Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5320 - Extraintestinal Manifestations and Disease Characteristics in Crohn’s Disease Patients on Risankizumab or Ustekinumab
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpeg.jpg)
Caroline J. Young, MS (she/her/hers)
Weill Cornell Medicine
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Caroline J. Young, MS1, Rishav Agrawal, MD2, Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Aiya Aboubakr, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG3
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 2NewYork-Presbyterian / Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 3Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: An estimated 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have comorbid extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs). Risankizumab (RZB), a selective interleukin (IL)-23 antagonist, may be more effective and have fewer adverse effects in Crohn’s disease (CD) treatment than ustekinumab (UST), an IL-12/23 antagonist. The real-world effect of risankizumab on EIMs in CD is unknown. We present analyses of CD patients with EIMs on RZB or UST.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study for CD patients treated with RZB or UST for at least 8 weeks between 7/2022-8/2024 and 3/2009-1/2019, respectively. Patients with current or previously–active EIMs (rheumatologic, dermatologic, ophthalmologic, or hepatobiliary) were included for analysis. Baseline demographics, disease characteristics, and EIM activity were noted, with improvement or resolution of EIMs by last follow up (up to 1 year) as the primary outcome of interest. Secondary outcomes included the follow-up Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI), IBD clinical and biochemical remission (no steroids & HBI ≤ 4; CRP ≤ 0.9 mg/dL & fecal calprotectin < 250 ug/g), and the Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD).
Results: 127 patients (RZB: 86, UST: 41) met inclusion criteria, with a mean age of 41 ±16 years and mean follow-up of 309 ±135 days. 45 patients had multiple EIMs. Most had rheumatologic EIMs (93%), followed by dermatologic (29%), ophthalmologic (11%), and hepatobiliary (1.6%). A lower proportion of patients on RZB had elevated CRP or active EIMs at baseline compared to UST (23% vs. 61%, p=0.005; 67% vs. 88%, p=0.02). Patients on RZB and UST had similar rates of EIM improvement or resolution (62% vs. 69%, p=0.61). RZB was associated with a longer mean time to improvement of any EIM (224 vs. 108 days, p< 0.001) as well as rheumatologic (220 vs. 110 days, p< 0.001) and dermatologic EIMs (267 vs. 126 days, p=0.025). Patients on RZB had lower HBI scores than those on UST at baseline (6.81 vs. 10.00, p=0.01) and at follow-up (3.23 vs. 5.41, p=0.06). There was no significant difference between RZB and UST for clinical remission, biochemical remission, or SES-CD (3.43 vs. 7.23, p=0.3).
Discussion: The majority of patients on both RZB and UST had improvement or resolution of EIMs in the first year of therapy, though patients on RZB may have a slower response for rheumatologic or dermatologic EIMs. Further understanding of the effectiveness of RZB on EIMs will help inform positioning of CD therapies.
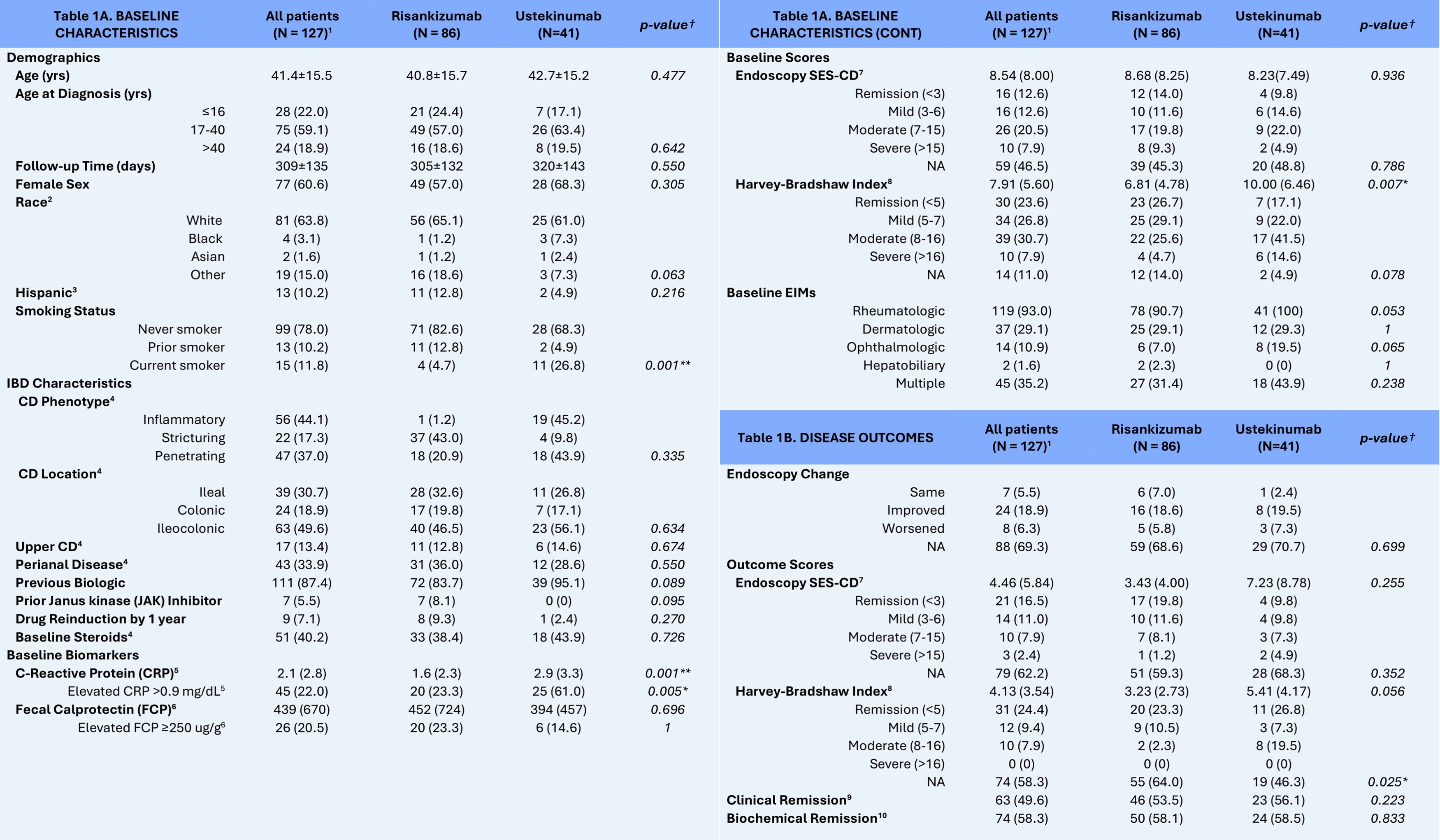
Figure: Table 1A and 1B: Baseline Characteristics and Disease Outcomes of Crohn’s Disease (CD) Patients with Extraintestinal Manifestations (EIMs) (N=127), Stratified by Biologic status (Risankizumab or Ustekinumab).
Legend:
[1] Values indicated are mean ± SD for continuous variables or n (%) for categorical variables.
[2] N/A for 21(16.5) patients (12 on risankizumab, 9 on ustekinumab).
[3] N/A for 24(18.9) patients (16 on risankizumab, 8 on ustekinumab).
[4] N/A for 1(0.01) patient (1 on risankizumab).
[5] N/A for 28(21.8) patients (26 on risankizumab, 2 on ustekinumab).
[6] N/A for 61(48.0) patients (35 on risankizumab, 26 on ustekinumab).
