Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5475 - Escalating the Dosage: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Standard and Intensified Infliximab for ASUC
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- PD
Priyata Dutta, MD (she/her/hers)
Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital
Ypsilanti, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB1, Priyata Dutta, MD2, Jeffrey Berinstein, MD, MS3, Matthew C. Choy, MBBS, PhD4, Elliot Berinstein, MD, MS5, Syed A. Hassan, MBBS3, Christopher F.D.. Li Wai Suen, MBBS6, Danny Con, MD4, Peter D. R.. Higgins, MD, PhD, MSc3, Peter De Cruz, MBBS, PhD4, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM7, Vishal Sharma, MBBS8, Shrinivas Bishu, MD3
1Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 2Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 3University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 4University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; 5Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI; 6Austin Health, Melbourne, Australia & The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; 7All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 8AIIMS, Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: The standard dosing strategy for infliximab (IFX), set at 5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6 for treating acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC), remains a subject of debate. Intensified IFX dosing, which involves administering 5 mg/kg at shorter intervals, increasing the dose to 10 mg/kg, or using combinations, aims to quickly achieve therapeutic drug levels. However,evidence supporting this approach remains insufficient. Herein, we aim to evaluate the efficacy of standard versus intensified IFX induction regimens in adult ASUC patients.
Methods: Electronic databases were searched from their inception until December 2024, following PRISMA guidelines. The primary outcome measured was the 3-month colectomy rate with ASUC receiving either standard or intensified IFX induction. Event rates were converted into log odds ratios (logOR) and standard errors (SE). IFX randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were utilized to determine historical pooled colectomy rates for standard IFX dosing through a random-effects model meta-analysis. A fixed-effects generalized linear model (GLM) was used to compare colectomy rates between IFX RCTs and the PREDICT-UC study.
Results: Out of 2180 screened studies, 41 full-text articles were reviewed, resulting in the inclusion of 11 studies (10 retrospective studies and 1 randomized controlled trial [RCT]) to compare intensified versus standard infliximab (IFX) dosing. Among these, four RCTs evaluated standard dose IFX against other agents for ASUC (Table 1). Given that our search identified 10 retrospective studies but only one RCT comparing standard versus intensified IFX, we employed two analytical approaches. Initially, we conducted a meta-analysis of the retrospective studies. Subsequently, we aggregated RCTs of standard dose IFX versus other agents in ASUC to establish a historical 3-month colectomy rate for standard dose IFX, which was then compared to the rates reported in the RCT of standard versus intensified dose IFX (Table 2). The meta-analysis of retrospective studies, involving 530 patients on standard IFX and 406 on intensified IFX, showed a reduced risk of colectomy at 3 months with intensified dosing (P< 0.05). The four RCTs with standard IFX dosing indicated a historical 3-month colectomy rate of 28% (95% CI: 22%-34%).
Discussion: Intensified dosing of IFX serves as a protective measure against colectomy in patients with ASUC. Future prospective studies are needed to consider the integration of adaptive IFX dosing strategies.
