Tuesday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P5218 - The Overlooked Comorbidity: Impact of Esophageal Varices on Liver Cirrhosis-Related Mortality Trends in the U.S. Population from 1999-2023
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- TS
Talha Sajjad, MBBS, MD (he/him/his)
Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan
Sadiqabad, Punjab, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS1, Hamza Hameed, 2, Talha Sajjad, MBBS, MD1, Anfal Hamza, MBBS1, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS1, Manahil Shafique, 2, Muhammad Younas, 3, Talha Adil, 4, Muhammad Umair Choudhary, MBBS1, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD5, Ahmad Sarim Aziz, MBBS6, Iqra Baig, 7, Bisher Sawaf, MD8
1Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Azad Jammu and Kashmir Medical College, Muzzafarabad, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan; 5Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Azra Naheed Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Shiekh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Sadiqabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 8University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Cirrhosis is the 11th most significant cause of mortality in the United States as of 2023. Trends in mortality due to liver cirrhosis with esophageal varices remain inadequately documented. This study examines 25 years mortality trends for cirrhosis and esophageal varices among U.S. adults aged ≥45 years (1999 to 2023).
Methods: We extracted mortality data from CDC WONDER database, including only adults aged ≥45 years coded for liver cirrhosis (ICD-10 K74) and esophageal varices (ICD-10 I85) from 1999 to 2023. Extracted data included age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) categorized by sex, race/ethnicity, U.S. Census regions, and 2013 urbanization categories. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to calculate Annual Percent Change (APC) with 95% confidence intervals and p-values to assess the mortality trends. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: From 1999 to 2023, cirrhosis with esophageal varices caused 18,392 deaths, with an overall AAMR of 0.6 per 100,000 population and an upward trend from 2006 to onwards (APC: 2.2953, 95% CI: -5.6901 - 6.4933, p = 0.085983). Females exhibited a significant AAMR increase from 2008 to 2023 (APC: 3.73443, 95% CI: 2.4262-5.9046, p = 0.00). Among racial groups, Whites showed a significant post-2009 AAMR increase (APC: 2.84, 95% CI: 1.5070-5.0851, p = 0.00), while African Americans and Whites had declines from 1999 to 2009. Hispanics (1999-2006) and non-Hispanics (1999 - 2007) saw significant declines in AAMR (APC: -9.0381, 95% CI: -24.4016 to -3.3782, p = 0.00; APC: -6.7366 (95% CI: -11.3960 to -4.1338, p = 0.00), respectively. The Midwest and South had elevated AAMRs from 2006 to 2023, with APC = 1.2123 (95% CI: 0.1201 -2.6384, p = 0.036) and APC = 2.2918 (95% CI: 1.5172 - 3.3469, p = 0.00), West showing a significant post-2006 increase (APC: 2.13, 95% CI: 0.0113 - 8.2959, p= 0.049). Medium Metro (post-2006) and Micropolitan (post - 2005) areas had significant AAMR increases with APC: 1.3645 (95% CI: 0.0728 - 3.8164, p=0.04) and APC: 1.9806, (95% CI: 0.9504-6.6945, p = 0.008), respectively.
