Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P4907 - Efficacy of Potassium Channel Acid Blockers for Non-Erosive Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MA
Maram Albandak, MD
The University of Toledo
Toledo, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Maram Albandak, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD8, Bisher Sawaf, MD9, Elias Battikh, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 3Department of Internal Medicine, TriHealth Inc., Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH; 4University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 5Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 6Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 7Saint Agnes Medical Center, Fresno CA, Fresno, CA; 8Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Cleveland, OH; 9University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 10John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 11Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 12University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) is a prevalent subset of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) characterized by typical reflux symptoms without visible esophageal mucosal damage. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), the traditional mainstay of GERD treatment, have limited efficacy in NERD due to slower onset of action and reduced effectiveness for nighttime symptoms. Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) are a newer class of acid suppressants offering rapid, potent, and sustained acid suppression. They have demonstrated superior symptom relief and mucosal healing in severe reflux esophagitis and efficacy in PPI-resistant GERD. We aim to evaluate the comparative efficacy of P-CABs in treating NERD.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase up to October 2024, targeting randomized clinical trials involving adult patients with NERD treated with P-CABs or placebo. Studies reporting outcomes such as the proportion of heartburn-free days, healing rates, complete symptom resolution, and quality of life assessed by the GERD-HRQL questionnaire were included. The primary outcome analyzed was the proportion of heartburn-free days. Data was extracted and analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software.
Results: Our analysis included four phase III double-blind randomized trials comparing the efficacy of P-CABs (tegoprazan 50 mg and vonoprazan 10 mg) to placebo in the treatment of NERD. A total of 1760 patients were analyzed, with 880 (50%) patients receiving P-CABS, and 880 (50%) receiving placebo. Table 1 describes the main characteristics of the included studies and their patients. The mean proportion of males in the P-CABs group was 33.2%, compared to 41.4% in the placebo group. The mean age of patients in the P-CABs group was 50.3 (13.7), and 50.3 (14.5) in the placebo group. The average BMI for the P-CABs group was 24.8 (4.2) kg/m2 versus 24.7 (4.2) kg/m2 in the placebo group. Patients in the P-CABs group had a significantly higher proportion of heartburn-free days over four weeks compared to the placebo group, with a mean difference of 10.9 days (95% CI: 4.2–17; p = 0.001) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Our meta-analysis provides strong evidence that P-CABs significantly alleviate symptoms in patients with NERD. Given the challenges in managing NERD due to the absence of endoscopic abnormalities and the limitations of PPIs, P-CABs emerge as an effective therapeutic alternative to enhance symptom control and reduce morbidity in this patient population.
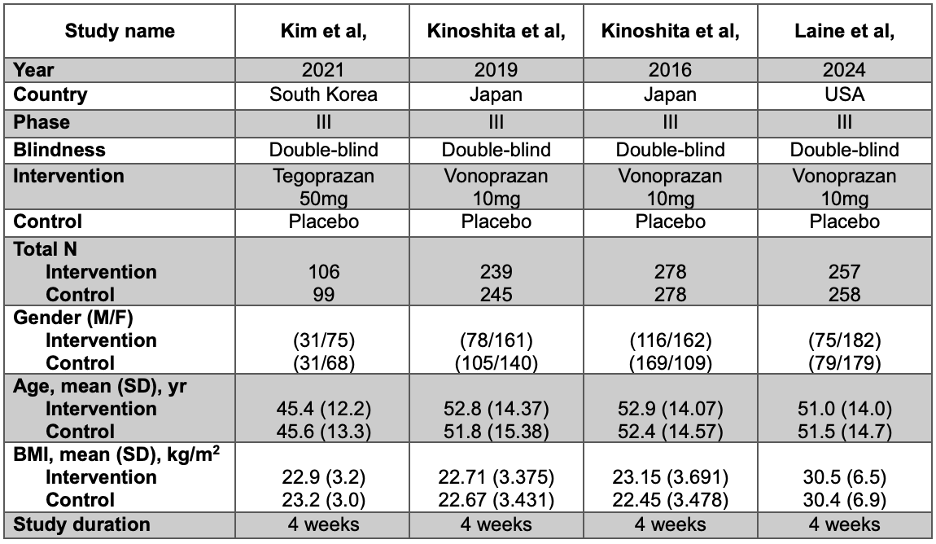
Figure: Table1: General characteristics of the four included studies and their patients.