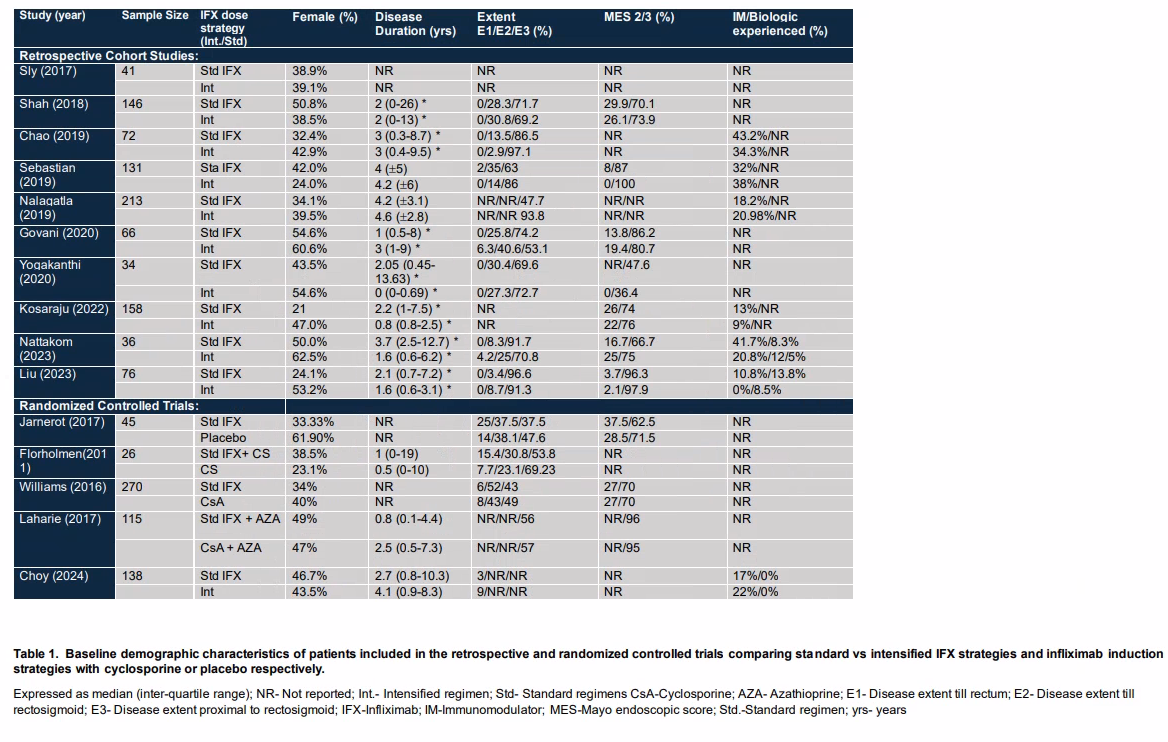
Figure: Table 1. Baseline demographic characteristics of patients included in the retrospective and randomized controlled trials comparing standard vs intensified IFX strategies and infliximab induction strategies with cyclosporine or placebo respectively.
Expressed as median (inter-quartile range); NR- Not reported; Int.- Intensified regimen; Std- Standard regimens CsA-Cyclosporine; AZA- Azathioprine; E1- Disease extent till rectum; E2- Disease extent till rectosigmoid; E3- Disease extent proximal to rectosigmoid;
IFX-Infliximab; IM-Immunomodulator; MES-Mayo endoscopic score; Std.-Standard regimen; yrs- years
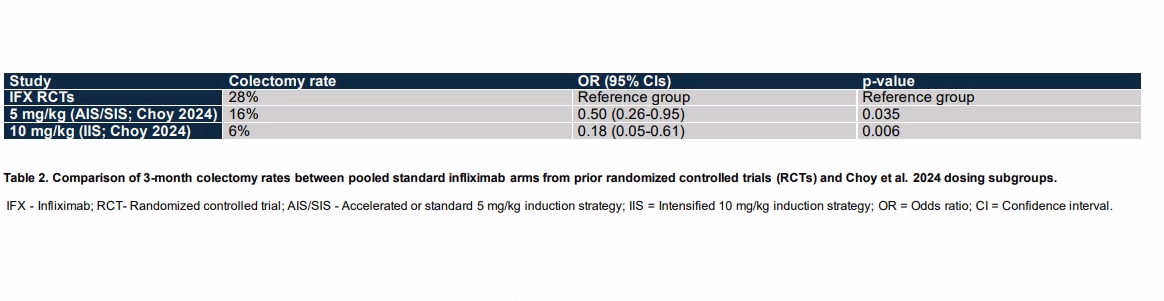
Figure: Table 2. Comparison of 3-month colectomy rates between pooled standard infliximab arms from prior randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and Choy et al. 2024 dosing subgroups.
IFX - Infliximab; RCT- Randomized controlled trial; AIS/SIS - Accelerated or standard 5 mg/kg induction strategy; IIS = Intensified 10 mg/kg induction strategy; OR = Odds ratio; CI = Confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Manjeet Kumar Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyata Dutta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Berinstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Choy: Gandel Philanthropy – Grant/Research Support. Janssen Cilag – Grant/Research Support.
Elliot Berinstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Li Wai Suen: Diasorin – Grant/Research Support. Dr Falk Pharma – educational support. Essange Reagents – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Grant/Research Support.
Danny Con indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Higgins: AbbVie – Consultant.
Peter De Cruz: AbbVie, Baxter, Ferring, Janssen, Celltrion, Emerge Health, Shire, and Take – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Vineet Ahuja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishal Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shrinivas Bishu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB1, Priyata Dutta, MD2, Jeffrey Berinstein, MD, MS3, Matthew C. Choy, MBBS, PhD4, Elliot Berinstein, MD, MS5, Syed A. Hassan, MBBS3, Christopher F.D.. Li Wai Suen, MBBS6, Danny Con, MD4, Peter D. R.. Higgins, MD, PhD, MSc3, Peter De Cruz, MBBS, PhD4, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM7, Vishal Sharma, MBBS8, Shrinivas Bishu, MD3. P5475 - Escalating the Dosage: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Standard and Intensified Infliximab for ASUC, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 2Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ypsilanti, MI; 3University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI; 4University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; 5Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI; 6Austin Health, Melbourne, Australia & The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; 7All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 8AIIMS, Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: The standard dosing strategy for infliximab (IFX), set at 5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6 for treating acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC), remains a subject of debate. Intensified IFX dosing, which involves administering 5 mg/kg at shorter intervals, increasing the dose to 10 mg/kg, or using combinations, aims to quickly achieve therapeutic drug levels. However,evidence supporting this approach remains insufficient. Herein, we aim to evaluate the efficacy of standard versus intensified IFX induction regimens in adult ASUC patients.
