Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P4906 - Endoscopic Anti-Reflux Mucosectomy versus Stretta Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Fariha Hasan, MD
Cooper University Hospital
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD6
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) unresponsive to proton pump inhibitors (PPI) poses a significant clinical challenge as the treatment options are limited. Recently minimally invasive procedures including Endoscopic anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) and Stretta radiofrequency ablation (SRF) have emerged as newer treatment modalities for resistant GERD, however, direct comparison between the two are sparse. This meta-analysis compares the safety and efficacy of the ARMS and SRF for GERD.
Methods: Electronic databases including PubMed, Cochrane Central and ScienceDirect were searched from inception till January 2025. Risk Ratios (RR) and Mean Differences (MD) along with 95% Confidence Interval (CI) were pooled under the random effects model using the Review Manager version 5.4.1 for the dichotomous and continuous outcomes respectively. The primary and secondary endpoints of interest are the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GERDQ) score, PPI withdrawal rate, symptom improvement rate, technical success rate and adverse effects. Quality assessment was done through the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) 2.0 tool and the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was performed to investigate the cause of heterogeneity. Publication bias was assessed visually through funnel plot and statistically through Egger's regression test.
Results: Three studies pooling a total of 480 patients were included in the quantitative synthesis. The ARMS group decreased the GERDQ score, but the results were statistically insignificant (RR= -0.36;95%CI:[-0.87,0.15]; p=0.16; I2=0%). Other efficacy outcomes including PPI withdrawal rate (RR= 0.84;95%CI:[0.55,1.29]; p=0.43; I2=77%), symptom improvement rate (RR= 1.02;95%CI:[0.94,1.10]; p=0.66; I2=0%), and technical success rate (RR= 1.00;95%CI:[0.99,1.01]; p=1.00; I2=0%) were comparable between the ARMS and SRF group. Similarly, regarding the safety profile, the two groups showed no significant difference in the adverse effects (RR= 7.80;95%CI:[0.18,341.10]; p=0.29; I2=89%).
Discussion: Both ARMS and SRF demonstrated comparable outcomes in terms of efficacy and safety for the treatment of GERD unresponsive to proton pump inhibitors, suggesting that either of these minimally invasive procedures may be considered viable therapeutic options, with the choice of intervention potentially guided by physician expertise, patient preference, and resource availability.
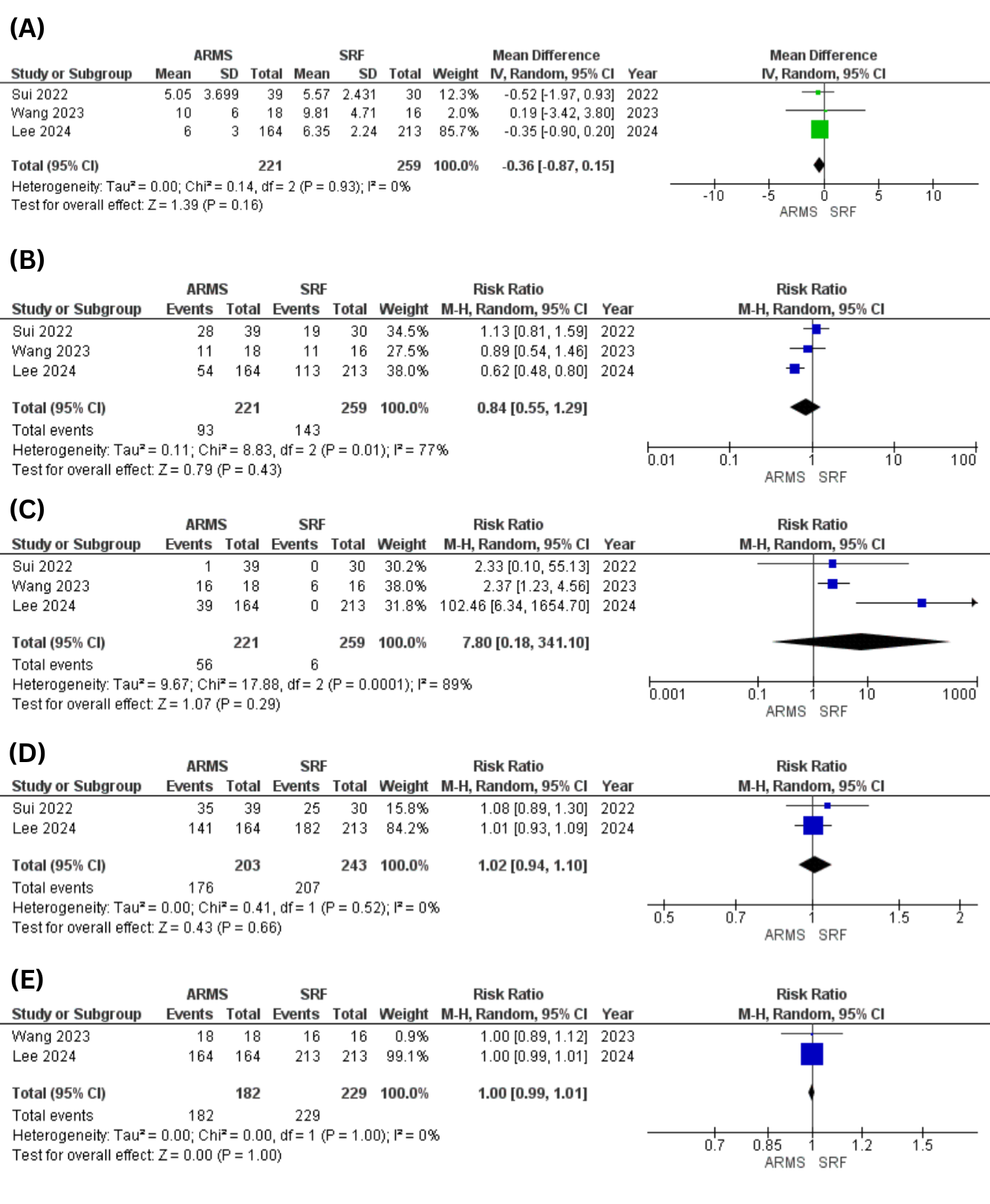
Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot for (A)GERDQ Score (B)Proton Pump Inhibitor Withdrawal Rate (C)Adverse Effects (D)Symptom Improvement Rate (E)Technical Success Rate
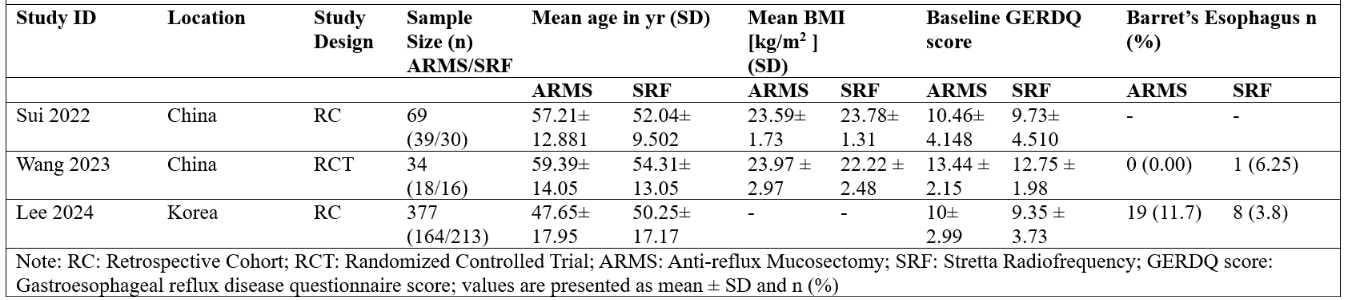
Figure: Figure 2: Baseline Characteristics of the Included Studies
Disclosures:
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD6. P4906 - Endoscopic Anti-Reflux Mucosectomy versus Stretta Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 6Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) unresponsive to proton pump inhibitors (PPI) poses a significant clinical challenge as the treatment options are limited. Recently minimally invasive procedures including Endoscopic anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) and Stretta radiofrequency ablation (SRF) have emerged as newer treatment modalities for resistant GERD, however, direct comparison between the two are sparse. This meta-analysis compares the safety and efficacy of the ARMS and SRF for GERD.
Methods: Electronic databases including PubMed, Cochrane Central and ScienceDirect were searched from inception till January 2025. Risk Ratios (RR) and Mean Differences (MD) along with 95% Confidence Interval (CI) were pooled under the random effects model using the Review Manager version 5.4.1 for the dichotomous and continuous outcomes respectively. The primary and secondary endpoints of interest are the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GERDQ) score, PPI withdrawal rate, symptom improvement rate, technical success rate and adverse effects. Quality assessment was done through the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) 2.0 tool and the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was performed to investigate the cause of heterogeneity. Publication bias was assessed visually through funnel plot and statistically through Egger's regression test.
Results: Three studies pooling a total of 480 patients were included in the quantitative synthesis. The ARMS group decreased the GERDQ score, but the results were statistically insignificant (RR= -0.36;95%CI:[-0.87,0.15]; p=0.16; I2=0%). Other efficacy outcomes including PPI withdrawal rate (RR= 0.84;95%CI:[0.55,1.29]; p=0.43; I2=77%), symptom improvement rate (RR= 1.02;95%CI:[0.94,1.10]; p=0.66; I2=0%), and technical success rate (RR= 1.00;95%CI:[0.99,1.01]; p=1.00; I2=0%) were comparable between the ARMS and SRF group. Similarly, regarding the safety profile, the two groups showed no significant difference in the adverse effects (RR= 7.80;95%CI:[0.18,341.10]; p=0.29; I2=89%).
Discussion: Both ARMS and SRF demonstrated comparable outcomes in terms of efficacy and safety for the treatment of GERD unresponsive to proton pump inhibitors, suggesting that either of these minimally invasive procedures may be considered viable therapeutic options, with the choice of intervention potentially guided by physician expertise, patient preference, and resource availability.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot for (A)GERDQ Score (B)Proton Pump Inhibitor Withdrawal Rate (C)Adverse Effects (D)Symptom Improvement Rate (E)Technical Success Rate

Figure: Figure 2: Baseline Characteristics of the Included Studies
Disclosures:
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD5, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD6. P4906 - Endoscopic Anti-Reflux Mucosectomy versus Stretta Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