[7] Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) as calculated by providers at the time of endoscopy or retrospectively by clinicians using the endoscopic information provided, if available. Categorical disease severity was based off of the American Gastroenterological Association guidelines; Remission < 3; Mild 3-6; Moderate 7-15; Severe SES-CD >15.
[8] N/A was coded if not enough information given in the charts to calculate HBI, or if patient had an ostomy and the provider did not calculate an HBI for that visit.
[9] Clinical Remission defined as endpoint HBI ≤ 4 and no steroids; patients with missing HBI were still eligible to be considered for clinical remission based off of clinical note and medical expertise. N/A for 5(3.9) patients (4 on risankizumab, 1 on ustekinumab patient).
[10] Biochemical Remission defined as endpoint FCP < 250 and CRP ≤ 0.9 mg/dL, or either if 1 value was N/A and seemed clinically appropriate. N/A for 21(16.5) patients (13 on risankizumab, 8 on ustekinumab).
† p-values for significant difference between patients on risankizumab and patients on ustekinumab in the study population. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.

Figure: Table 2B. EIMs in CD patients on Risankizumab (N=86) and Ustekinumab (N=41), Stratified by Biologic Type.
Legend:
[1] Values indicated are n (%).
[2] Values indicated are n (% of active patients).
[3] Average mean time to improvement in days (standard deviation).
[4] Not included: 3 patients who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
[5] Not included: 1 patient who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
[6] Not included: 2 patients who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
† p-values for significant difference between the proportion of baseline active, endpoint-improved EIMs between the risankizumab and ustekinumab groups. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.
†† p-values for significant difference between time to improvement of active baseline EIMs between the risankizumab and ustekinumab groups. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.
Disclosures:
Caroline Young indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishav Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacob Jamison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aiya Aboubakr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Sahyoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana Lukin: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prime – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Caroline J. Young, MS1, Rishav Agrawal, MD2, Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Aiya Aboubakr, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG3. P5320 - Extraintestinal Manifestations and Disease Characteristics in Crohn’s Disease Patients on Risankizumab or Ustekinumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 2NewYork-Presbyterian / Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 3Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
Introduction: An estimated 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have comorbid extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs). Risankizumab (RZB), a selective interleukin (IL)-23 antagonist, may be more effective and have fewer adverse effects in Crohn’s disease (CD) treatment than ustekinumab (UST), an IL-12/23 antagonist. The real-world effect of risankizumab on EIMs in CD is unknown. We present analyses of CD patients with EIMs on RZB or UST.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study for CD patients treated with RZB or UST for at least 8 weeks between 7/2022-8/2024 and 3/2009-1/2019, respectively. Patients with current or previously–active EIMs (rheumatologic, dermatologic, ophthalmologic, or hepatobiliary) were included for analysis. Baseline demographics, disease characteristics, and EIM activity were noted, with improvement or resolution of EIMs by last follow up (up to 1 year) as the primary outcome of interest. Secondary outcomes included the follow-up Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI), IBD clinical and biochemical remission (no steroids & HBI ≤ 4; CRP ≤ 0.9 mg/dL & fecal calprotectin < 250 ug/g), and the Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD).
