Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P5312 - Comparative Analysis of Healthcare Resource Utilization and Direct Costs in Crohn's Disease from U.S. Claims: Early vs Late Biologic Initiation
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AP
Alyssa Parian, MD
John Hopkins University, Baltimore
Baltimore, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Alyssa Parian, MD1, Deborah A.. Fisher, MD2, Alan Brnabic, 3, Nicholas Bires, 3, Debbie Tinsley, 3, Zbigniew Kadziola, 3, Wai Man Maria Chan, 3
1John Hopkins University, Baltimore, Baltimore, MD; 2Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA, Indianapolis, IN; 3Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: While early intervention with biologics improves clinical response in Crohn’s disease (CD), the optimal timing to reduce healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and direct costs remains unclear. This study examined the impact of biologic initiation on HCRU and direct costs over 5 years in adults recently diagnosed with CD in the US.
Methods: Adults with >2 non-ancillary outpatient claims (30 days apart) or 1 inpatient claim for CD (ICD-10: K50.x) from 1/1/2015 to 7/31/2024 were identified using Optum® Clinformatics® Data Mart. Patients with CD who started biologic treatment within 2 years of diagnosis (index date) and had continuous enrolment for 1 year pre- and 5 years post-index were stratified into early (< 12 months) or late ( >12-24 months) initiators. Due to skewed distributions, CD-related and non-CD-related costs at 5-year post-index were analyzed using gamma log. Poisson or negative binomial (with zero-inflated models in some cases) were used to model HCRU. All models were adjusted for demographic and clinical characteristics at biologic initiation.
Results: Early initiators (EI) were significantly younger (mean[SD] age: 43.2[16.9] vs 48.0[16.6] years, p< 0.001), predominantly male (50.6% vs 44.5%), had significantly higher commercial insurance (84.5% vs 77.2%, p=0.004) than late initiators (LI), and had similar Deyo Charlson comorbidity index scores (mean[SD]: 0.7[1.2] vs 0.7[1.3]). EI had significantly lower total mean medical costs ($63,761 vs $66,282), significantly lower IBD-related mean medical and pharmacy costs ($1074 vs $1494), as well as significantly lower mean pharmacy costs to treat depression ($28 vs $346), and anxiety ($38 vs $79) than LI (Table). Additionally, EI had significantly fewer emergency visits (1.5 vs 1.6), fewer all-cause (4.2 vs 4.9 days), and CD-related hospitalizations days (3.9 vs 4.7 days) than LI. Other HCRUs and costs were similar between the two groups.
Discussion: Early initiators of biologics had lower HCRU and reduced non-CD medication pharmacy costs at 5 years post-index compared to starting biologics after a year, potentially leading to overall cost savings and improving patient health outcomes.
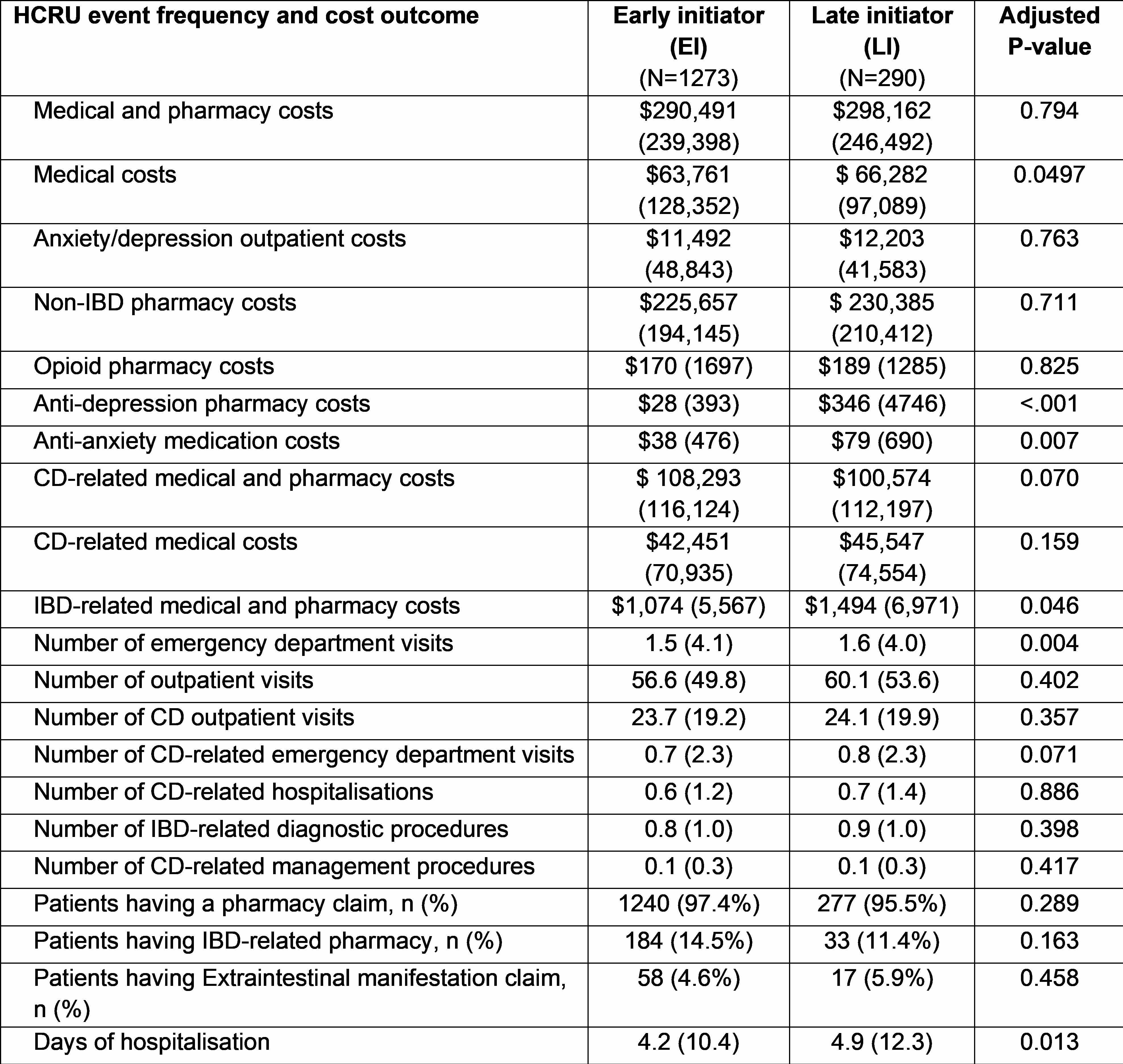
Figure: Healthcare resource utilization and direct cost between early and late biologic initiators
Disclosures:
Alyssa Parian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deborah Fisher: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Alan Brnabic: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Speakers Bureau.