Methods: Electronic databases were searched from their inception until December 2024, following PRISMA guidelines. The primary outcome measured was the 3-month colectomy rate with ASUC receiving either standard or intensified IFX induction. Event rates were converted into log odds ratios (logOR) and standard errors (SE). IFX randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were utilized to determine historical pooled colectomy rates for standard IFX dosing through a random-effects model meta-analysis. A fixed-effects generalized linear model (GLM) was used to compare colectomy rates between IFX RCTs and the PREDICT-UC study.
Results: Out of 2180 screened studies, 41 full-text articles were reviewed, resulting in the inclusion of 11 studies (10 retrospective studies and 1 randomized controlled trial [RCT]) to compare intensified versus standard infliximab (IFX) dosing. Among these, four RCTs evaluated standard dose IFX against other agents for ASUC (Table 1). Given that our search identified 10 retrospective studies but only one RCT comparing standard versus intensified IFX, we employed two analytical approaches. Initially, we conducted a meta-analysis of the retrospective studies. Subsequently, we aggregated RCTs of standard dose IFX versus other agents in ASUC to establish a historical 3-month colectomy rate for standard dose IFX, which was then compared to the rates reported in the RCT of standard versus intensified dose IFX (Table 2). The meta-analysis of retrospective studies, involving 530 patients on standard IFX and 406 on intensified IFX, showed a reduced risk of colectomy at 3 months with intensified dosing (P< 0.05). The four RCTs with standard IFX dosing indicated a historical 3-month colectomy rate of 28% (95% CI: 22%-34%).
Discussion: Intensified dosing of IFX serves as a protective measure against colectomy in patients with ASUC. Future prospective studies are needed to consider the integration of adaptive IFX dosing strategies.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline demographic characteristics of patients included in the retrospective and randomized controlled trials comparing standard vs intensified IFX strategies and infliximab induction strategies with cyclosporine or placebo respectively.
Expressed as median (inter-quartile range); NR- Not reported; Int.- Intensified regimen; Std- Standard regimens CsA-Cyclosporine; AZA- Azathioprine; E1- Disease extent till rectum; E2- Disease extent till rectosigmoid; E3- Disease extent proximal to rectosigmoid;
IFX-Infliximab; IM-Immunomodulator; MES-Mayo endoscopic score; Std.-Standard regimen; yrs- years

Figure: Table 2. Comparison of 3-month colectomy rates between pooled standard infliximab arms from prior randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and Choy et al. 2024 dosing subgroups.
IFX - Infliximab; RCT- Randomized controlled trial; AIS/SIS - Accelerated or standard 5 mg/kg induction strategy; IIS = Intensified 10 mg/kg induction strategy; OR = Odds ratio; CI = Confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Manjeet Kumar Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyata Dutta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Berinstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Choy: Gandel Philanthropy – Grant/Research Support. Janssen Cilag – Grant/Research Support.
Elliot Berinstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Li Wai Suen: Diasorin – Grant/Research Support. Dr Falk Pharma – educational support. Essange Reagents – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Grant/Research Support.
Danny Con indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Peter Higgins: AbbVie – Consultant.
Peter De Cruz: AbbVie, Baxter, Ferring, Janssen, Celltrion, Emerge Health, Shire, and Take – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Vineet Ahuja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishal Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shrinivas Bishu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manjeet Kumar Goyal, MBBS, MD, DM, DNB1, Priyata Dutta, MD2, Jeffrey Berinstein, MD, MS3, Matthew C. Choy, MBBS, PhD4, Elliot Berinstein, MD, MS5, Syed A. Hassan, MBBS3, Christopher F.D.. Li Wai Suen, MBBS6, Danny Con, MD4, Peter D. R.. Higgins, MD, PhD, MSc3, Peter De Cruz, MBBS, PhD4, Vineet Ahuja, MBBS, MD, DM7, Vishal Sharma, MBBS8, Shrinivas Bishu, MD3. P5475 - Escalating the Dosage: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Standard and Intensified Infliximab for ASUC, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