Results: 127 patients (RZB: 86, UST: 41) met inclusion criteria, with a mean age of 41 ±16 years and mean follow-up of 309 ±135 days. 45 patients had multiple EIMs. Most had rheumatologic EIMs (93%), followed by dermatologic (29%), ophthalmologic (11%), and hepatobiliary (1.6%). A lower proportion of patients on RZB had elevated CRP or active EIMs at baseline compared to UST (23% vs. 61%, p=0.005; 67% vs. 88%, p=0.02). Patients on RZB and UST had similar rates of EIM improvement or resolution (62% vs. 69%, p=0.61). RZB was associated with a longer mean time to improvement of any EIM (224 vs. 108 days, p< 0.001) as well as rheumatologic (220 vs. 110 days, p< 0.001) and dermatologic EIMs (267 vs. 126 days, p=0.025). Patients on RZB had lower HBI scores than those on UST at baseline (6.81 vs. 10.00, p=0.01) and at follow-up (3.23 vs. 5.41, p=0.06). There was no significant difference between RZB and UST for clinical remission, biochemical remission, or SES-CD (3.43 vs. 7.23, p=0.3).
Discussion: The majority of patients on both RZB and UST had improvement or resolution of EIMs in the first year of therapy, though patients on RZB may have a slower response for rheumatologic or dermatologic EIMs. Further understanding of the effectiveness of RZB on EIMs will help inform positioning of CD therapies.

Figure: Table 1A and 1B: Baseline Characteristics and Disease Outcomes of Crohn’s Disease (CD) Patients with Extraintestinal Manifestations (EIMs) (N=127), Stratified by Biologic status (Risankizumab or Ustekinumab).
Legend:
[1] Values indicated are mean ± SD for continuous variables or n (%) for categorical variables.
[2] N/A for 21(16.5) patients (12 on risankizumab, 9 on ustekinumab).
[3] N/A for 24(18.9) patients (16 on risankizumab, 8 on ustekinumab).
[4] N/A for 1(0.01) patient (1 on risankizumab).
[5] N/A for 28(21.8) patients (26 on risankizumab, 2 on ustekinumab).
[6] N/A for 61(48.0) patients (35 on risankizumab, 26 on ustekinumab).
[7] Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) as calculated by providers at the time of endoscopy or retrospectively by clinicians using the endoscopic information provided, if available. Categorical disease severity was based off of the American Gastroenterological Association guidelines; Remission < 3; Mild 3-6; Moderate 7-15; Severe SES-CD >15.
[8] N/A was coded if not enough information given in the charts to calculate HBI, or if patient had an ostomy and the provider did not calculate an HBI for that visit.
[9] Clinical Remission defined as endpoint HBI ≤ 4 and no steroids; patients with missing HBI were still eligible to be considered for clinical remission based off of clinical note and medical expertise. N/A for 5(3.9) patients (4 on risankizumab, 1 on ustekinumab patient).
[10] Biochemical Remission defined as endpoint FCP < 250 and CRP ≤ 0.9 mg/dL, or either if 1 value was N/A and seemed clinically appropriate. N/A for 21(16.5) patients (13 on risankizumab, 8 on ustekinumab).
† p-values for significant difference between patients on risankizumab and patients on ustekinumab in the study population. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.

Figure: Table 2B. EIMs in CD patients on Risankizumab (N=86) and Ustekinumab (N=41), Stratified by Biologic Type.
Legend:
[1] Values indicated are n (%).
[2] Values indicated are n (% of active patients).
[3] Average mean time to improvement in days (standard deviation).
[4] Not included: 3 patients who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
[5] Not included: 1 patient who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
[6] Not included: 2 patients who experienced relapse during treatment and then improvement.
† p-values for significant difference between the proportion of baseline active, endpoint-improved EIMs between the risankizumab and ustekinumab groups. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.
†† p-values for significant difference between time to improvement of active baseline EIMs between the risankizumab and ustekinumab groups. P-values based on the chi-squared test (or Fischer’s exact test) for categorical variables and the two-sample Student’s t-test (or Mann Whitney U test) for continuous variables.
Disclosures:
Caroline Young indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishav Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacob Jamison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aiya Aboubakr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Sahyoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana Lukin: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prime – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Caroline J. Young, MS1, Rishav Agrawal, MD2, Jacob K. Jamison, BA1, Aiya Aboubakr, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD, PhD, FACG3. P5320 - Extraintestinal Manifestations and Disease Characteristics in Crohn’s Disease Patients on Risankizumab or Ustekinumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