Discussion: A marked rise in mortality from cirrhosis complicated by esophageal varices has risen significantly since 2018, with disproportionate increases among demographic and geographic regions. These results highlight critical gaps in the existing scientific understanding, requiring planned public health interventions, enhanced screening, and persistent surveillance to address escalating mortality in susceptible populations
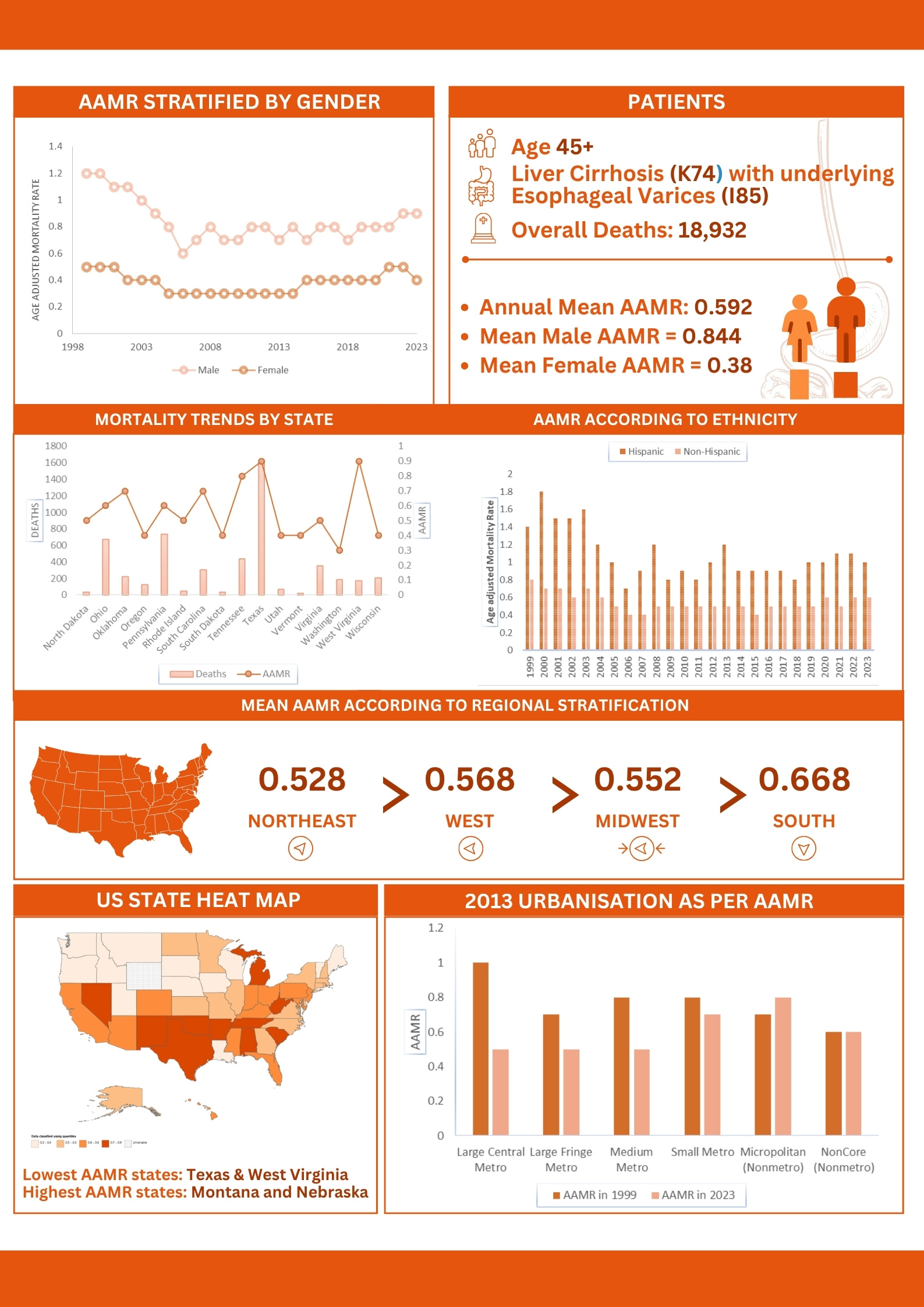
Figure: The Overlooked Comorbidity: Impact of Esophageal Varices on Liver Cirrhosis-Related Mortality Trends in the U.S. Population from 1999-2023
Disclosures:
Atif Nawaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Hameed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Sajjad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anfal Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arbaz Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manahil Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Younas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Adil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Umair Choudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Sarim Aziz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Baig indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS1, Hamza Hameed, 2, Talha Sajjad, MBBS, MD1, Anfal Hamza, MBBS1, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS1, Manahil Shafique, 2, Muhammad Younas, 3, Talha Adil, 4, Muhammad Umair Choudhary, MBBS1, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD5, Ahmad Sarim Aziz, MBBS6, Iqra Baig, 7, Bisher Sawaf, MD8. P5218 - The Overlooked Comorbidity: Impact of Esophageal Varices on Liver Cirrhosis-Related Mortality Trends in the U.S. Population from 1999-2023, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Azad Jammu and Kashmir Medical College, Muzzafarabad, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan; 5Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Azra Naheed Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Shiekh Zayed Medical College, Rahim Yar Khan, Sadiqabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 8University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Cirrhosis is the 11th most significant cause of mortality in the United States as of 2023. Trends in mortality due to liver cirrhosis with esophageal varices remain inadequately documented. This study examines 25 years mortality trends for cirrhosis and esophageal varices among U.S. adults aged ≥45 years (1999 to 2023).
