Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5531 - Esophageal Crohn’s Disease Successfully Treated With Risankizumab: A Case Series
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Taylor Hallcox, MD (she/her/hers)
Medical College of Wisconsin
Milwaukee, WI
Presenting Author(s)
Taylor Hallcox, MD1, Daniel J. Stein, MD2
1Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI; 2Medical College of Wisconsin, Wauwatosa, WI
Introduction: Esophageal Crohn’s disease (CD) has been poorly studied despite being a significant predictor of intestinal CD progression and recurrence. Management has historically focused on steroids and acid suppression, with some success from immunosuppressants and biologics like anti-tumor necrosis alpha agents. However, no specific guidelines exist for treating esophageal CD. Risankizumab, a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits interleukin-23 (IL-23), has shown promise in treating both induction and maintenance of remission in CD. This case series explores the use of risankizumab in treating esophageal CD.
Case Description/
Methods: Case 1: A 24-year-old female with moderate to severe esophageal and ileocolonic CD, post-bowel surgery, and previous failure of several biologics, began risankizumab in August 2022. She had a significant clinical response, and her endoscopy in 2023 revealed no active disease, both endoscopically and histologically.
Case 2: A 31-year-old female with severe esophageal and colonic fistulizing CD, peri-anal involvement, and prior bowel surgery, who had failed multiple biologics, started risankizumab in July 2022. She experienced significant clinical improvement, and her endoscopy in 2023 suggested endoscopic/histologic remission.
Case 3: A 28-year-old female with moderate esophageal and ileocolonic medication-refractory CD began risankizumab in April 2023. Follow-up endoscopy in 2024 showed significant improvement in esophageal scarring, with histologic response confirmed.
