Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Infections and Microbiome
P5644 - Fungal Intestinal Perforation Requiring Hemicolectomy in an Immunocompromised Patient With Stage IV Lung Adenocarcinoma
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Woodly Dominique, DO
Valley Health System
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Woodly Dominique, DO1, Arezou Abbasi, MD1, Melanie De Shadarevian, DO2, Sara Alleyasin, DO1, Brian Carlson, MD1
1Valley Health System, Las Vegas, NV; 2Valley Hospital Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Intestinal perforation in immunocompromised patients presents unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Fungal invasion of the gastrointestinal mucosa can lead to tissue necrosis and life-threatening perforations, particularly in patients with prolonged hospitalization and multiple risk factors for opportunistic infections.
Case Description/
Methods: A 68-year-old male with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma underwent prolonged ICU care requiring mechanical ventilation and central venous access. After initial successful treatment of Candida albicans candidemia with micafungin, the patient developed acute abdominal distention and respiratory distress 24 days later. CT imaging revealed large-volume pneumoperitoneum consistent with perforated viscus. Emergency exploratory laparotomy identified two perforations in the proximal right colon requiring right hemicolectomy. Intraoperative findings included friable, necrotic bowel wall with purulent peritoneal contamination. Peritoneal fluid cultures grew Candida glabrata and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, confirming polymicrobial fungal-bacterial peritonitis. Despite aggressive surgical source control and appropriate antimicrobial therapy, the patient developed post-operative multisystem organ failure and expired three days after surgery.
Discussion: This case illustrates the challenging intersection of fungal pathogenesis and gastrointestinal complications in critically ill patients. Fungal invasion likely contributed to bowel wall necrosis through direct tissue invasion, compounded by immunosuppression and compromised mesenteric perfusion. The polymicrobial nature of the peritoneal infection reflects translocation across a compromised mucosal barrier. Surgical decision-making in this high-risk patient required balancing aggressive source control against operative mortality risk.
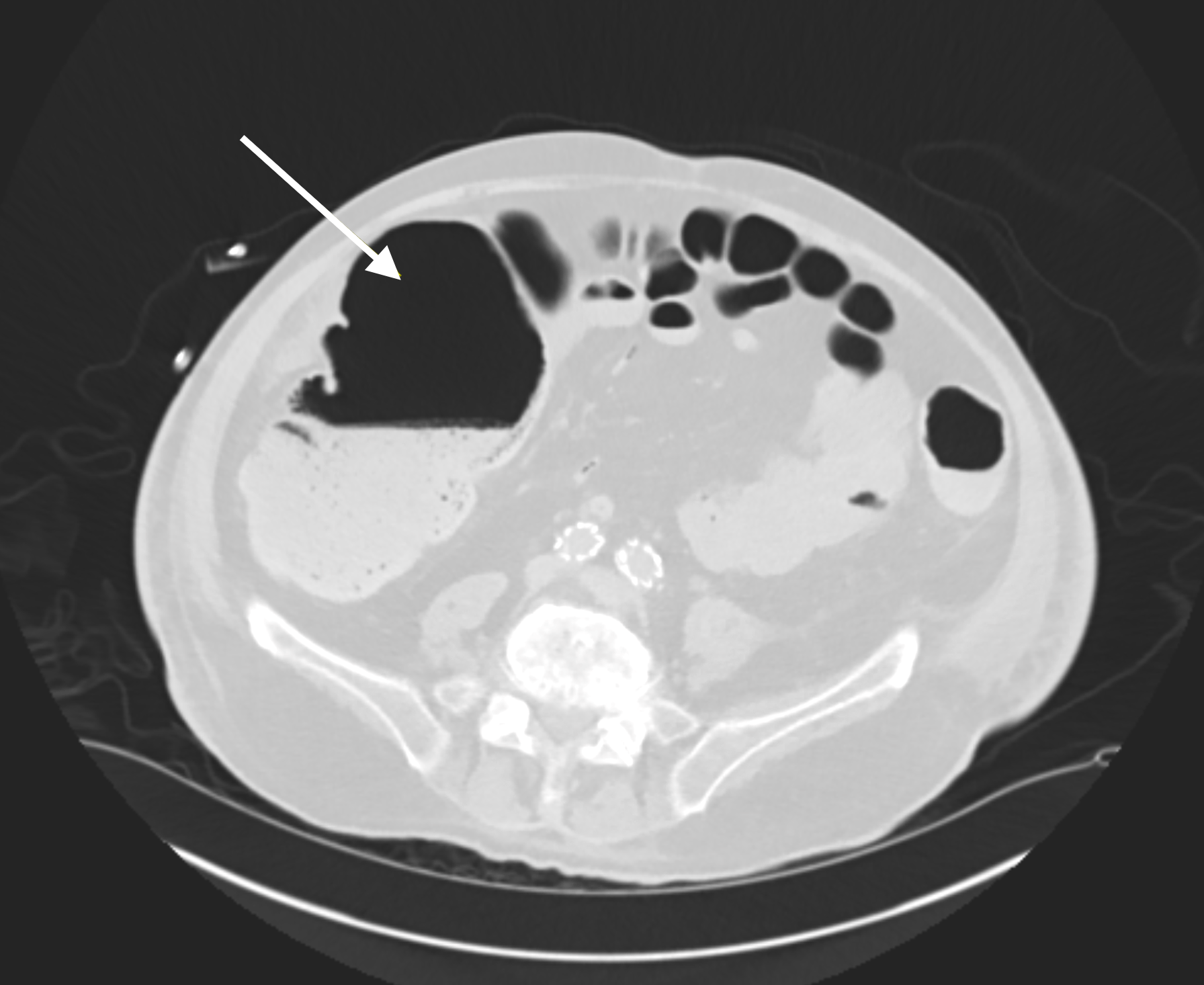
Figure: Figure 1: Gastric Perforation seen on CT, requiring urgent Surgical Intervention
Disclosures:
Woodly Dominique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arezou Abbasi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melanie De Shadarevian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Alleyasin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Carlson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Woodly Dominique, DO1, Arezou Abbasi, MD1, Melanie De Shadarevian, DO2, Sara Alleyasin, DO1, Brian Carlson, MD1. P5644 - Fungal Intestinal Perforation Requiring Hemicolectomy in an Immunocompromised Patient With Stage IV Lung Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Valley Health System, Las Vegas, NV; 2Valley Hospital Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Intestinal perforation in immunocompromised patients presents unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Fungal invasion of the gastrointestinal mucosa can lead to tissue necrosis and life-threatening perforations, particularly in patients with prolonged hospitalization and multiple risk factors for opportunistic infections.
Case Description/
Methods: A 68-year-old male with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma underwent prolonged ICU care requiring mechanical ventilation and central venous access. After initial successful treatment of Candida albicans candidemia with micafungin, the patient developed acute abdominal distention and respiratory distress 24 days later. CT imaging revealed large-volume pneumoperitoneum consistent with perforated viscus. Emergency exploratory laparotomy identified two perforations in the proximal right colon requiring right hemicolectomy. Intraoperative findings included friable, necrotic bowel wall with purulent peritoneal contamination. Peritoneal fluid cultures grew Candida glabrata and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, confirming polymicrobial fungal-bacterial peritonitis. Despite aggressive surgical source control and appropriate antimicrobial therapy, the patient developed post-operative multisystem organ failure and expired three days after surgery.
Discussion: This case illustrates the challenging intersection of fungal pathogenesis and gastrointestinal complications in critically ill patients. Fungal invasion likely contributed to bowel wall necrosis through direct tissue invasion, compounded by immunosuppression and compromised mesenteric perfusion. The polymicrobial nature of the peritoneal infection reflects translocation across a compromised mucosal barrier. Surgical decision-making in this high-risk patient required balancing aggressive source control against operative mortality risk.

Figure: Figure 1: Gastric Perforation seen on CT, requiring urgent Surgical Intervention
Disclosures:
Woodly Dominique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arezou Abbasi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melanie De Shadarevian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Alleyasin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Carlson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Woodly Dominique, DO1, Arezou Abbasi, MD1, Melanie De Shadarevian, DO2, Sara Alleyasin, DO1, Brian Carlson, MD1. P5644 - Fungal Intestinal Perforation Requiring Hemicolectomy in an Immunocompromised Patient With Stage IV Lung Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
