Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5368 - Clear Enough to Drink? A Head-to-Head Comparison of Large Language Model-Generated Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ryan Njeim, MD (he/him/his)
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health
Staten Island, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ryan Njeim, MD, Joelle Sleiman, MD, Elie Moussa, MD, Harika Kandlakunta, MD, Alia Hasham, MD
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Patient communication poses a significant challenge in medicine due to literacy gaps and time constraints. Recently, large language models (LLMs) are being used to help with documentation and communication but their medical accuracy and readability vary. High-quality instructions for procedures such as colonoscopy are critical to ensure patient adherence, and safety. This study compared the readability and quality of colonoscopy preparation instructions generated by five leading LLMs.
Methods: A standardized prompt was used to generate colonoscopy preparation instructions from five LLMs: ChatGPT-4, DeepSeek (R1), Gemini 2.5 Flash, Claude Sonnet 4, and Perplexity AI. Outputs were limited to < 500 words. Readability was assessed using Flesch Reading Ease Score (FRES), Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FKGL), and SMOG Index. 3 independent reviewers (RN, EM and JS) evaluated quality using the Patient Education Materials Assessment Tool (PEMAT), the DISCERN score, and a custom Likert-type rubric assessing accuracy, clinical appropriateness, completeness, clarity, harm potential, and bias. Descriptive statistics were used for comparison.