Nicholas Bires: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Debbie Tinsley: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Zbigniew Kadziola: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Wai Man Maria Chan: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Alyssa Parian, MD1, Deborah A.. Fisher, MD2, Alan Brnabic, 3, Nicholas Bires, 3, Debbie Tinsley, 3, Zbigniew Kadziola, 3, Wai Man Maria Chan, 3. P5312 - Comparative Analysis of Healthcare Resource Utilization and Direct Costs in Crohn's Disease from U.S. Claims: Early vs Late Biologic Initiation, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1John Hopkins University, Baltimore, Baltimore, MD; 2Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA, Indianapolis, IN; 3Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: While early intervention with biologics improves clinical response in Crohn’s disease (CD), the optimal timing to reduce healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and direct costs remains unclear. This study examined the impact of biologic initiation on HCRU and direct costs over 5 years in adults recently diagnosed with CD in the US.
Methods: Adults with >2 non-ancillary outpatient claims (30 days apart) or 1 inpatient claim for CD (ICD-10: K50.x) from 1/1/2015 to 7/31/2024 were identified using Optum® Clinformatics® Data Mart. Patients with CD who started biologic treatment within 2 years of diagnosis (index date) and had continuous enrolment for 1 year pre- and 5 years post-index were stratified into early (< 12 months) or late ( >12-24 months) initiators. Due to skewed distributions, CD-related and non-CD-related costs at 5-year post-index were analyzed using gamma log. Poisson or negative binomial (with zero-inflated models in some cases) were used to model HCRU. All models were adjusted for demographic and clinical characteristics at biologic initiation.
Results: Early initiators (EI) were significantly younger (mean[SD] age: 43.2[16.9] vs 48.0[16.6] years, p< 0.001), predominantly male (50.6% vs 44.5%), had significantly higher commercial insurance (84.5% vs 77.2%, p=0.004) than late initiators (LI), and had similar Deyo Charlson comorbidity index scores (mean[SD]: 0.7[1.2] vs 0.7[1.3]). EI had significantly lower total mean medical costs ($63,761 vs $66,282), significantly lower IBD-related mean medical and pharmacy costs ($1074 vs $1494), as well as significantly lower mean pharmacy costs to treat depression ($28 vs $346), and anxiety ($38 vs $79) than LI (Table). Additionally, EI had significantly fewer emergency visits (1.5 vs 1.6), fewer all-cause (4.2 vs 4.9 days), and CD-related hospitalizations days (3.9 vs 4.7 days) than LI. Other HCRUs and costs were similar between the two groups.
Discussion: Early initiators of biologics had lower HCRU and reduced non-CD medication pharmacy costs at 5 years post-index compared to starting biologics after a year, potentially leading to overall cost savings and improving patient health outcomes.

Figure: Healthcare resource utilization and direct cost between early and late biologic initiators
Disclosures:
Alyssa Parian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deborah Fisher: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Alan Brnabic: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Speakers Bureau.
Nicholas Bires: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Debbie Tinsley: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Zbigniew Kadziola: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Wai Man Maria Chan: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Alyssa Parian, MD1, Deborah A.. Fisher, MD2, Alan Brnabic, 3, Nicholas Bires, 3, Debbie Tinsley, 3, Zbigniew Kadziola, 3, Wai Man Maria Chan, 3. P5312 - Comparative Analysis of Healthcare Resource Utilization and Direct Costs in Crohn's Disease from U.S. Claims: Early vs Late Biologic Initiation, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
