Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P5070 - Social Determinants of Health Impact IBS and Other Abdominal Pain-Related Disorders of Gut Brain Interaction
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Amulya Anumolu, MD (she/her/hers)
CAMPBELL UNIVERSITY
Fayetteville, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Amulya Anumolu, MD1, Rebecca Petrovski, DO1, Lin Chang, MD2, Sarah Ballou, PhD3, Andrea Shin, MD, MSCR4, Alexander C. Ford, MBChB, MD, MRCP5, Miranda A.L. van Tilburg, PhD6
1CAMPBELL UNIVERSITY, Fayetteville, NC; 2Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, US, Los Angeles, CA; 3Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Chestnut Hill, MA; 4David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 5University of Leeds School of Medicine, Leeds, England, United Kingdom; 6Cape Fear Valley Health, Fayetteville, NC
Introduction: The biopsychosocial model has spurred a better understanding of Disorders of Brain Gut Interaction (DGBI). While multiple factors related to the presence or severity of DGBI have been studied, social factors, beyond immediate family or support, have received notably less attention in the literature. We conducted the first systematic review of Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) in abdominal pain-related DGBI (AP-DGBI). Our aim was twofold: (1) To examine if SDOH differ between patients with AP-DGBI and controls, and (2) to examine if SDOH are associated with negative outcomes for AP-DGBI, including symptom severity/frequency, disability/quality of life, and mental health disorders.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the literature from 1987 to 2024 using PubMed, Embase, PsychInfo, and CINAHL. Search strategies were based on previously published systematic reviews of SDOH in other diseases. Study inclusion criteria included: Published after 1987 when diagnostic criteria for DGBI were established, peer reviewed, primary study population of AP- DGBI, age of participants above 4 years old, sample size ≥ 50 participants, and included SDOH factors. Study exclusion criteria included: SDOH factors that have been previously studied in DGBI (e.g., adverse life experiences, psychosocial and biological factors), and lack of a control group. Each article was screened by two independent reviewers and disagreements were resolved by one senior author not involved in the screening.
Results: Of the 4229 studies were screened, 3953 were deemed irrelevant. Out of the 275 full text studies, 173 were eligible. Lower education, income, and unpaid employment were commonly associated with AP-DGBI, although some studies reported higher prevalence among highly educated or higher-income individuals (Table 1). Marital status showed no consistent association. Living in rural areas, unstable housing, or away from family was linked to greater risk, while stable home environments appeared protective. Reduced social support and non-traditional family structures were more common in AP-DGBI. Associations with race/ethnicity and insurance were inconsistent, though disparities in healthcare access were noted. Food insecurity was also linked to increased risk.
Discussion: Overall, SDOH may contribute to AP-DGBI, but findings vary depending on population characteristics and study design. Further prospective studies are needed to understand the impact of SDOH in children and adults with AP-DGBI.
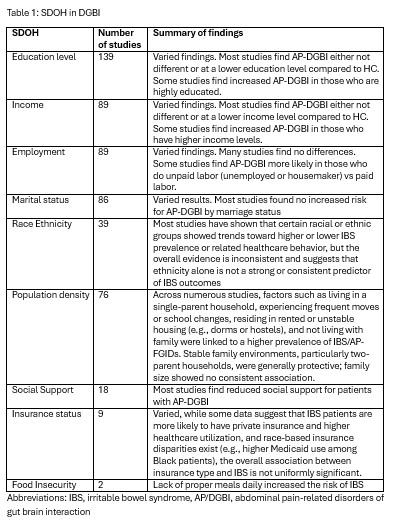
Figure: Table 1: SDOH in DGBI
Disclosures:
Amulya Anumolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rebecca Petrovski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lin Chang: AnX Robotica – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Atmo BioSciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch Health – Consultant. FoodMarble Digestive Health – Consultant, Stock Options. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Consultant. ModifyHealth – Stock Options. Trellus Health – Consultant, Stock Options. Vibrant Gastro – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Sarah Ballou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrea Shin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander C. Ford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miranda van Tilburg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amulya Anumolu, MD1, Rebecca Petrovski, DO1, Lin Chang, MD2, Sarah Ballou, PhD3, Andrea Shin, MD, MSCR4, Alexander C. Ford, MBChB, MD, MRCP5, Miranda A.L. van Tilburg, PhD6. P5070 - Social Determinants of Health Impact IBS and Other Abdominal Pain-Related Disorders of Gut Brain Interaction, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1CAMPBELL UNIVERSITY, Fayetteville, NC; 2Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, US, Los Angeles, CA; 3Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Chestnut Hill, MA; 4David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 5University of Leeds School of Medicine, Leeds, England, United Kingdom; 6Cape Fear Valley Health, Fayetteville, NC
Introduction: The biopsychosocial model has spurred a better understanding of Disorders of Brain Gut Interaction (DGBI). While multiple factors related to the presence or severity of DGBI have been studied, social factors, beyond immediate family or support, have received notably less attention in the literature. We conducted the first systematic review of Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) in abdominal pain-related DGBI (AP-DGBI). Our aim was twofold: (1) To examine if SDOH differ between patients with AP-DGBI and controls, and (2) to examine if SDOH are associated with negative outcomes for AP-DGBI, including symptom severity/frequency, disability/quality of life, and mental health disorders.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the literature from 1987 to 2024 using PubMed, Embase, PsychInfo, and CINAHL. Search strategies were based on previously published systematic reviews of SDOH in other diseases. Study inclusion criteria included: Published after 1987 when diagnostic criteria for DGBI were established, peer reviewed, primary study population of AP- DGBI, age of participants above 4 years old, sample size ≥ 50 participants, and included SDOH factors. Study exclusion criteria included: SDOH factors that have been previously studied in DGBI (e.g., adverse life experiences, psychosocial and biological factors), and lack of a control group. Each article was screened by two independent reviewers and disagreements were resolved by one senior author not involved in the screening.
Results: Of the 4229 studies were screened, 3953 were deemed irrelevant. Out of the 275 full text studies, 173 were eligible. Lower education, income, and unpaid employment were commonly associated with AP-DGBI, although some studies reported higher prevalence among highly educated or higher-income individuals (Table 1). Marital status showed no consistent association. Living in rural areas, unstable housing, or away from family was linked to greater risk, while stable home environments appeared protective. Reduced social support and non-traditional family structures were more common in AP-DGBI. Associations with race/ethnicity and insurance were inconsistent, though disparities in healthcare access were noted. Food insecurity was also linked to increased risk.
Discussion: Overall, SDOH may contribute to AP-DGBI, but findings vary depending on population characteristics and study design. Further prospective studies are needed to understand the impact of SDOH in children and adults with AP-DGBI.

Figure: Table 1: SDOH in DGBI
Disclosures:
Amulya Anumolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rebecca Petrovski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lin Chang: AnX Robotica – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Atmo BioSciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch Health – Consultant. FoodMarble Digestive Health – Consultant, Stock Options. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Consultant. ModifyHealth – Stock Options. Trellus Health – Consultant, Stock Options. Vibrant Gastro – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Sarah Ballou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrea Shin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander C. Ford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miranda van Tilburg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amulya Anumolu, MD1, Rebecca Petrovski, DO1, Lin Chang, MD2, Sarah Ballou, PhD3, Andrea Shin, MD, MSCR4, Alexander C. Ford, MBChB, MD, MRCP5, Miranda A.L. van Tilburg, PhD6. P5070 - Social Determinants of Health Impact IBS and Other Abdominal Pain-Related Disorders of Gut Brain Interaction, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