Methods: We extracted mortality data from CDC WONDER database, including only adults aged ≥45 years coded for liver cirrhosis (ICD-10 K74) and esophageal varices (ICD-10 I85) from 1999 to 2023. Extracted data included age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) categorized by sex, race/ethnicity, U.S. Census regions, and 2013 urbanization categories. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to calculate Annual Percent Change (APC) with 95% confidence intervals and p-values to assess the mortality trends. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: From 1999 to 2023, cirrhosis with esophageal varices caused 18,392 deaths, with an overall AAMR of 0.6 per 100,000 population and an upward trend from 2006 to onwards (APC: 2.2953, 95% CI: -5.6901 - 6.4933, p = 0.085983). Females exhibited a significant AAMR increase from 2008 to 2023 (APC: 3.73443, 95% CI: 2.4262-5.9046, p = 0.00). Among racial groups, Whites showed a significant post-2009 AAMR increase (APC: 2.84, 95% CI: 1.5070-5.0851, p = 0.00), while African Americans and Whites had declines from 1999 to 2009. Hispanics (1999-2006) and non-Hispanics (1999 - 2007) saw significant declines in AAMR (APC: -9.0381, 95% CI: -24.4016 to -3.3782, p = 0.00; APC: -6.7366 (95% CI: -11.3960 to -4.1338, p = 0.00), respectively. The Midwest and South had elevated AAMRs from 2006 to 2023, with APC = 1.2123 (95% CI: 0.1201 -2.6384, p = 0.036) and APC = 2.2918 (95% CI: 1.5172 - 3.3469, p = 0.00), West showing a significant post-2006 increase (APC: 2.13, 95% CI: 0.0113 - 8.2959, p= 0.049). Medium Metro (post-2006) and Micropolitan (post - 2005) areas had significant AAMR increases with APC: 1.3645 (95% CI: 0.0728 - 3.8164, p=0.04) and APC: 1.9806, (95% CI: 0.9504-6.6945, p = 0.008), respectively.
Discussion: A marked rise in mortality from cirrhosis complicated by esophageal varices has risen significantly since 2018, with disproportionate increases among demographic and geographic regions. These results highlight critical gaps in the existing scientific understanding, requiring planned public health interventions, enhanced screening, and persistent surveillance to address escalating mortality in susceptible populations

Figure: The Overlooked Comorbidity: Impact of Esophageal Varices on Liver Cirrhosis-Related Mortality Trends in the U.S. Population from 1999-2023
Disclosures:
Atif Nawaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Hameed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Sajjad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anfal Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arbaz Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manahil Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Younas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talha Adil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Umair Choudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Sarim Aziz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Baig indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atif Nawaz Malik, MBBS1, Hamza Hameed, 2, Talha Sajjad, MBBS, MD1, Anfal Hamza, MBBS1, Arbaz Hassan, MBBS1, Manahil Shafique, 2, Muhammad Younas, 3, Talha Adil, 4, Muhammad Umair Choudhary, MBBS1, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD5, Ahmad Sarim Aziz, MBBS6, Iqra Baig, 7, Bisher Sawaf, MD8. P5218 - The Overlooked Comorbidity: Impact of Esophageal Varices on Liver Cirrhosis-Related Mortality Trends in the U.S. Population from 1999-2023, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
