Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P5100 - Digital Gut-directed Hypnotherapy Reduce Core IBS Symptoms: A Large-scale Spline-Enhanced Multivariable Regression Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mauricio F. Jin, MD
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Mauricio F. Jin, MD1, Claire Hall, 2, Xiao Jing Wang, MD1
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Mindset Health, Boston, MA
Introduction: Gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH) has demonstrated efficacy in improving severity of symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), but widespread access remains limited due to provider availability and cost. Digitally delivered GDH provides a scalable, self-guided alternative with prior data showing efficacy in symptom improvement with greater adherence. However, large-scale real world digital delivery outcomes remain understudied, and nonlinear dose-response patterns have not been previously characterized in the literature.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of adult users of a digital GDH app (Nerva) who engaged in a 6-week self-guided digital program. Symptom scores were collected using IBS-VAS scale at baseline and at week 6. Multiple linear regression models were used to estimate associations, adjusting for age, gender, baseline severity, IBS subtype, and other interventions (e.g. diaphragmatic breathing, supplement use). Analysis focused on abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, and passage of wind. To capture nonlinear relationships between session adherence and outcomes, we used natural cubic splines for hypnotherapy counts. Models were selected based on the Bayesian Information Criterion and influential data points were excluded based on standardized residuals, leverage, and Cook’s distance.
Results: Data from 38,454 adult users were included in our retrospective cohort study. Patient characteristics are included in table 1. Average symptom reductions were 22.3% for bloating (SD:17.1), 22.1% for pain (SD:18.7), and 17.0% for passage of wind (SD:17.1). Participants with baseline IBS-VAS scores >60 achieved significantly greater reductions: 32.2%, 34.4%, and 29.5% respectively. Hypnotherapy session count was a strong nonlinear predictor of symptom improvement across all three symptom domains (p< 0.001 for spine terms), with most optimal benefit at moderate use (20-30 sessions). Spline modeled dose-response curves across core IBS symptoms are highlighted in figure 1.
Discussion: Digital gut-directed hypnotherapy via Nerva was associated with symptom reductions in this large real-world IBS cohort. Our data expands upon prior findings of digital GDH in our large-scale and real-world evaluation. Our use of spline enhanced regression reveals nonlinear dose-response relationship, suggesting an optimal treatment window for hypnotherapy adherence. These findings support the scalable use of digital GDH.
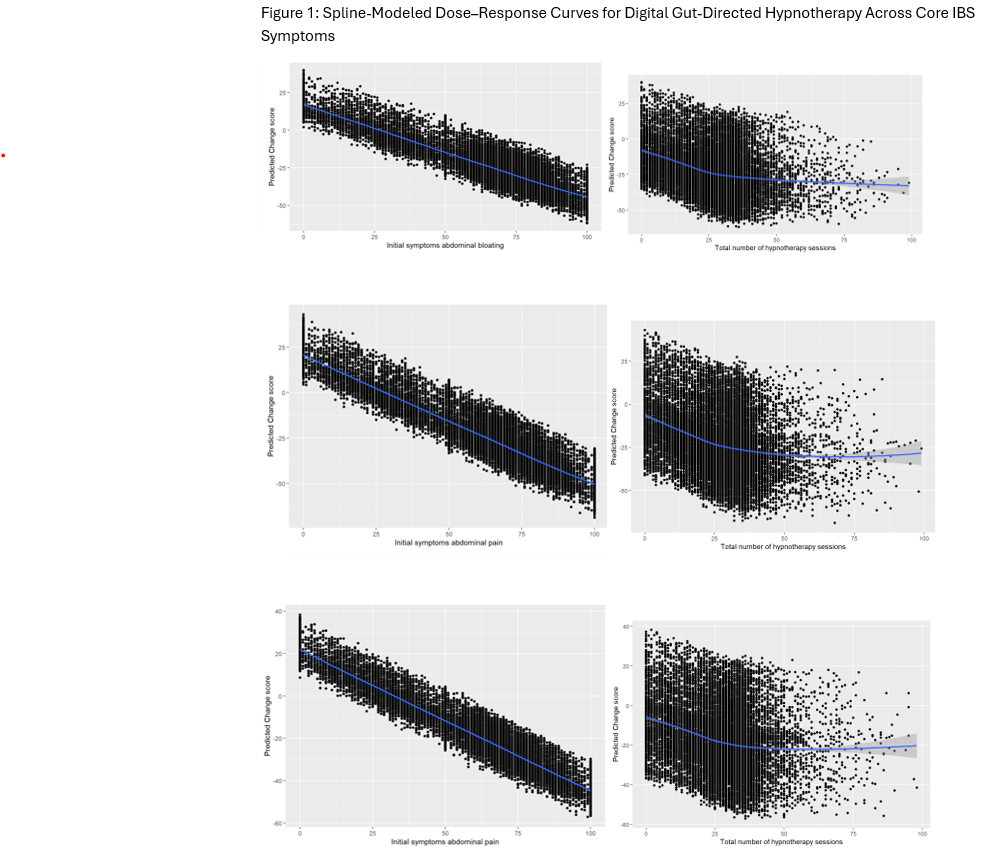
Figure: Table 1. participant characteristics by IBS subtype
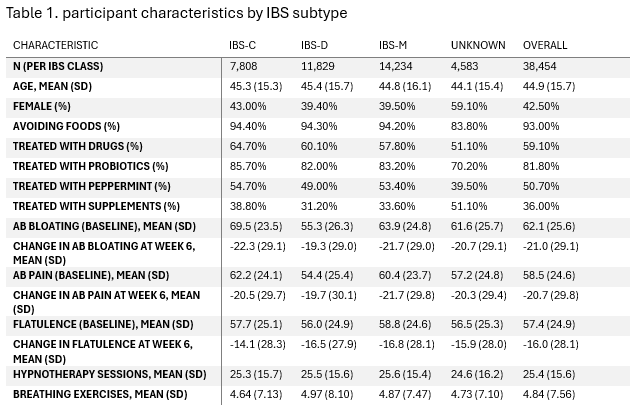
Figure: Figure 1. Spline-Modeled Dose–Response Curves for Digital Gut-Directed Hypnotherapy Across Core IBS Symptoms
Disclosures:
Mauricio Jin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Claire Hall: Mindset Health – Employee.
