Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5451 - Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis on the Safety and Efficacy of Ustekinumab Treatment for Crohn’s Disease Patients
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AE
Abdelwahap Elghezewi, MD
Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine
Barboursville, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Abdelwahap Elghezewi, MD1, Mohamed L. Hammad, MD2, Mohamed Y. Elnaghy, MD3, Youssef Ragab, MD4, Mohamed Seoudy, MD4, Mostafa M. Abdelbary, MD4, Ahmed Samy Ali, MD4, Mohammed Elsayed Elkholy, MD4, Abdelrahman Abdelhamid, MD4, Wesam Frandah, MD2, Ahmed Sherif, MD2
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Barboursville, WV; 2Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 3Alexandria University, N/A, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt; 4Alexandria University, NA, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a heterogeneous, immune-mediated inflammatory condition characterized by transmural inflammation and skip lesions, affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus. Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the p40 subunit of interleukins 12 and 23 which is approved for moderate to severe CD patients, but its pharmacokinetics and optimal serum concentrations are not well defined. We aim to evaluate safety and efficacy of Ustekinumab Treatment in comparison to Adalimumab, Anti-TNF, Vedolizumab, and placebo in different follow up durations.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive literature search through multiple search engines (Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane) to include eligible studies using the appropriate keywords until 10th June 2024. We included 14 studies in our analysis in addition to eight studies as narrative without being included in analysis. The network meta-analysis was performed through the R software.
