Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P4767 - Automated Clinical Decision Support Enhances Post-Adenoma Surveillance Tracking in the Electronic Medical Record
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Michael T. O'Brien, MD
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Nashville, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Michael O'Brien, MD1, Ashley Spann, MD1, Laura Zahn, MS1, Allison McCoy, PhD1, Sara Horst, MD, MPH, FACG2
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN
Introduction: Surveillance colonoscopy following adenoma detection is essential for colorectal cancer prevention, yet systematic implementation within electronic health record (EHR) systems remains challenging. Current health maintenance modules frequently depend on manual data entry, resulting in incomplete surveillance tracking and potential gaps in care continuity. Enhanced clinical decision support tools are needed to optimize post-polypectomy surveillance protocols.
Methods: This single-center retrospective study analyzed patients (pts) undergoing colonoscopy between November 2017 to December 2024 within a large healthcare organization using Epic EHR with Health Maintenance functionality utilized to track colon cancer surveillance. Pts aged ≥50-75 years undergoing colonoscopy for screening, surveillance, or diagnostic indications were included. Exclusion criteria included pts with inflammatory bowel disease, known colorectal cancer, or hereditary cancer syndromes. In June 2022, automated clinical decision support was implemented. Pre-intervention, gastroenterologists and primary care providers manually updated surveillance intervals. Post-intervention, an automated tool integrated into templated polyp notification letters triggered simultaneous updates to Health Maintenance for corresponding appropriate surveillance intervals.
Results: 35,802 pts met criteria and adenomas were detected in 44% (8004/18027) in the pre-intervention and 47% (8396/17775) in the post intervention period. (Table 1 for details) Health Maintenance updates for pts with adenomas requiring closer surveillance increased significantly from 83% (6672/8004) to 94% (7913/8396) post-intervention (p < 0.05). Gastroenterology team completion of Health Maintenance updates increased post-intervention from 68% (5413/8004) to 91% (7717/8396) (p < 0.05). Conversely, primary care team updates decreased significantly from 9% (746/8004) to 1% (118/8396) post-intervention (p < 0.05). Population health automatic updates occurred in a small number of pts in both periods. (Table 2)
Discussion: Implementation of automatic updates to Health Maintenance significantly increased the reliability of post-adenoma surveillance documentation in the EHR. Post-intervention, gastroenterology reporting increased while reducing primary care burden. Clinical decision support implementation is critical for accurate adenoma surveillance intervals.
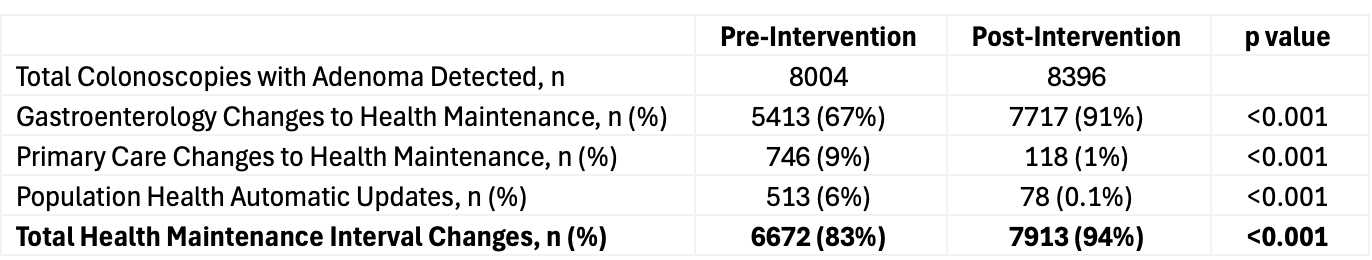
Figure: Table 1. Patient characteristics
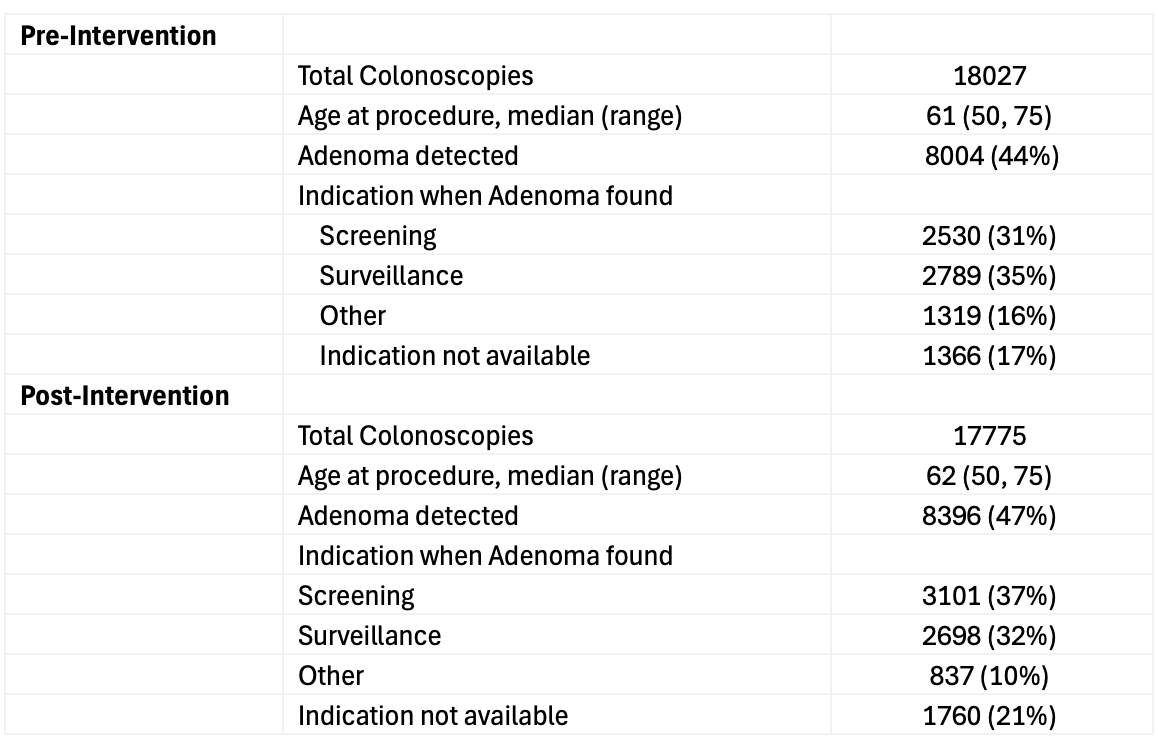
Figure: Table 2. Health Maintenance updates after adenoma detection in the pre- and post-clinical decision support intervention period
Disclosures:
Michael O'Brien indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashley Spann: Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Consultant.
Laura Zahn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allison McCoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Horst: Abbvie – Consultant. Biocon – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. J&J – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant.