Discussion: This series represents the first reported use of risankizumab in esophageal CD. Current literature supports its effectiveness for induction (ADVANCE and MOTIVATE trials) and maintenance (FORTIFY trial) in moderately to severely active CD. Risankizumab's safety profile is consistent with other IL-23 inhibitors, with common adverse events including upper respiratory infections, headache, and fatigue. Despite the absence of guidelines for esophageal CD management, these cases suggest risankizumab may offer a valuable treatment option. Further research is needed to evaluate its long-term safety and efficacy across broader patient populations and compare its effectiveness with other biologics.
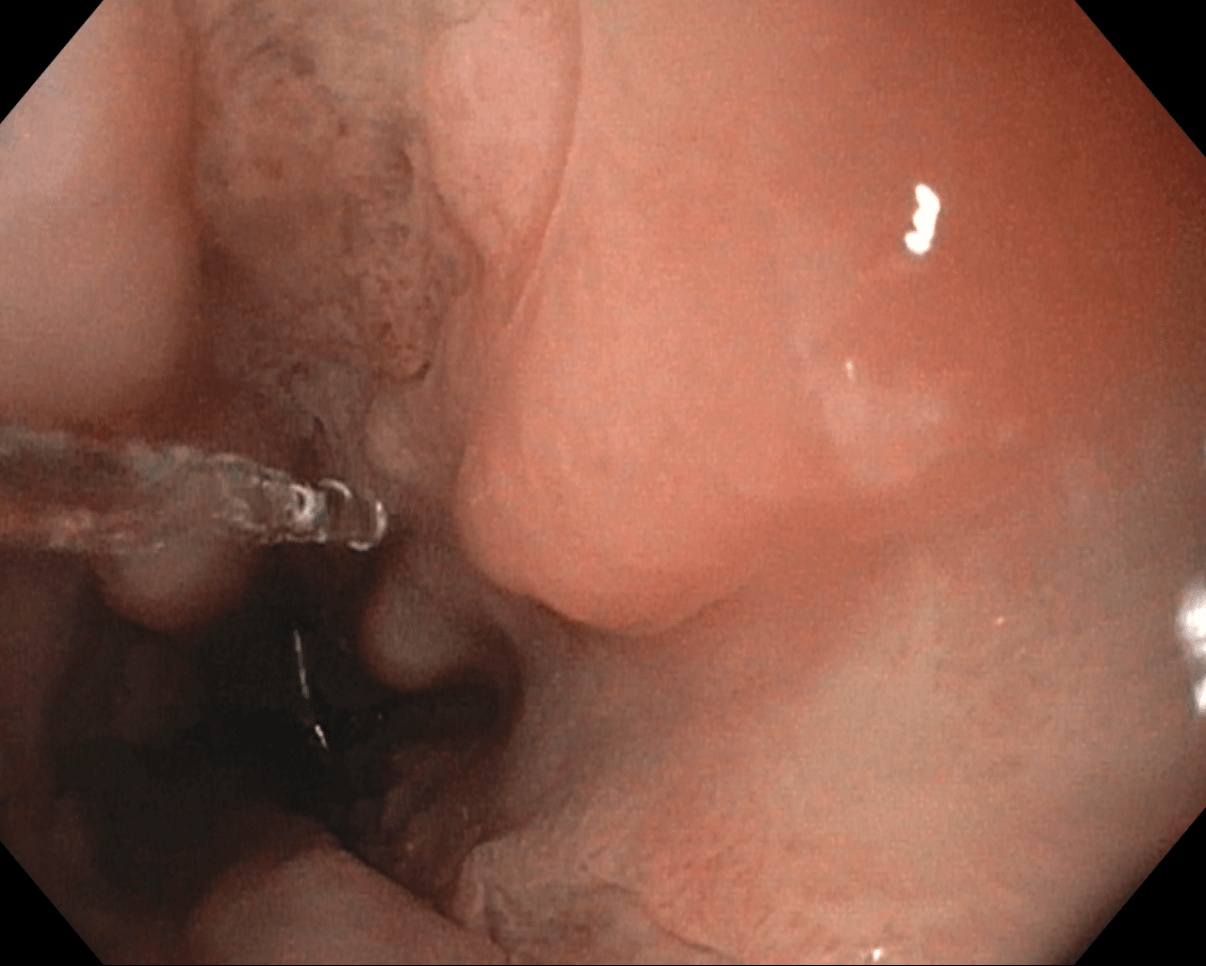
Figure: Image 1: Esophageal ulcers in the distal esophagus seen in Case 1.
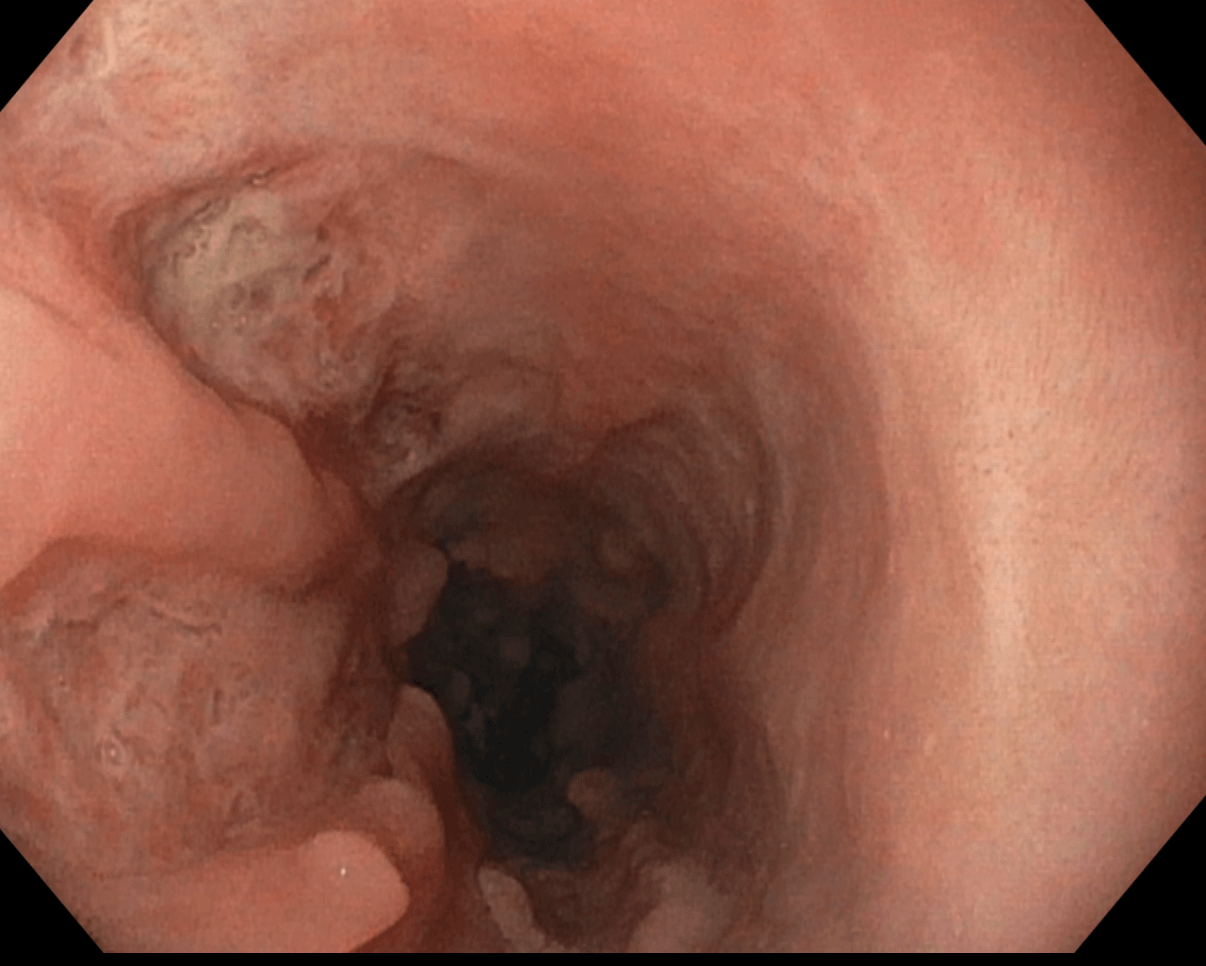
Figure: Image 2: Esophageal ulcers in the proximal esophagus from in Case 1.
Disclosures:
Taylor Hallcox indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Stein: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Speakers Bureau.
Taylor Hallcox, MD1, Daniel J. Stein, MD2. P5531 - Esophageal Crohn’s Disease Successfully Treated With Risankizumab: A Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI; 2Medical College of Wisconsin, Wauwatosa, WI
Introduction: Esophageal Crohn’s disease (CD) has been poorly studied despite being a significant predictor of intestinal CD progression and recurrence. Management has historically focused on steroids and acid suppression, with some success from immunosuppressants and biologics like anti-tumor necrosis alpha agents. However, no specific guidelines exist for treating esophageal CD. Risankizumab, a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits interleukin-23 (IL-23), has shown promise in treating both induction and maintenance of remission in CD. This case series explores the use of risankizumab in treating esophageal CD.
Case Description/
