Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Diet, Nutrition, and Obesity
P4844 - Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery vs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- WG
Wissam Ghusn, MD
Boston Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Noura Jawhar, MBBS2, Tala Abedalqader, MD2, Nour El Ghazal, MBBS2, Maria Antonia Espinosa, MD2, Jose Villamarin, MD2, Rene J. Rivera Gutierrez, MD3, Regina Castaneda, MD3, Dima Bechenati, MD2, Maria D. Hurtado, MD3, Andres Acosta, MD2, Omar M. Ghanem, MD2
1Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are established treatments for weight loss and cardiometabolic risk reduction. While both have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, few real-world studies have directly compared their impact on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk. This study compares changes in ASCVD risk, lipids, blood pressure, and body weight following MBS (sleeve gastrectomy [SG], Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB], and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch [BPD-DS]) versus GLP-1RA therapy (semaglutide or tirzepatide) over one year.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients treated with MBS or GLP-1RAs for ≥1 year. ASCVD 10-year and lifetime risk scores were calculated using pooled cohort equations at baseline and follow-up. Between-group comparisons used t-tests and chi-squared tests, and multivariate linear regression adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, baseline ASCVD risk, and weight loss.
Results: A total of 1,891 patients were included in the analysis (MBS n=1,088; GLP-1RA n=803). Baseline demographic data are presented in Table 1. MBS resulted in significantly greater reductions in lifetime ASCVD risk compared to GLP-1RA (−8.4 ± 12.0% vs. −1.7 ± 9.3%, p< 0.0001; Figure 1A). Changes in 10-year ASCVD risk were not significantly different between groups (−0.72 ± 2.6% vs. −0.92 ± 5.8%, p=0.62; Figure 1B). MBS led to markedly greater total body weight loss at 1 year (−28.5 ± 10.0%) versus GLP-1RA (−11.2 ± 9.3%, p< 0.0001; Figure 1C). Improvements in total cholesterol favored MBS (−22.6 vs. −8.1 mg/dL, p< 0.0001; Figure 1D). LDL cholesterol declined more in the MBS group (−19.5 vs. −6.4 mg/dL, p< 0.0001; Figure 1E), while HDL increased by +7.0 mg/dL with MBS versus +2.0 mg/dL with GLP-1RA (p< 0.0001; Figure 1F). Systolic blood pressure decreased by −7.1 mmHg with MBS and −5.0 mmHg with GLP-1RA (p=0.0058; Figure 1G), while diastolic blood pressure dropped by −4.1 mmHg with MBS compared to −2.5 mmHg with GLP-1RA (p=0.0029; Figure 1H). In a multivariate linear regression, MBS remained independently associated with greater lifetime ASCVD risk reduction.
Discussion: In a large real-world cohort, MBS led to significantly greater improvements in weight, lipid profiles, and lifetime ASCVD risk compared to GLP-1RA therapy. These findings provide real-world evidence to inform clinical decision-making in obesity and cardiovascular risk management.
