Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5383 - Glucagon Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahmed Telbany, MD
University of New Mexico
Albuquerque, New Mexico
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmed Telbany, MD1, Niven Wang, DO2, Abdelrahman Yousef, MD2, Pooja Viswanath, DO1, Abhishek Patel, MD3, Evelyn Inga, MD1, Kara Eileen. Rieth, DO4, Swathi Paleti, MD3
1University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 2University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, NM; 3University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM; 4UNM, Albuquerque, NM
Introduction: Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP- RA) have anti inflammatory properties, yet their effect on the clinical course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is unclear.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective multicenter cohort study using a national multi-institution database. Adults with Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis receiving a GLP-1 RA (dulaglutide, liraglutide, tirzepatide, or semaglutide) formed the exposure cohort. A one-to-one propensity matched comparator cohort of IBD patients without GLP-1 RA exposure was created (29 203 in each cohort) balancing demographics, comorbidities, and IBD medications. Outcomes within 365 days after index prescription were colectomy, bowel resection, intravenous (IV) steroid use, oral (PO) steroid use, emergency department (ED) visits, and hospitalizations. Adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were calculated from matched data. Analysis of de-identified data was exempt from institutional review board oversight.
Results: Baseline characteristics were well balanced (Table 1). Mean age was 56.9 ± 13.2 versus 57.6 ± 14.1 years; female sex 18,181 [62.3 %] versus 18,146 [62.1 %]; White race 21,663 [74.2 %] versus 21 562 [73.8 %]. Comorbidities and medication class use were similar after matching. During follow up, GLP 1 analog use was associated with lower risks of all escalation outcomes (Figure 1). Colectomy occurred in 48 patients [0.2 %] versus 198 [0.7 %] (aOR 0.241, 95 % CI 0.176 0.331). Bowel resection was 0.015 % versus 0.036 % (aOR 0.411, 95 % CI 0.367 0.460). IV steroid use was 23.7 % versus 25.0 % (aOR 0.934, 95 % CI 0.899 0.969); PO steroid initiation 15.4 % versus 18.5 % (aOR 0.799, 95 % CI 0.766 0.835); ED visits 19.1 % versus 23.8 % (aOR 0.756, 95 % CI 0.727 0.787); and hospitalizations 13.1 % versus 23.3 % (aOR 0.495, 95 % CI 0.474 0.517).