Results: All LLMs adhered to the output limit except Gemini (863 words). DeepSeek had the highest FRES (68.2) and lowest FKGL (5), indicating superior readability while Gemini scored the lowest (FRES 59.6, FKGL 7). SMOG scores ranged from 8 (Claude) to 10 (Gemini) (Table 1). All LLMs achieved 100% audience reach and had similar tone profiles. PEMAT scores were consistent across models (actionability 60%, understandability 84.6%). Perplexity scored highest in DISCERN reliability (3.78) due to inclusion of references, while Gemini had the highest quality score (3.22). Overall DISCERN scores ranged 3.17-3.37. ChatGPT had the highest accuracy (4.67), and Gemini provided the most complete content (4.17). Claude was noted for slightly lower harm safety (4) and appropriateness (3.33), while all others scored 4.67. Most models performed well on clarity and neutrality (Table 2).
Discussion: LLMs can produce colonoscopy preparation instructions with generally acceptable readability and quality. DeepSeek offered the best readability, while Perplexity had better reliability and referencing. ChatGPT generated the most accurate content, and Gemini was the most comprehensive but more complex. Minor safety concerns were noted with Claude. Overall, LLMs are promising tools for patient education but require clinician oversight to ensure safety and suitability for clinical use.
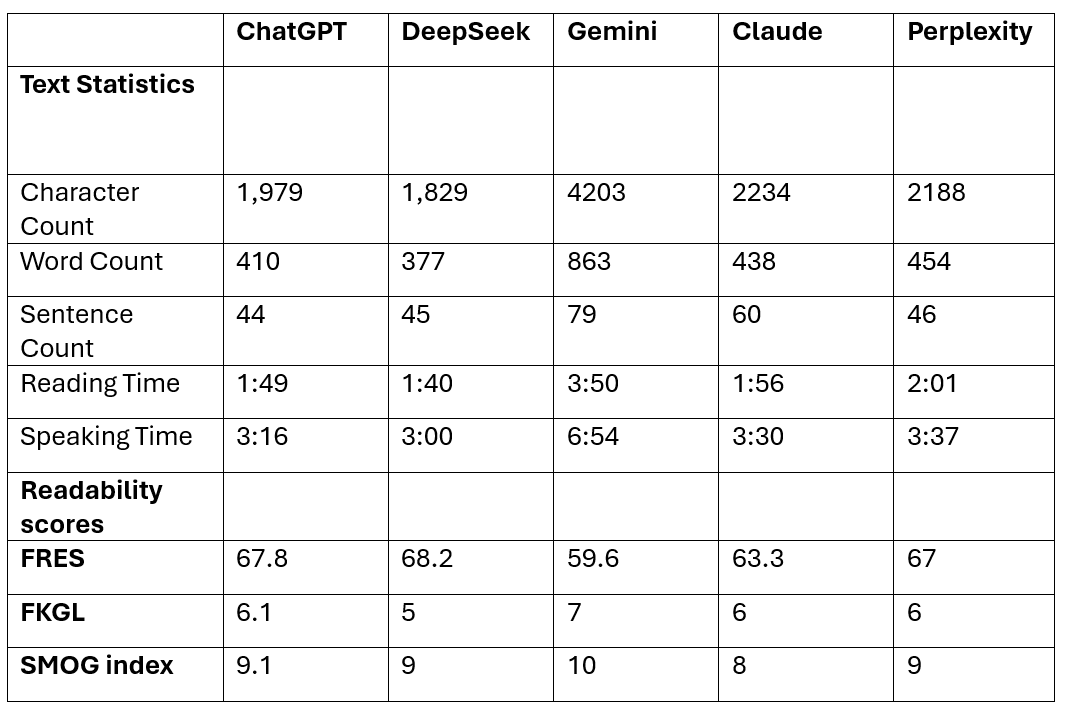
Figure: Table 1: Text statistics and readability metrics of colonoscopy preparation instructions generated by five large language models. (FRES: Flesch Reading Ease Score, FKGL: Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, and SMOG: Simple Measure of Gobbledygook)
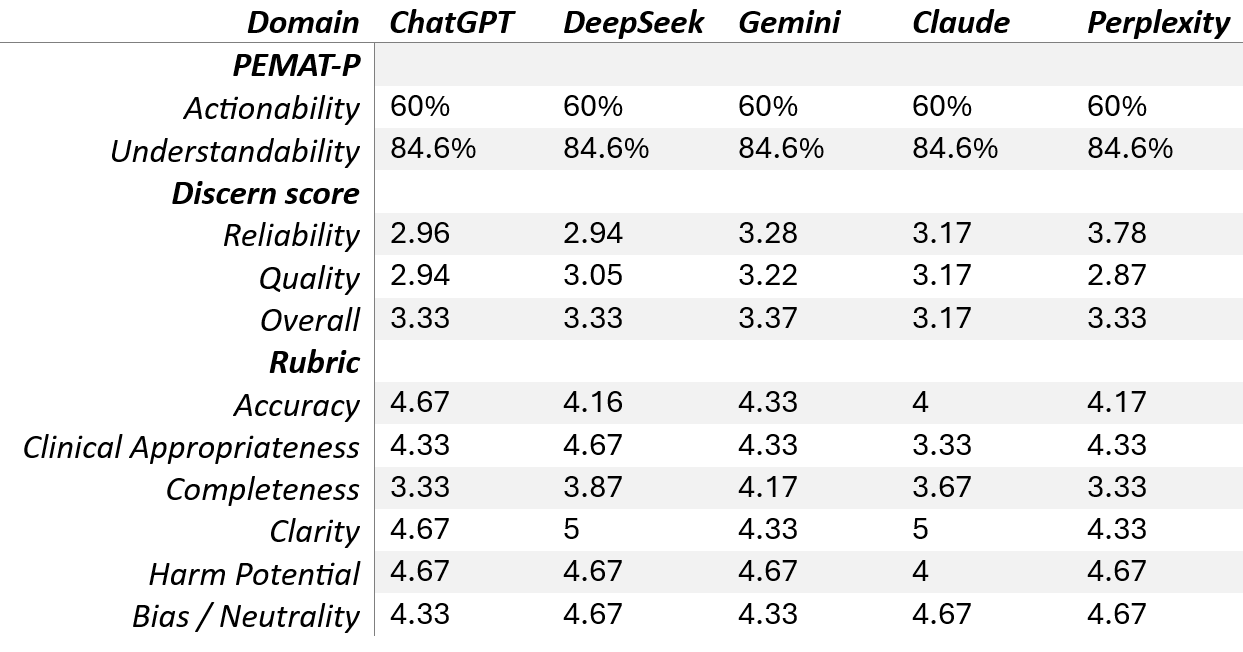
Figure: Table 2: Comparative scores across 5 large language models for colonoscopy preparation instructions using PEMAT-P (Patient Education Materials Assessment Tool for Printable material), DISCERN, and Likert-type rubric assessments.
