 points (95% CI: 4.22-7.07; p = 0.00000107). At 2 years, the mean improvement from baseline was 4.07 points (95% CI: 2.05–6.09; p = 0.0008). A statistically significant increase in symptoms was observed between the early post-procedure and 2-year follow-up scores (mean difference = -1.57; 95% CI: -2.89 to -0.26; p = 0.0228), though overall improvement remained clinically and statistically significant.
Discussion: E-POEM provides significant short-term and long-term symptom relief in patients with NAEMDs, as measured by sustained improvement in Eckardt scores over two years. While a modest increase in symptom burden was noted over time, most patients continued to benefit from the procedure. These findings support E-POEM as an effective treatment for selected NAEMD patients. Further long term follow up and large-scale studies are warranted.

Figure:
Disclosures:
Rawia Aburumman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Okuampa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lena Kawji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Alfrad Nobel Bhuiyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qiang Cai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rawia Aburumman, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Lena Kawji, MD3, Mohammad Alfrad Nobel Bhuiyan, MD3, Qiang Cai, MD, PhD, MACG4. P5648 - Two-Year Outcomes Following Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (E-POEM) for Non-Achalasia Esophageal Motility Disorders, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
