Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5324 - Duvakitug, an anti-TL1a mAb, Demonstrates Efficacy and Favorable Safety as an Induction Treatment in Adults With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the RELIEVE UCCD Phase 2b Basket Trial
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD
Medical University of Vienna, Department of Internal Medicine III, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Spitalgasse, Wien, Austria
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD1, David Štěpek, MD2, Radoslaw Kempinski, MD, PhD3, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD4, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG5, Bogdan Ratiu-Duma, 6, Rajendra Singh, PhD7, Hadas Barkay, PhD8, Gordon Raphael, MD9, Vipul Jairath, MBChB, DPhil, MRCP10
1Medical University of Vienna, Department of Internal Medicine III, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Spitalgasse, Wien, Austria; 2Military Hospital Brno, Internal Department, Brno, Jihomoravsky kraj, Czech Republic; 3Wrocław Medical University, Wrocław, Lubelskie, Poland; 4Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 5Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY; 6Teva Pharmaceuticals S.R.L., Pharmacovigilance, Bucharest, Bucuresti, Romania; 7Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Products, Research and Development, West Chester, PA; 8Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Research and Development, Netanya, HaDarom, Israel; 9Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, West Chester, PA; 10Department of Medicine and Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Western University, London, ON, Canada
Introduction: Duvakitug is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody selected for its preferential inhibition of TL1A-DR3 signaling over DcR3 binding. Duvakitug has demonstrated reduced inflammation and fibrosis in colitis animal models.1 The efficacy and safety of duvakitug in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease was assessed in a phase 2b basket trial (NCT05499130).
Methods: RELIEVE UCCD was a randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind induction study. The UC cohort comprised of adults with moderately to severely active disease with inadequate response, loss of response or intolerance to previous conventional and/or advanced therapies (ATs). Eligible patients were randomized to receive subcutaneously a 2250 mg loading dose of duvakitug or PBO, followed by either duvakitug 450 mg, 900 mg or PBO (1:1:1; stratified by prior AT) every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was clinical remission (per modified Mayo score) at week 14. Safety was assessed by adverse event (AE) reporting and laboratory monitoring.
Results: In total, 137 patients were randomized, treated and included in the UC cohort analysis (450 mg: n=47; 900 mg: n=46; PBO: n=44). Demographics and baseline characteristics were generally similar across arms (Table 1). Both duvakitug doses successfully achieved the week 14 primary endpoint of clinical remission (36% [450 mg], 48% [900 mg] versus 20% [PBO]; PBO-adjusted rates: 16% [450 mg], 27% [900 mg]). The results were statistically significant based on the prespecified Bayesian analysis, with a >0.90 posterior probability that each duvakitug dose is superior to PBO. Duvakitug treatment effect was observed in both AT-experienced and -naïve patients (Table 2). AE incidence was lower for duvakitug (49% [450 mg], 43% [900 mg]) versus PBO (52%), as was incidence of AEs leading to discontinuation (0% [450 mg], 2% [900 mg] vs 5% [PBO]).
Discussion: Duvakitug demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful treatment responses compared to PBO in patients with UC; it was well tolerated with no emergent safety signals observed. These induction study results support further development of duvakitug as a potential treatment option for patients with moderately to severely active UC.