Disclosures:
Ryan Njeim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joelle Sleiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elie Moussa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harika Kandlakunta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alia Hasham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Njeim, MD, Joelle Sleiman, MD, Elie Moussa, MD, Harika Kandlakunta, MD, Alia Hasham, MD. P5368 - Clear Enough to Drink? A Head-to-Head Comparison of Large Language Model-Generated Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Patient communication poses a significant challenge in medicine due to literacy gaps and time constraints. Recently, large language models (LLMs) are being used to help with documentation and communication but their medical accuracy and readability vary. High-quality instructions for procedures such as colonoscopy are critical to ensure patient adherence, and safety. This study compared the readability and quality of colonoscopy preparation instructions generated by five leading LLMs.
Methods: A standardized prompt was used to generate colonoscopy preparation instructions from five LLMs: ChatGPT-4, DeepSeek (R1), Gemini 2.5 Flash, Claude Sonnet 4, and Perplexity AI. Outputs were limited to < 500 words. Readability was assessed using Flesch Reading Ease Score (FRES), Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FKGL), and SMOG Index. 3 independent reviewers (RN, EM and JS) evaluated quality using the Patient Education Materials Assessment Tool (PEMAT), the DISCERN score, and a custom Likert-type rubric assessing accuracy, clinical appropriateness, completeness, clarity, harm potential, and bias. Descriptive statistics were used for comparison.
Results: All LLMs adhered to the output limit except Gemini (863 words). DeepSeek had the highest FRES (68.2) and lowest FKGL (5), indicating superior readability while Gemini scored the lowest (FRES 59.6, FKGL 7). SMOG scores ranged from 8 (Claude) to 10 (Gemini) (Table 1). All LLMs achieved 100% audience reach and had similar tone profiles. PEMAT scores were consistent across models (actionability 60%, understandability 84.6%). Perplexity scored highest in DISCERN reliability (3.78) due to inclusion of references, while Gemini had the highest quality score (3.22). Overall DISCERN scores ranged 3.17-3.37. ChatGPT had the highest accuracy (4.67), and Gemini provided the most complete content (4.17). Claude was noted for slightly lower harm safety (4) and appropriateness (3.33), while all others scored 4.67. Most models performed well on clarity and neutrality (Table 2).
Discussion: LLMs can produce colonoscopy preparation instructions with generally acceptable readability and quality. DeepSeek offered the best readability, while Perplexity had better reliability and referencing. ChatGPT generated the most accurate content, and Gemini was the most comprehensive but more complex. Minor safety concerns were noted with Claude. Overall, LLMs are promising tools for patient education but require clinician oversight to ensure safety and suitability for clinical use.

Figure: Table 1: Text statistics and readability metrics of colonoscopy preparation instructions generated by five large language models. (FRES: Flesch Reading Ease Score, FKGL: Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level, and SMOG: Simple Measure of Gobbledygook)

Figure: Table 2: Comparative scores across 5 large language models for colonoscopy preparation instructions using PEMAT-P (Patient Education Materials Assessment Tool for Printable material), DISCERN, and Likert-type rubric assessments.
Disclosures:
Ryan Njeim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joelle Sleiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elie Moussa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harika Kandlakunta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alia Hasham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Njeim, MD, Joelle Sleiman, MD, Elie Moussa, MD, Harika Kandlakunta, MD, Alia Hasham, MD. P5368 - Clear Enough to Drink? A Head-to-Head Comparison of Large Language Model-Generated Colonoscopy Preparation Instructions, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