Discussion: In a real world matched cohort of 58,406 IBD patients, GLP-1 RA use was linked to significantly lower colectomy, bowel resection, corticosteroid use, ED utilization, and hospitalization. Further data are needed from prospective trials to evaluate GLP-1 RA therapy as an adjunct for inflammatory bowel disease.
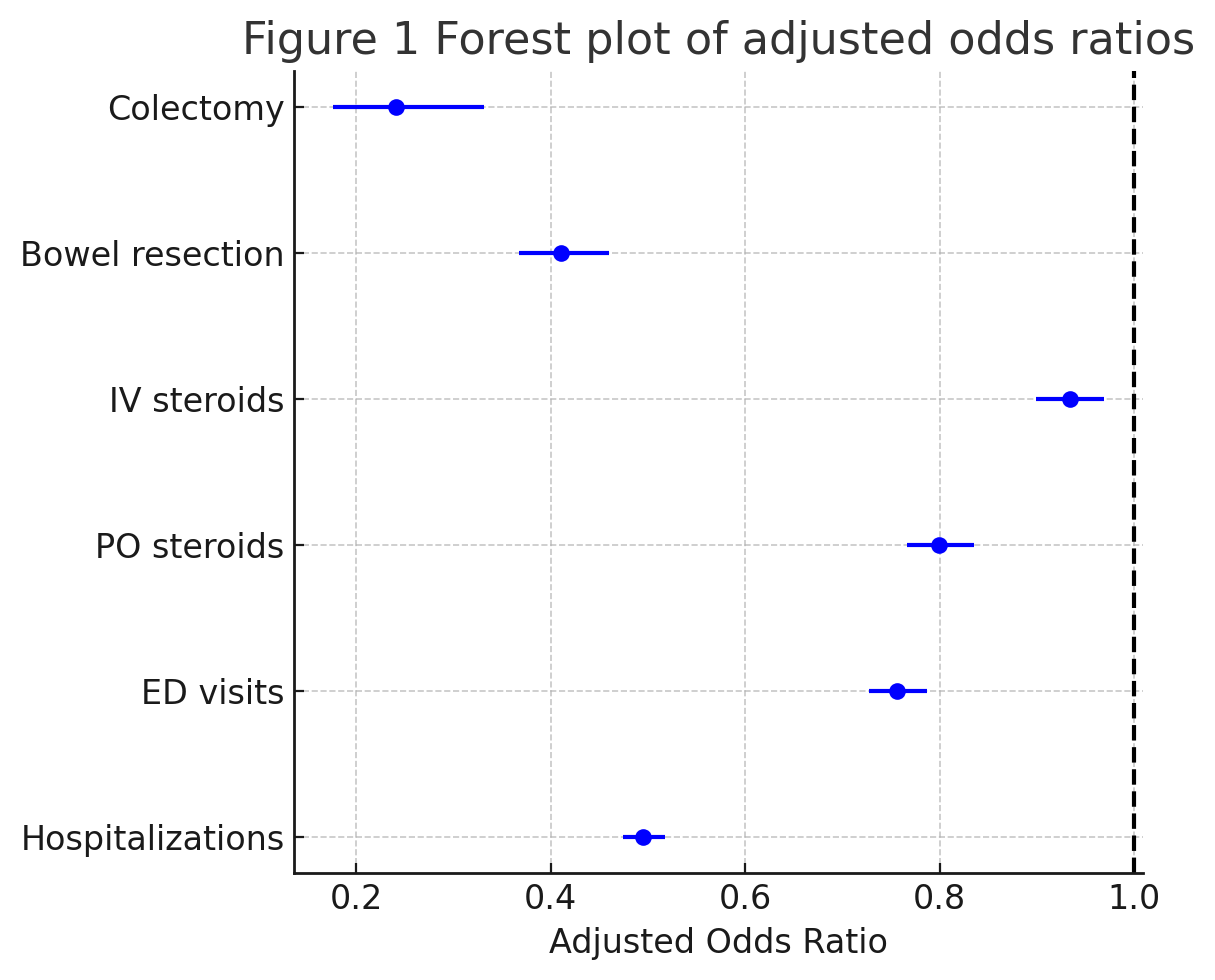
Figure: Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of IBD Patients
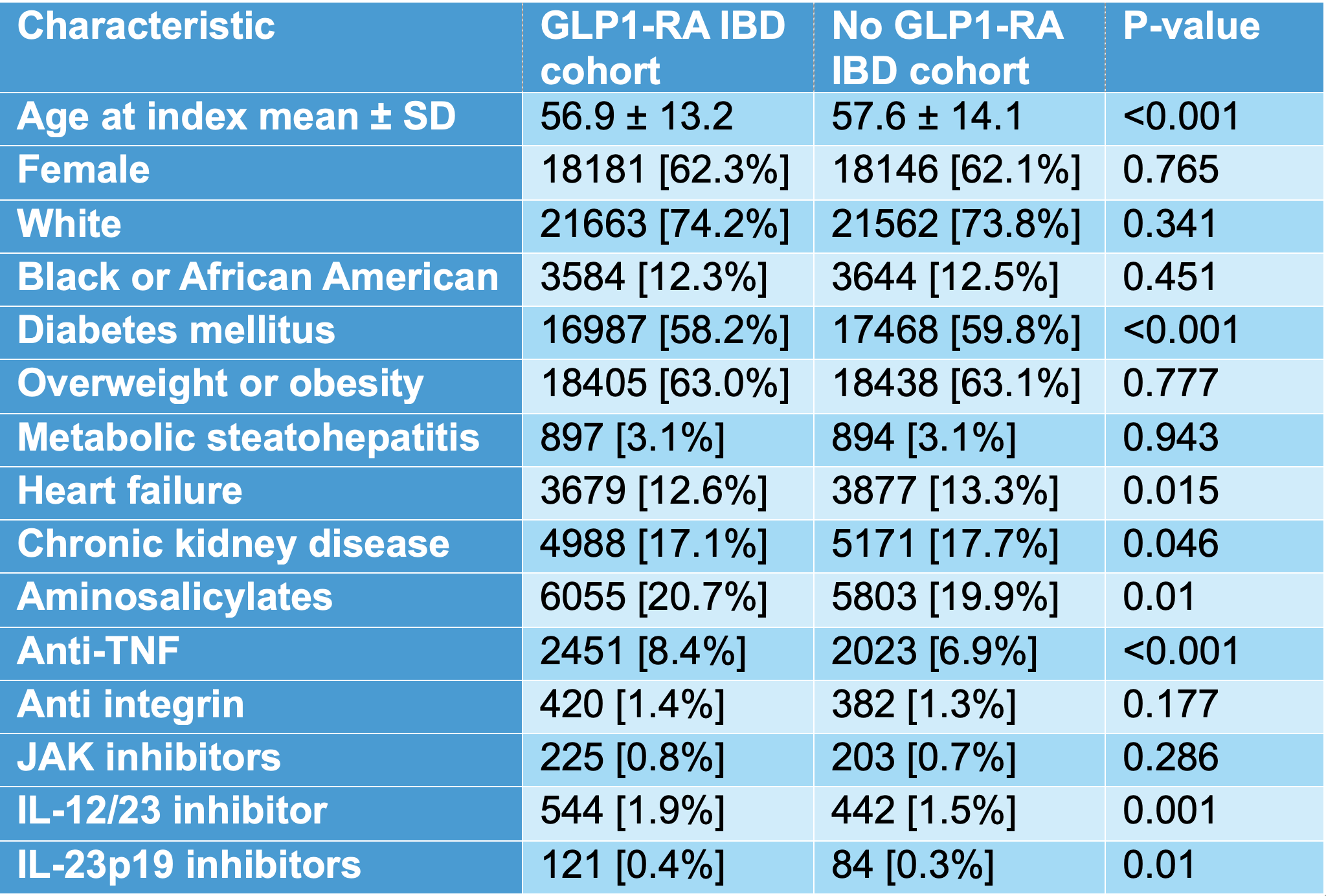
Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot Of Adjusted Odds Ratios of GLP1-RA IBD Patients
Disclosures:
Ahmed Telbany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Niven Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Yousef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pooja Viswanath indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evelyn Inga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kara Rieth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swathi Paleti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Telbany, MD1, Niven Wang, DO2, Abdelrahman Yousef, MD2, Pooja Viswanath, DO1, Abhishek Patel, MD3, Evelyn Inga, MD1, Kara Eileen. Rieth, DO4, Swathi Paleti, MD3. P5383 - Glucagon Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 2University of New Mexico Hospital, Albuquerque, NM; 3University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM; 4UNM, Albuquerque, NM
Introduction: Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP- RA) have anti inflammatory properties, yet their effect on the clinical course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is unclear.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective multicenter cohort study using a national multi-institution database. Adults with Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis receiving a GLP-1 RA (dulaglutide, liraglutide, tirzepatide, or semaglutide) formed the exposure cohort. A one-to-one propensity matched comparator cohort of IBD patients without GLP-1 RA exposure was created (29 203 in each cohort) balancing demographics, comorbidities, and IBD medications. Outcomes within 365 days after index prescription were colectomy, bowel resection, intravenous (IV) steroid use, oral (PO) steroid use, emergency department (ED) visits, and hospitalizations. Adjusted odds ratios (aOR) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were calculated from matched data. Analysis of de-identified data was exempt from institutional review board oversight.