Results: In terms of CDAI clinical response, no significant differences were observed between any of the comparison arms at any follow-up period. However, ustekinumab demonstrated superior results for CDAI clinical remission between 15 and 26 weeks, showing significant improvements compared to vedolizumab (RR=1.15 [1.00; 1.33], 95% CI) and placebo (RR=1.59 [1.28; 1.97], 95% CI). Additionally, for CDAI clinical remission between 30 and 60 weeks, both adalimumab and ustekinumab yielded the best outcomes, significantly outperforming vedolizumab and placebo. Furthermore, adalimumab was associated with a significantly lower incidence of CDAI clinical remission compared to anti-TNF agents (RR=1.93 [1.03; 3.64], 95% CI).
Discussion: Although there were no significant differences in CDAI clinical response across comparison arms at any follow-up period, ustekinumab demonstrated promising results. Specifically, ustekinumab significantly improved CDAI clinical remission rates between 15 and 26 weeks compared to vedolizumab and placebo. Additionally, both adalimumab and ustekinumab showed the best outcomes for CDAI clinical remission between 30 and 60 weeks. These findings suggest that ustekinumab is a promising therapeutic option for Crohn's disease.
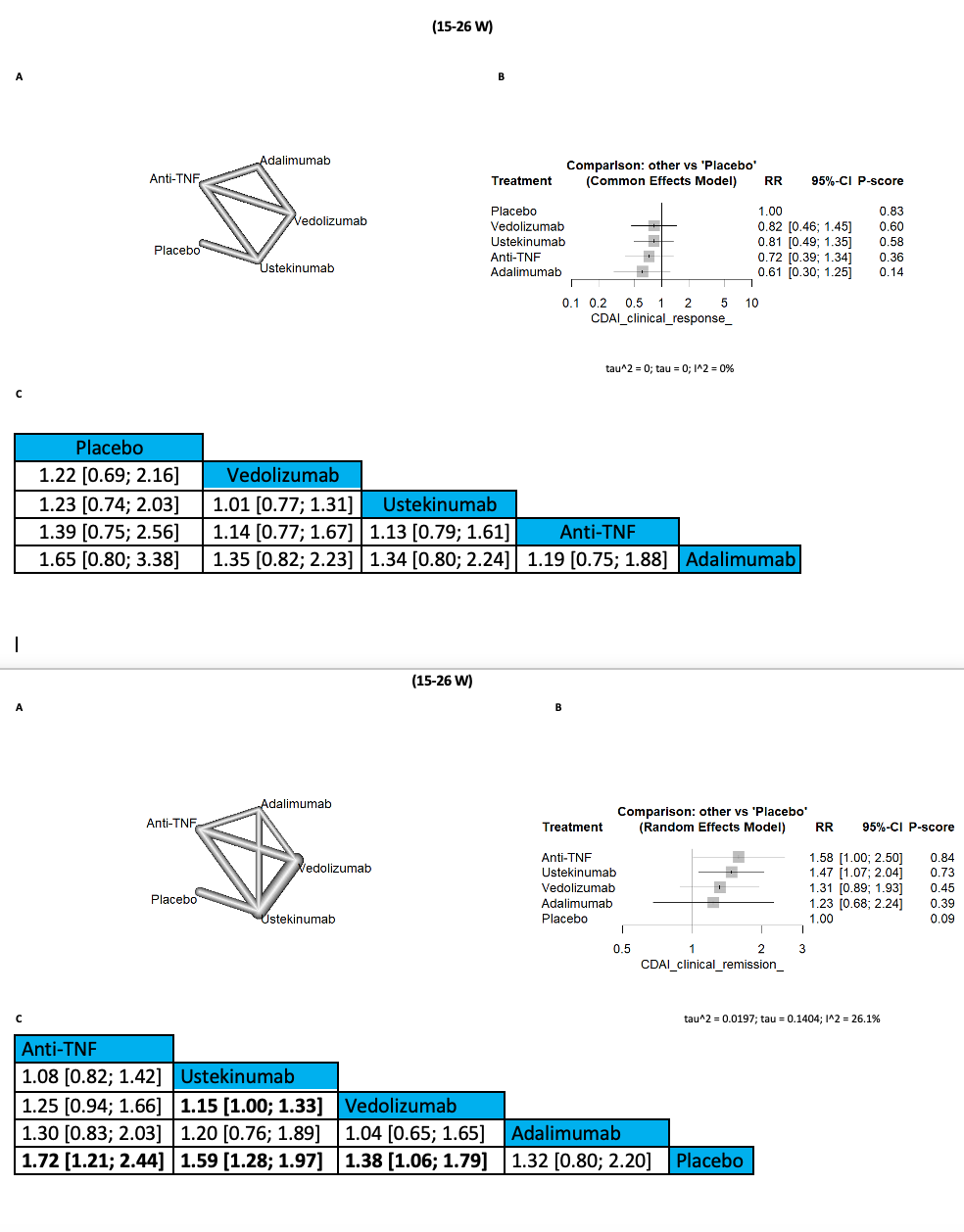
Figure: (15 to 26 W)
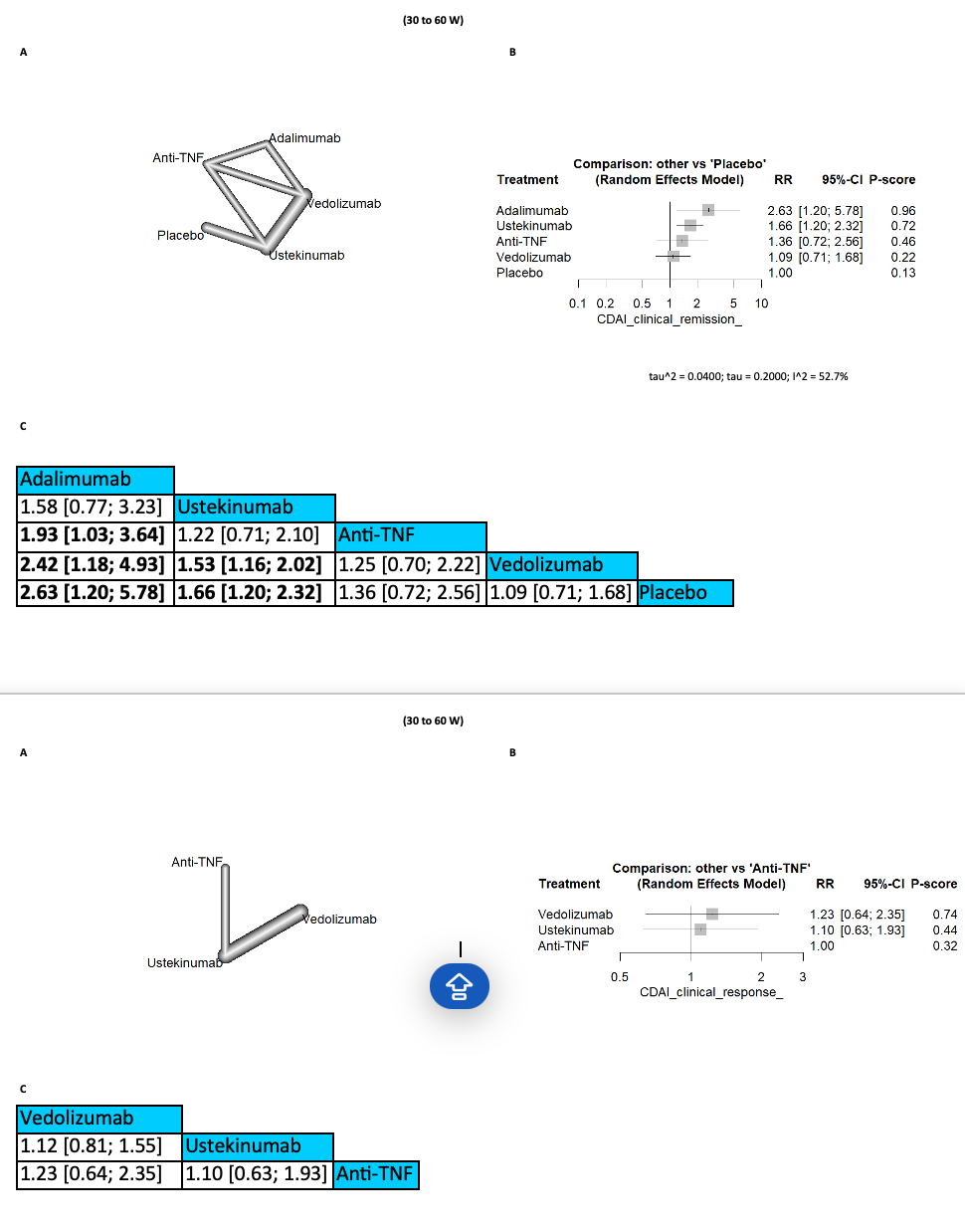
Figure: (30 to 60 W)
Disclosures:
Abdelwahap Elghezewi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Y. Elnaghy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Youssef Ragab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Seoudy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa M. Abdelbary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Samy Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Elsayed Elkholy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Abdelhamid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wesam Frandah: Boston Scientific – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant. Merritt – Consultant. Olympus corporation of America – Consultant.