Michael O'Brien, MD1, Ashley Spann, MD1, Laura Zahn, MS1, Allison McCoy, PhD1, Sara Horst, MD, MPH, FACG2. P4767 - Automated Clinical Decision Support Enhances Post-Adenoma Surveillance Tracking in the Electronic Medical Record, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN
Introduction: Surveillance colonoscopy following adenoma detection is essential for colorectal cancer prevention, yet systematic implementation within electronic health record (EHR) systems remains challenging. Current health maintenance modules frequently depend on manual data entry, resulting in incomplete surveillance tracking and potential gaps in care continuity. Enhanced clinical decision support tools are needed to optimize post-polypectomy surveillance protocols.
Methods: This single-center retrospective study analyzed patients (pts) undergoing colonoscopy between November 2017 to December 2024 within a large healthcare organization using Epic EHR with Health Maintenance functionality utilized to track colon cancer surveillance. Pts aged ≥50-75 years undergoing colonoscopy for screening, surveillance, or diagnostic indications were included. Exclusion criteria included pts with inflammatory bowel disease, known colorectal cancer, or hereditary cancer syndromes. In June 2022, automated clinical decision support was implemented. Pre-intervention, gastroenterologists and primary care providers manually updated surveillance intervals. Post-intervention, an automated tool integrated into templated polyp notification letters triggered simultaneous updates to Health Maintenance for corresponding appropriate surveillance intervals.
Results: 35,802 pts met criteria and adenomas were detected in 44% (8004/18027) in the pre-intervention and 47% (8396/17775) in the post intervention period. (Table 1 for details) Health Maintenance updates for pts with adenomas requiring closer surveillance increased significantly from 83% (6672/8004) to 94% (7913/8396) post-intervention (p < 0.05). Gastroenterology team completion of Health Maintenance updates increased post-intervention from 68% (5413/8004) to 91% (7717/8396) (p < 0.05). Conversely, primary care team updates decreased significantly from 9% (746/8004) to 1% (118/8396) post-intervention (p < 0.05). Population health automatic updates occurred in a small number of pts in both periods. (Table 2)
Discussion: Implementation of automatic updates to Health Maintenance significantly increased the reliability of post-adenoma surveillance documentation in the EHR. Post-intervention, gastroenterology reporting increased while reducing primary care burden. Clinical decision support implementation is critical for accurate adenoma surveillance intervals.

Figure: Table 1. Patient characteristics

Figure: Table 2. Health Maintenance updates after adenoma detection in the pre- and post-clinical decision support intervention period
Disclosures:
Michael O'Brien indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashley Spann: Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Consultant.
Laura Zahn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allison McCoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Horst: Abbvie – Consultant. Biocon – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. J&J – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant.
Michael O'Brien, MD1, Ashley Spann, MD1, Laura Zahn, MS1, Allison McCoy, PhD1, Sara Horst, MD, MPH, FACG2. P4767 - Automated Clinical Decision Support Enhances Post-Adenoma Surveillance Tracking in the Electronic Medical Record, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