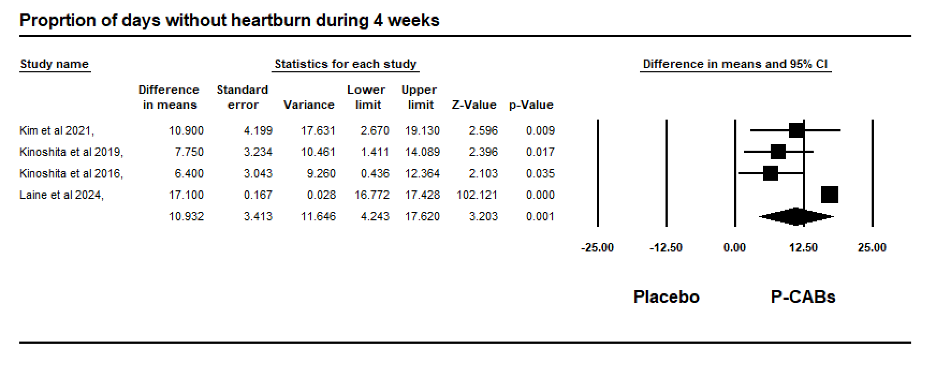
Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot of the difference in means in patients with NERD treated with P-CABs versus placebo.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maram Albandak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umberto Battistin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hayder Alamily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mhd Kutaiba Albuni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamad Oum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muaz Alsabbagh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Battikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Maram Albandak, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD8, Bisher Sawaf, MD9, Elias Battikh, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12. P4907 - Efficacy of Potassium Channel Acid Blockers for Non-Erosive Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, CO; 3Department of Internal Medicine, TriHealth Inc., Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH; 4University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 5Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 6Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 7Saint Agnes Medical Center, Fresno CA, Fresno, CA; 8Detroit Medical Center/Wayne State University, Cleveland, OH; 9University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 10John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Toledo, OH; 11Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 12University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) is a prevalent subset of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) characterized by typical reflux symptoms without visible esophageal mucosal damage. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), the traditional mainstay of GERD treatment, have limited efficacy in NERD due to slower onset of action and reduced effectiveness for nighttime symptoms. Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) are a newer class of acid suppressants offering rapid, potent, and sustained acid suppression. They have demonstrated superior symptom relief and mucosal healing in severe reflux esophagitis and efficacy in PPI-resistant GERD. We aim to evaluate the comparative efficacy of P-CABs in treating NERD.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase up to October 2024, targeting randomized clinical trials involving adult patients with NERD treated with P-CABs or placebo. Studies reporting outcomes such as the proportion of heartburn-free days, healing rates, complete symptom resolution, and quality of life assessed by the GERD-HRQL questionnaire were included. The primary outcome analyzed was the proportion of heartburn-free days. Data was extracted and analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) software.
Results: Our analysis included four phase III double-blind randomized trials comparing the efficacy of P-CABs (tegoprazan 50 mg and vonoprazan 10 mg) to placebo in the treatment of NERD. A total of 1760 patients were analyzed, with 880 (50%) patients receiving P-CABS, and 880 (50%) receiving placebo. Table 1 describes the main characteristics of the included studies and their patients. The mean proportion of males in the P-CABs group was 33.2%, compared to 41.4% in the placebo group. The mean age of patients in the P-CABs group was 50.3 (13.7), and 50.3 (14.5) in the placebo group. The average BMI for the P-CABs group was 24.8 (4.2) kg/m2 versus 24.7 (4.2) kg/m2 in the placebo group. Patients in the P-CABs group had a significantly higher proportion of heartburn-free days over four weeks compared to the placebo group, with a mean difference of 10.9 days (95% CI: 4.2–17; p = 0.001) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Our meta-analysis provides strong evidence that P-CABs significantly alleviate symptoms in patients with NERD. Given the challenges in managing NERD due to the absence of endoscopic abnormalities and the limitations of PPIs, P-CABs emerge as an effective therapeutic alternative to enhance symptom control and reduce morbidity in this patient population.

Figure: Table1: General characteristics of the four included studies and their patients.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot of the difference in means in patients with NERD treated with P-CABs versus placebo.
Disclosures:
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Rabeeah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maram Albandak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umberto Battistin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hayder Alamily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mhd Kutaiba Albuni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Al-Obaidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamad Oum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muaz Alsabbagh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Battikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abu-Rumaileh, MD1, Sana Rabeeah, MD1, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD1, Maram Albandak, MD1, Umberto Battistin, MD1, Hayder Alamily, MD2, Mhd Kutaiba Albuni, MD3, Hasan Al-Obaidi, MD4, Shahem Abbarh, MD5, Mulham Alom, MD6, Muhamad Oum, MD7, Muaz Alsabbagh, MD8, Bisher Sawaf, MD9, Elias Battikh, MD10, Amine Rakab, MD11, Yaseen Alastal, MD12. P4907 - Efficacy of Potassium Channel Acid Blockers for Non-Erosive Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