Ahmed Sherif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelwahap Elghezewi, MD1, Mohamed L. Hammad, MD2, Mohamed Y. Elnaghy, MD3, Youssef Ragab, MD4, Mohamed Seoudy, MD4, Mostafa M. Abdelbary, MD4, Ahmed Samy Ali, MD4, Mohammed Elsayed Elkholy, MD4, Abdelrahman Abdelhamid, MD4, Wesam Frandah, MD2, Ahmed Sherif, MD2. P5451 - Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis on the Safety and Efficacy of Ustekinumab Treatment for Crohn’s Disease Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Barboursville, WV; 2Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 3Alexandria University, N/A, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt; 4Alexandria University, NA, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a heterogeneous, immune-mediated inflammatory condition characterized by transmural inflammation and skip lesions, affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus. Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the p40 subunit of interleukins 12 and 23 which is approved for moderate to severe CD patients, but its pharmacokinetics and optimal serum concentrations are not well defined. We aim to evaluate safety and efficacy of Ustekinumab Treatment in comparison to Adalimumab, Anti-TNF, Vedolizumab, and placebo in different follow up durations.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive literature search through multiple search engines (Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane) to include eligible studies using the appropriate keywords until 10th June 2024. We included 14 studies in our analysis in addition to eight studies as narrative without being included in analysis. The network meta-analysis was performed through the R software.
Results: In terms of CDAI clinical response, no significant differences were observed between any of the comparison arms at any follow-up period. However, ustekinumab demonstrated superior results for CDAI clinical remission between 15 and 26 weeks, showing significant improvements compared to vedolizumab (RR=1.15 [1.00; 1.33], 95% CI) and placebo (RR=1.59 [1.28; 1.97], 95% CI). Additionally, for CDAI clinical remission between 30 and 60 weeks, both adalimumab and ustekinumab yielded the best outcomes, significantly outperforming vedolizumab and placebo. Furthermore, adalimumab was associated with a significantly lower incidence of CDAI clinical remission compared to anti-TNF agents (RR=1.93 [1.03; 3.64], 95% CI).
Discussion: Although there were no significant differences in CDAI clinical response across comparison arms at any follow-up period, ustekinumab demonstrated promising results. Specifically, ustekinumab significantly improved CDAI clinical remission rates between 15 and 26 weeks compared to vedolizumab and placebo. Additionally, both adalimumab and ustekinumab showed the best outcomes for CDAI clinical remission between 30 and 60 weeks. These findings suggest that ustekinumab is a promising therapeutic option for Crohn's disease.

Figure: (15 to 26 W)

Figure: (30 to 60 W)
Disclosures:
Abdelwahap Elghezewi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Y. Elnaghy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Youssef Ragab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Seoudy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa M. Abdelbary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Samy Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Elsayed Elkholy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Abdelhamid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wesam Frandah: Boston Scientific – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant. Merritt – Consultant. Olympus corporation of America – Consultant.
Ahmed Sherif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelwahap Elghezewi, MD1, Mohamed L. Hammad, MD2, Mohamed Y. Elnaghy, MD3, Youssef Ragab, MD4, Mohamed Seoudy, MD4, Mostafa M. Abdelbary, MD4, Ahmed Samy Ali, MD4, Mohammed Elsayed Elkholy, MD4, Abdelrahman Abdelhamid, MD4, Wesam Frandah, MD2, Ahmed Sherif, MD2. P5451 - Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis on the Safety and Efficacy of Ustekinumab Treatment for Crohn’s Disease Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