Reference:
1. Clarke AW, et al. MAbs. 2018;10:664–77
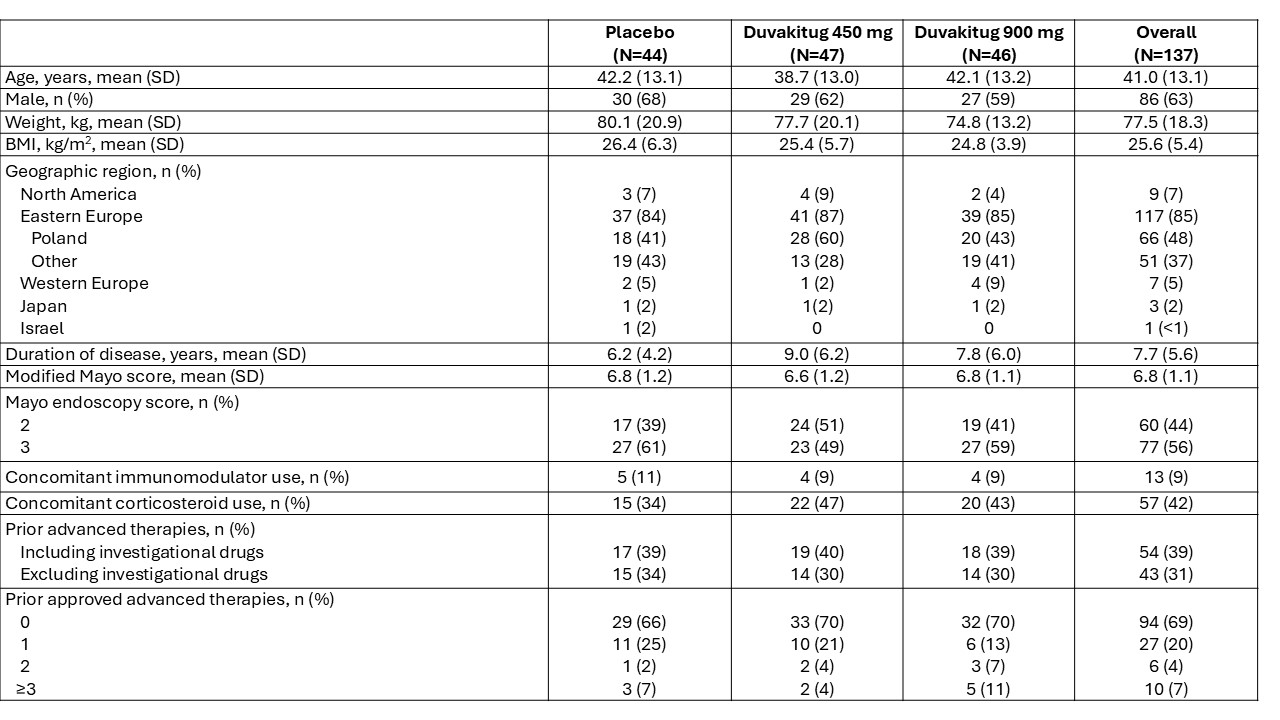
Figure: Table 1: Demographics and baseline characteristics
Advanced therapies include approved therapies: biologics (TNF inhibitors, integrins inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors or anti-IL-23), JAK inhibitors and S1P receptor modulators. Drugs currently in development for IBD are included in the investigational drugs category. Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
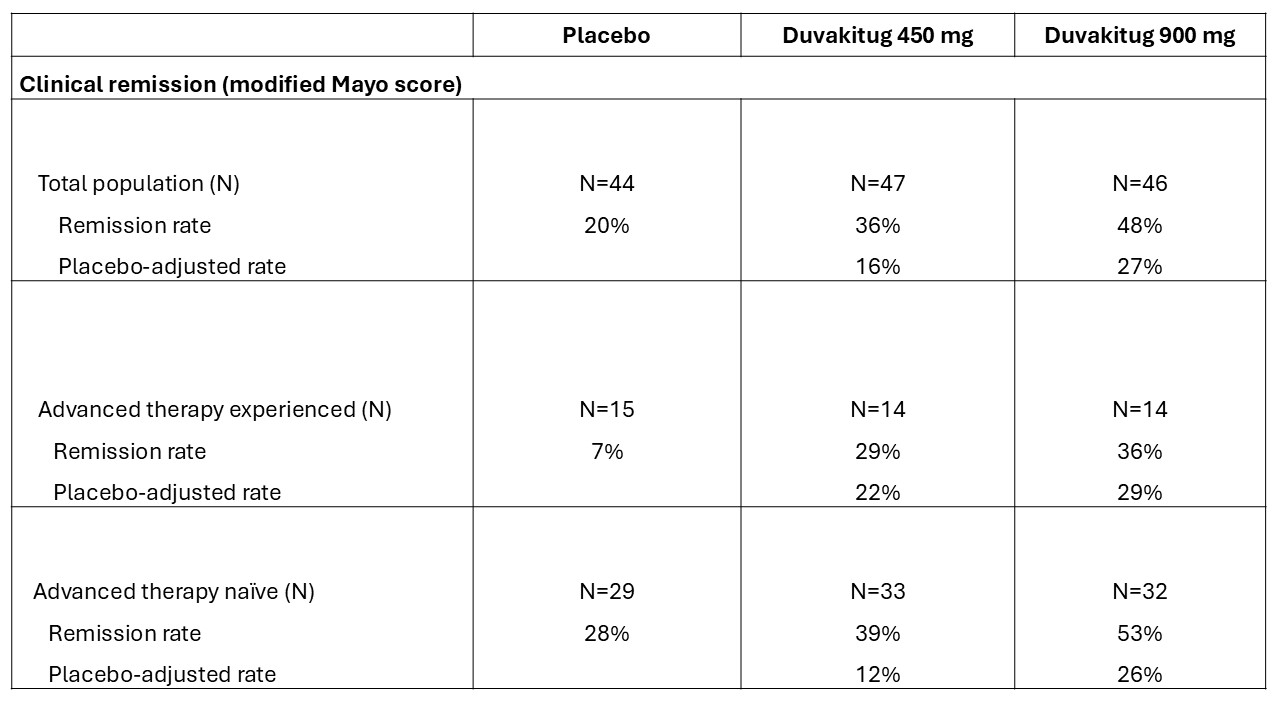
Figure: Table 2: Week 14 clinical remission rates (per modified Mayo score)
Advanced therapy experience includes prior exposure to approved biologics, S1P receptor modulators and/or JAK inhibitors. Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Disclosures:
Walter Reinisch: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Actelion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Alpha Wasserman – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Cellerix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Cosmo Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Grunenthal – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Millennium – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novo Nordisk – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Nycomed – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Schering-Plough – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vifor Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
David Štěpek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Radoslaw Kempinski: AbbVie – Lecture fees. Aboca S.p.A. Società Agricola – Lecture fees. Eli Lilly and Company – Lecture fees. Ferring – Lecture fees. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, speaking fees. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab Therapeutics – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Company – Consultant, speaking fees. Enthera – Consultant. Enveda Biosciences – Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Fzatat – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen R&D – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Stock Options.
Bogdan Ratiu-Duma: Teva – Employee.
Rajendra Singh: Teva – Employee.
Hadas Barkay: Teva – Employee.
Gordon Raphael: Teva – Employee.
Vipul Jairath: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asahi Kasei Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asieris Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Avoro Capital – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Endpoint Health – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Flagship Pioneering – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Galapagos NV – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Gilde Healthcare – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Innomar – Consultant. JAMP – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Merck – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Metacrine – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Mylan – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pandion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pendopharm – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus Therapeutics and Diagnostics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roivant – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Second Genome – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Shire – Speakers Bureau. Sorriso Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Syndegen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Intellectual Property/Patents, Speakers Bureau. TD Securities – Consultant. Teva – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Topivert – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Vividion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD1, David Štěpek, MD2, Radoslaw Kempinski, MD, PhD3, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD4, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG5, Bogdan Ratiu-Duma, 6, Rajendra Singh, PhD7, Hadas Barkay, PhD8, Gordon Raphael, MD9, Vipul Jairath, MBChB, DPhil, MRCP10. P5324 - Duvakitug, an anti-TL1a mAb, Demonstrates Efficacy and Favorable Safety as an Induction Treatment in Adults With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the RELIEVE UCCD Phase 2b Basket Trial, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD1, David Štěpek, MD2, Radoslaw Kempinski, MD, PhD3, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD4, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG5, Bogdan Ratiu-Duma, 6, Rajendra Singh, PhD7, Hadas Barkay, PhD8, Gordon Raphael, MD9, Vipul Jairath, MBChB, DPhil, MRCP10
1Medical University of Vienna, Department of Internal Medicine III, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Spitalgasse, Wien, Austria; 2Military Hospital Brno, Internal Department, Brno, Jihomoravsky kraj, Czech Republic; 3Wrocław Medical University, Wrocław, Lubelskie, Poland; 4Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 5Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY; 6Teva Pharmaceuticals S.R.L., Pharmacovigilance, Bucharest, Bucuresti, Romania; 7Teva Branded Pharmaceutical Products, Research and Development, West Chester, PA; 8Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Research and Development, Netanya, HaDarom, Israel; 9Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, West Chester, PA; 10Department of Medicine and Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Western University, London, ON, Canada
Introduction: Duvakitug is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody selected for its preferential inhibition of TL1A-DR3 signaling over DcR3 binding. Duvakitug has demonstrated reduced inflammation and fibrosis in colitis animal models.1 The efficacy and safety of duvakitug in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease was assessed in a phase 2b basket trial (NCT05499130).