Xiao Jing Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio F. Jin, MD1, Claire Hall, 2, Xiao Jing Wang, MD1. P5100 - Digital Gut-directed Hypnotherapy Reduce Core IBS Symptoms: A Large-scale Spline-Enhanced Multivariable Regression Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Mindset Health, Boston, MA
Introduction: Gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH) has demonstrated efficacy in improving severity of symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), but widespread access remains limited due to provider availability and cost. Digitally delivered GDH provides a scalable, self-guided alternative with prior data showing efficacy in symptom improvement with greater adherence. However, large-scale real world digital delivery outcomes remain understudied, and nonlinear dose-response patterns have not been previously characterized in the literature.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of adult users of a digital GDH app (Nerva) who engaged in a 6-week self-guided digital program. Symptom scores were collected using IBS-VAS scale at baseline and at week 6. Multiple linear regression models were used to estimate associations, adjusting for age, gender, baseline severity, IBS subtype, and other interventions (e.g. diaphragmatic breathing, supplement use). Analysis focused on abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, and passage of wind. To capture nonlinear relationships between session adherence and outcomes, we used natural cubic splines for hypnotherapy counts. Models were selected based on the Bayesian Information Criterion and influential data points were excluded based on standardized residuals, leverage, and Cook’s distance.
Results: Data from 38,454 adult users were included in our retrospective cohort study. Patient characteristics are included in table 1. Average symptom reductions were 22.3% for bloating (SD:17.1), 22.1% for pain (SD:18.7), and 17.0% for passage of wind (SD:17.1). Participants with baseline IBS-VAS scores >60 achieved significantly greater reductions: 32.2%, 34.4%, and 29.5% respectively. Hypnotherapy session count was a strong nonlinear predictor of symptom improvement across all three symptom domains (p< 0.001 for spine terms), with most optimal benefit at moderate use (20-30 sessions). Spline modeled dose-response curves across core IBS symptoms are highlighted in figure 1.
Discussion: Digital gut-directed hypnotherapy via Nerva was associated with symptom reductions in this large real-world IBS cohort. Our data expands upon prior findings of digital GDH in our large-scale and real-world evaluation. Our use of spline enhanced regression reveals nonlinear dose-response relationship, suggesting an optimal treatment window for hypnotherapy adherence. These findings support the scalable use of digital GDH.

Figure: Table 1. participant characteristics by IBS subtype

Figure: Figure 1. Spline-Modeled Dose–Response Curves for Digital Gut-Directed Hypnotherapy Across Core IBS Symptoms
Disclosures:
Mauricio Jin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Claire Hall: Mindset Health – Employee.
Xiao Jing Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mauricio F. Jin, MD1, Claire Hall, 2, Xiao Jing Wang, MD1. P5100 - Digital Gut-directed Hypnotherapy Reduce Core IBS Symptoms: A Large-scale Spline-Enhanced Multivariable Regression Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