Results: Baseline characteristics were well balanced (Table 1). Mean age was 56.9 ± 13.2 versus 57.6 ± 14.1 years; female sex 18,181 [62.3 %] versus 18,146 [62.1 %]; White race 21,663 [74.2 %] versus 21 562 [73.8 %]. Comorbidities and medication class use were similar after matching. During follow up, GLP 1 analog use was associated with lower risks of all escalation outcomes (Figure 1). Colectomy occurred in 48 patients [0.2 %] versus 198 [0.7 %] (aOR 0.241, 95 % CI 0.176 0.331). Bowel resection was 0.015 % versus 0.036 % (aOR 0.411, 95 % CI 0.367 0.460). IV steroid use was 23.7 % versus 25.0 % (aOR 0.934, 95 % CI 0.899 0.969); PO steroid initiation 15.4 % versus 18.5 % (aOR 0.799, 95 % CI 0.766 0.835); ED visits 19.1 % versus 23.8 % (aOR 0.756, 95 % CI 0.727 0.787); and hospitalizations 13.1 % versus 23.3 % (aOR 0.495, 95 % CI 0.474 0.517).
Discussion: In a real world matched cohort of 58,406 IBD patients, GLP-1 RA use was linked to significantly lower colectomy, bowel resection, corticosteroid use, ED utilization, and hospitalization. Further data are needed from prospective trials to evaluate GLP-1 RA therapy as an adjunct for inflammatory bowel disease.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of IBD Patients

Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot Of Adjusted Odds Ratios of GLP1-RA IBD Patients
Disclosures:
Ahmed Telbany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Niven Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Yousef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pooja Viswanath indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evelyn Inga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kara Rieth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swathi Paleti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Telbany, MD1, Niven Wang, DO2, Abdelrahman Yousef, MD2, Pooja Viswanath, DO1, Abhishek Patel, MD3, Evelyn Inga, MD1, Kara Eileen. Rieth, DO4, Swathi Paleti, MD3. P5383 - Glucagon Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