Methods: RELIEVE UCCD was a randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind induction study. The UC cohort comprised of adults with moderately to severely active disease with inadequate response, loss of response or intolerance to previous conventional and/or advanced therapies (ATs). Eligible patients were randomized to receive subcutaneously a 2250 mg loading dose of duvakitug or PBO, followed by either duvakitug 450 mg, 900 mg or PBO (1:1:1; stratified by prior AT) every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was clinical remission (per modified Mayo score) at week 14. Safety was assessed by adverse event (AE) reporting and laboratory monitoring.
Results: In total, 137 patients were randomized, treated and included in the UC cohort analysis (450 mg: n=47; 900 mg: n=46; PBO: n=44). Demographics and baseline characteristics were generally similar across arms (Table 1). Both duvakitug doses successfully achieved the week 14 primary endpoint of clinical remission (36% [450 mg], 48% [900 mg] versus 20% [PBO]; PBO-adjusted rates: 16% [450 mg], 27% [900 mg]). The results were statistically significant based on the prespecified Bayesian analysis, with a >0.90 posterior probability that each duvakitug dose is superior to PBO. Duvakitug treatment effect was observed in both AT-experienced and -naïve patients (Table 2). AE incidence was lower for duvakitug (49% [450 mg], 43% [900 mg]) versus PBO (52%), as was incidence of AEs leading to discontinuation (0% [450 mg], 2% [900 mg] vs 5% [PBO]).
Discussion: Duvakitug demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful treatment responses compared to PBO in patients with UC; it was well tolerated with no emergent safety signals observed. These induction study results support further development of duvakitug as a potential treatment option for patients with moderately to severely active UC.
Reference:
1. Clarke AW, et al. MAbs. 2018;10:664–77

Figure: Table 1: Demographics and baseline characteristics
Advanced therapies include approved therapies: biologics (TNF inhibitors, integrins inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors or anti-IL-23), JAK inhibitors and S1P receptor modulators. Drugs currently in development for IBD are included in the investigational drugs category. Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding.

Figure: Table 2: Week 14 clinical remission rates (per modified Mayo score)
Advanced therapy experience includes prior exposure to approved biologics, S1P receptor modulators and/or JAK inhibitors. Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Disclosures:
Walter Reinisch: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Actelion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Alpha Wasserman – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Cellerix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Cosmo Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Grunenthal – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Millennium – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novo Nordisk – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Nycomed – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Schering-Plough – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vifor Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
David Štěpek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Radoslaw Kempinski: AbbVie – Lecture fees. Aboca S.p.A. Società Agricola – Lecture fees. Eli Lilly and Company – Lecture fees. Ferring – Lecture fees. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, speaking fees. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab Therapeutics – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Company – Consultant, speaking fees. Enthera – Consultant. Enveda Biosciences – Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Fzatat – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen R&D – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Stock Options.
Bogdan Ratiu-Duma: Teva – Employee.
Rajendra Singh: Teva – Employee.
Hadas Barkay: Teva – Employee.
Gordon Raphael: Teva – Employee.
Vipul Jairath: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asahi Kasei Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Asieris Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Avoro Capital – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Endpoint Health – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Flagship Pioneering – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Galapagos NV – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Gilde Healthcare – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Innomar – Consultant. JAMP – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Merck – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Metacrine – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Mylan – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pandion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pendopharm – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus Therapeutics and Diagnostics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Roivant – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Second Genome – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Shire – Speakers Bureau. Sorriso Pharmaceuticals – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Syndegen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Intellectual Property/Patents, Speakers Bureau. TD Securities – Consultant. Teva – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Topivert – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Vividion Therapeutics – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD1, David Štěpek, MD2, Radoslaw Kempinski, MD, PhD3, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD4, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG5, Bogdan Ratiu-Duma, 6, Rajendra Singh, PhD7, Hadas Barkay, PhD8, Gordon Raphael, MD9, Vipul Jairath, MBChB, DPhil, MRCP10. P5324 - Duvakitug, an anti-TL1a mAb, Demonstrates Efficacy and Favorable Safety as an Induction Treatment in Adults With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the RELIEVE UCCD Phase 2b Basket Trial, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