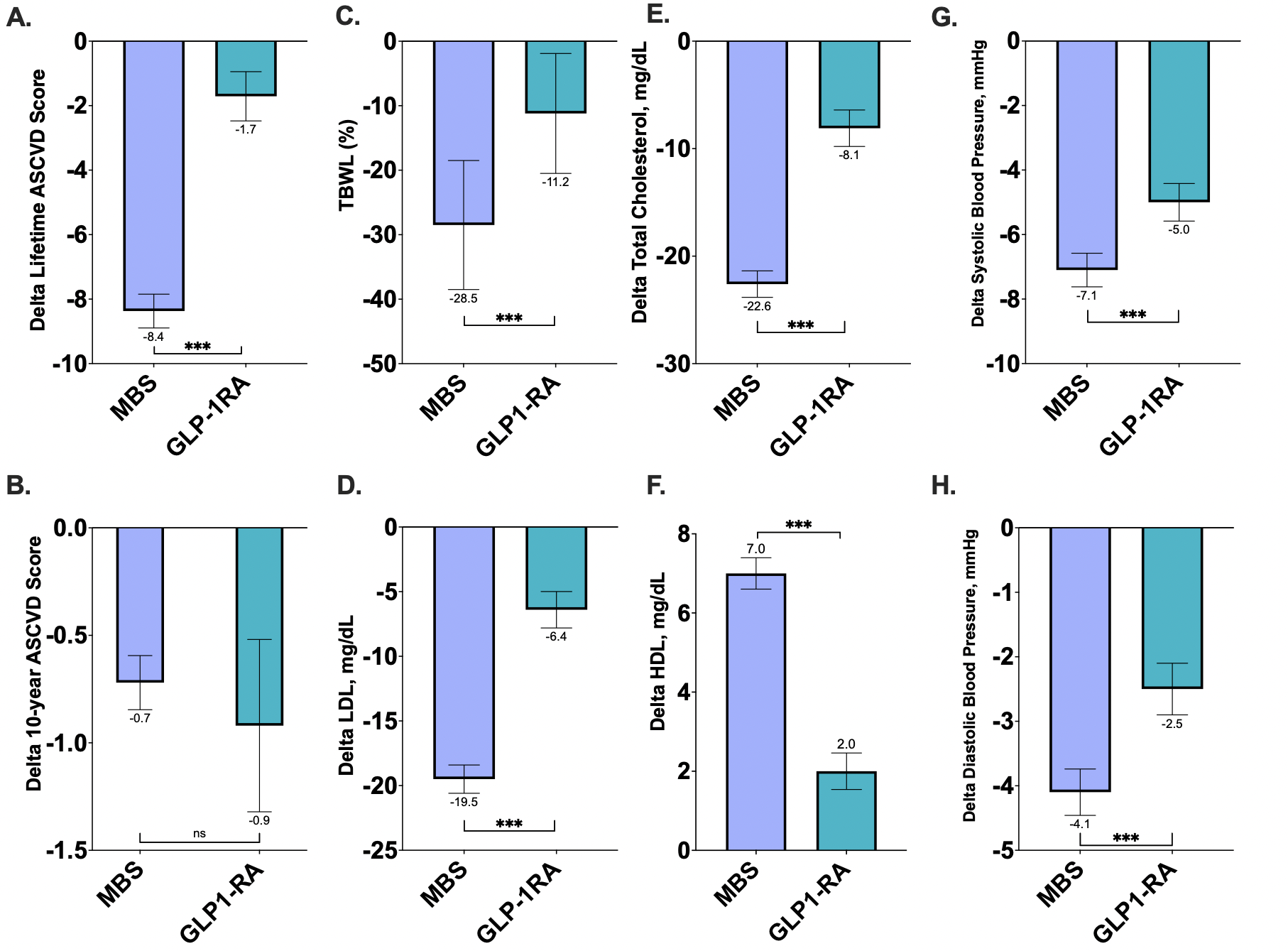
Figure: Table 1: Baseline Demographic and Cardiometabolic Characteristics of Patients Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Versus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy.