Methods: Case 1: A 24-year-old female with moderate to severe esophageal and ileocolonic CD, post-bowel surgery, and previous failure of several biologics, began risankizumab in August 2022. She had a significant clinical response, and her endoscopy in 2023 revealed no active disease, both endoscopically and histologically.
Case 2: A 31-year-old female with severe esophageal and colonic fistulizing CD, peri-anal involvement, and prior bowel surgery, who had failed multiple biologics, started risankizumab in July 2022. She experienced significant clinical improvement, and her endoscopy in 2023 suggested endoscopic/histologic remission.
Case 3: A 28-year-old female with moderate esophageal and ileocolonic medication-refractory CD began risankizumab in April 2023. Follow-up endoscopy in 2024 showed significant improvement in esophageal scarring, with histologic response confirmed.
Discussion: This series represents the first reported use of risankizumab in esophageal CD. Current literature supports its effectiveness for induction (ADVANCE and MOTIVATE trials) and maintenance (FORTIFY trial) in moderately to severely active CD. Risankizumab's safety profile is consistent with other IL-23 inhibitors, with common adverse events including upper respiratory infections, headache, and fatigue. Despite the absence of guidelines for esophageal CD management, these cases suggest risankizumab may offer a valuable treatment option. Further research is needed to evaluate its long-term safety and efficacy across broader patient populations and compare its effectiveness with other biologics.

Figure: Image 1: Esophageal ulcers in the distal esophagus seen in Case 1.

Figure: Image 2: Esophageal ulcers in the proximal esophagus from in Case 1.
Disclosures:
Taylor Hallcox indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Stein: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Speakers Bureau.
Taylor Hallcox, MD1, Daniel J. Stein, MD2. P5531 - Esophageal Crohn’s Disease Successfully Treated With Risankizumab: A Case Series, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