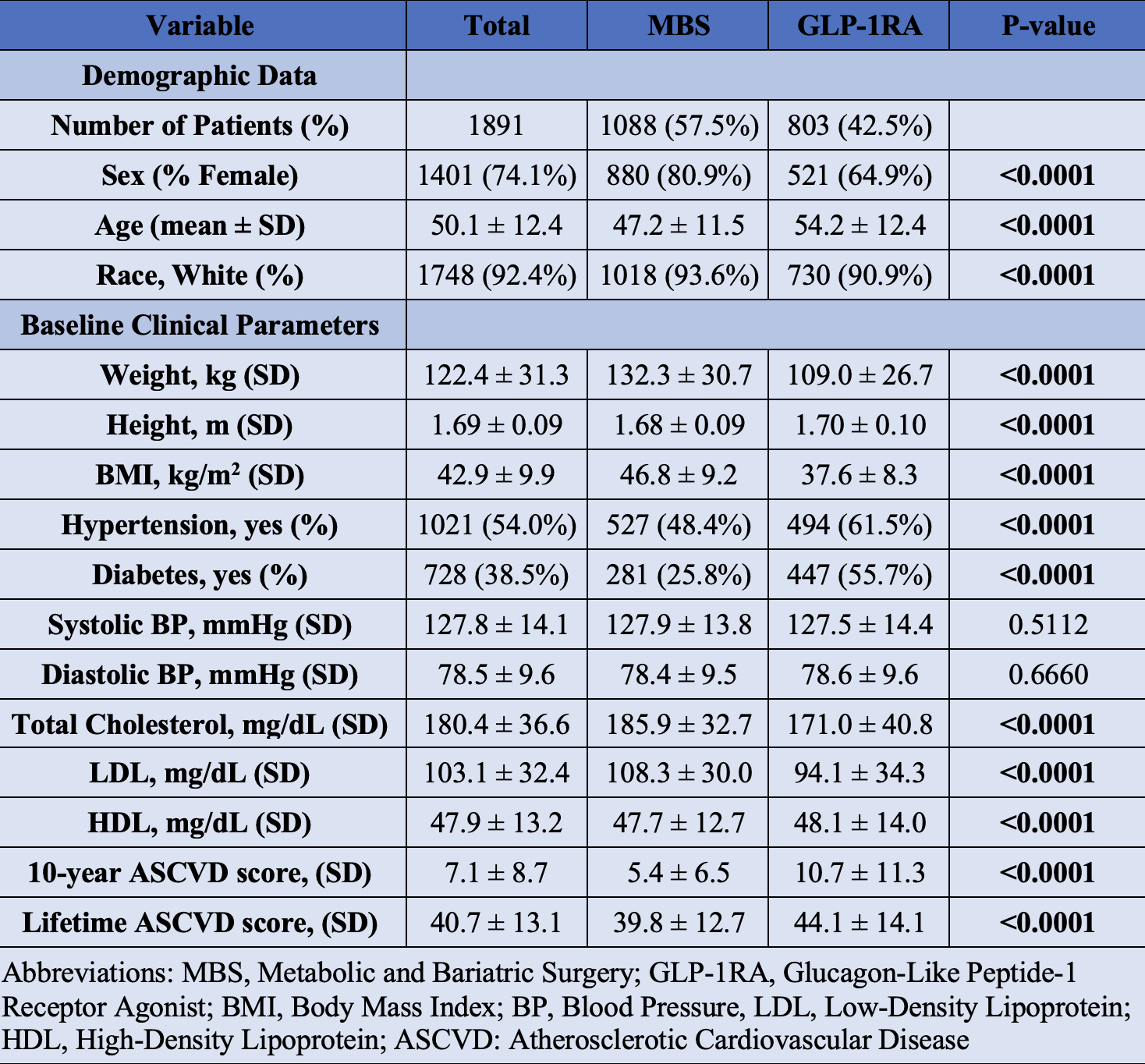
Figure: Figure 1: One-Year Changes in Cardiometabolic Risk Markers Following Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Versus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy
Disclosures:
Wissam Ghusn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noura Jawhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tala Abedalqader indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nour El Ghazal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Antonia Espinosa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose Villamarin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rene Rivera Gutierrez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Regina Castaneda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dima Bechenati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria D. Hurtado: NovoNordisk – Advisor or Review Panel Member, funding from the National Institute of Health (K12-AR084222), the Mayo Clinic Center for Women's Health Research, and Phenomix Sciences.
Andres Acosta: Phenomix sciences – Royalties. Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Gila Therapeutics, Amgen, General Mills, Regeneron, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Currax, Nestlé, Phenomix Sciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Omar Ghanem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Noura Jawhar, MBBS2, Tala Abedalqader, MD2, Nour El Ghazal, MBBS2, Maria Antonia Espinosa, MD2, Jose Villamarin, MD2, Rene J. Rivera Gutierrez, MD3, Regina Castaneda, MD3, Dima Bechenati, MD2, Maria D. Hurtado, MD3, Andres Acosta, MD2, Omar M. Ghanem, MD2. P4844 - Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery vs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are established treatments for weight loss and cardiometabolic risk reduction. While both have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials, few real-world studies have directly compared their impact on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk. This study compares changes in ASCVD risk, lipids, blood pressure, and body weight following MBS (sleeve gastrectomy [SG], Roux-en-Y gastric bypass [RYGB], and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch [BPD-DS]) versus GLP-1RA therapy (semaglutide or tirzepatide) over one year.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients treated with MBS or GLP-1RAs for ≥1 year. ASCVD 10-year and lifetime risk scores were calculated using pooled cohort equations at baseline and follow-up. Between-group comparisons used t-tests and chi-squared tests, and multivariate linear regression adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, baseline ASCVD risk, and weight loss.
Results: A total of 1,891 patients were included in the analysis (MBS n=1,088; GLP-1RA n=803). Baseline demographic data are presented in Table 1. MBS resulted in significantly greater reductions in lifetime ASCVD risk compared to GLP-1RA (−8.4 ± 12.0% vs. −1.7 ± 9.3%, p< 0.0001; Figure 1A). Changes in 10-year ASCVD risk were not significantly different between groups (−0.72 ± 2.6% vs. −0.92 ± 5.8%, p=0.62; Figure 1B). MBS led to markedly greater total body weight loss at 1 year (−28.5 ± 10.0%) versus GLP-1RA (−11.2 ± 9.3%, p< 0.0001; Figure 1C). Improvements in total cholesterol favored MBS (−22.6 vs. −8.1 mg/dL, p< 0.0001; Figure 1D). LDL cholesterol declined more in the MBS group (−19.5 vs. −6.4 mg/dL, p< 0.0001; Figure 1E), while HDL increased by +7.0 mg/dL with MBS versus +2.0 mg/dL with GLP-1RA (p< 0.0001; Figure 1F). Systolic blood pressure decreased by −7.1 mmHg with MBS and −5.0 mmHg with GLP-1RA (p=0.0058; Figure 1G), while diastolic blood pressure dropped by −4.1 mmHg with MBS compared to −2.5 mmHg with GLP-1RA (p=0.0029; Figure 1H). In a multivariate linear regression, MBS remained independently associated with greater lifetime ASCVD risk reduction.
Discussion: In a large real-world cohort, MBS led to significantly greater improvements in weight, lipid profiles, and lifetime ASCVD risk compared to GLP-1RA therapy. These findings provide real-world evidence to inform clinical decision-making in obesity and cardiovascular risk management.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline Demographic and Cardiometabolic Characteristics of Patients Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Versus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy.

Figure: Figure 1: One-Year Changes in Cardiometabolic Risk Markers Following Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Versus GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy
Disclosures:
Wissam Ghusn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noura Jawhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tala Abedalqader indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nour El Ghazal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Antonia Espinosa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose Villamarin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rene Rivera Gutierrez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Regina Castaneda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dima Bechenati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria D. Hurtado: NovoNordisk – Advisor or Review Panel Member, funding from the National Institute of Health (K12-AR084222), the Mayo Clinic Center for Women's Health Research, and Phenomix Sciences.
Andres Acosta: Phenomix sciences – Royalties. Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Gila Therapeutics, Amgen, General Mills, Regeneron, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Currax, Nestlé, Phenomix Sciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Omar Ghanem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wissam Ghusn, MD1, Noura Jawhar, MBBS2, Tala Abedalqader, MD2, Nour El Ghazal, MBBS2, Maria Antonia Espinosa, MD2, Jose Villamarin, MD2, Rene J. Rivera Gutierrez, MD3, Regina Castaneda, MD3, Dima Bechenati, MD2, Maria D. Hurtado, MD3, Andres Acosta, MD2, Omar M. Ghanem, MD2. P4844 - Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery vs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

