Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P4753 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Colonoscopy Increases Adenoma and Small Polyp Detection: A Meta-Analysis of 13 RCTs
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Prince Shah-Riar, MD (he/him/his)
DHR Health, Edinburg, Tx
Edinburg, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Prince Shah-Riar, MD1, Samia Sarker, MBBS2, Sumaiya Monjur, MBBS3, Tathagato Das, MBBS4, Tasnim Rahman, MBBS5, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG6
1DHR Health, Edinburg, Tx, McAllen, TX; 2Dhaka Medical College and Hospital, Houston, TX; 3Dhaka Medical College and Hospital, Spokane, WA; 4Jalalabad Ragib Rabeya Medical College, Sylhet, Bangladesh, Sylhet, Sylhet, Bangladesh; 5Wenzhou Medical University, Fort Collins, CO; 6DHR Health Gastroenterology, Edinburg, TX
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most commonly diagnosed malignancy and ranks third in cancer-related mortality in the United States. Early detection through colonoscopy is a cornerstone of CRC prevention. The adenoma detection rate (ADR) is a validated quality metric, with higher ADRs linked to decreased incidence of post-colonoscopy CRC. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising adjunct in endoscopy, capable of enhancing detection by reducing human error and highlighting subtle or overlooked lesions. While several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the utility of AI, a comprehensive meta-analytic comparison between AI-assisted and standard colonoscopy (SC), especially in detecting small adenomas (≤5 mm), remains lacking.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs published between 2019 and 2024. Databases searched included PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and PLOS One. Thirteen RCTs involving 11,521 patients were included (5,585 AI-assisted; 5,636 SC). Data were pooled using odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic. Subgroup analysis focused on the detection of diminutive lesions (≤5 mm).
Results: AI-assisted colonoscopy demonstrated a significantly higher overall ADR than SC (OR 1.43; 95% CI: 1.28–1.60; I² = 43%; P < 0.00001). In detecting small adenomas and polyps (≤5 mm), AI also showed superior performance (OR 1.56; 95% CI: 1.24–1.97; I² = 73%; P = 0.0002). These results reflect a robust and consistent benefit of AI integration across key outcome measures.
Discussion: AI-enhanced colonoscopy significantly improves the detection of adenomas, including diminutive lesions, compared to standard methods. These findings support the integration of AI into routine CRC screening protocols and justify continued research into AI-based diagnostic tools to advance precision endoscopy and reduce cancer burden.
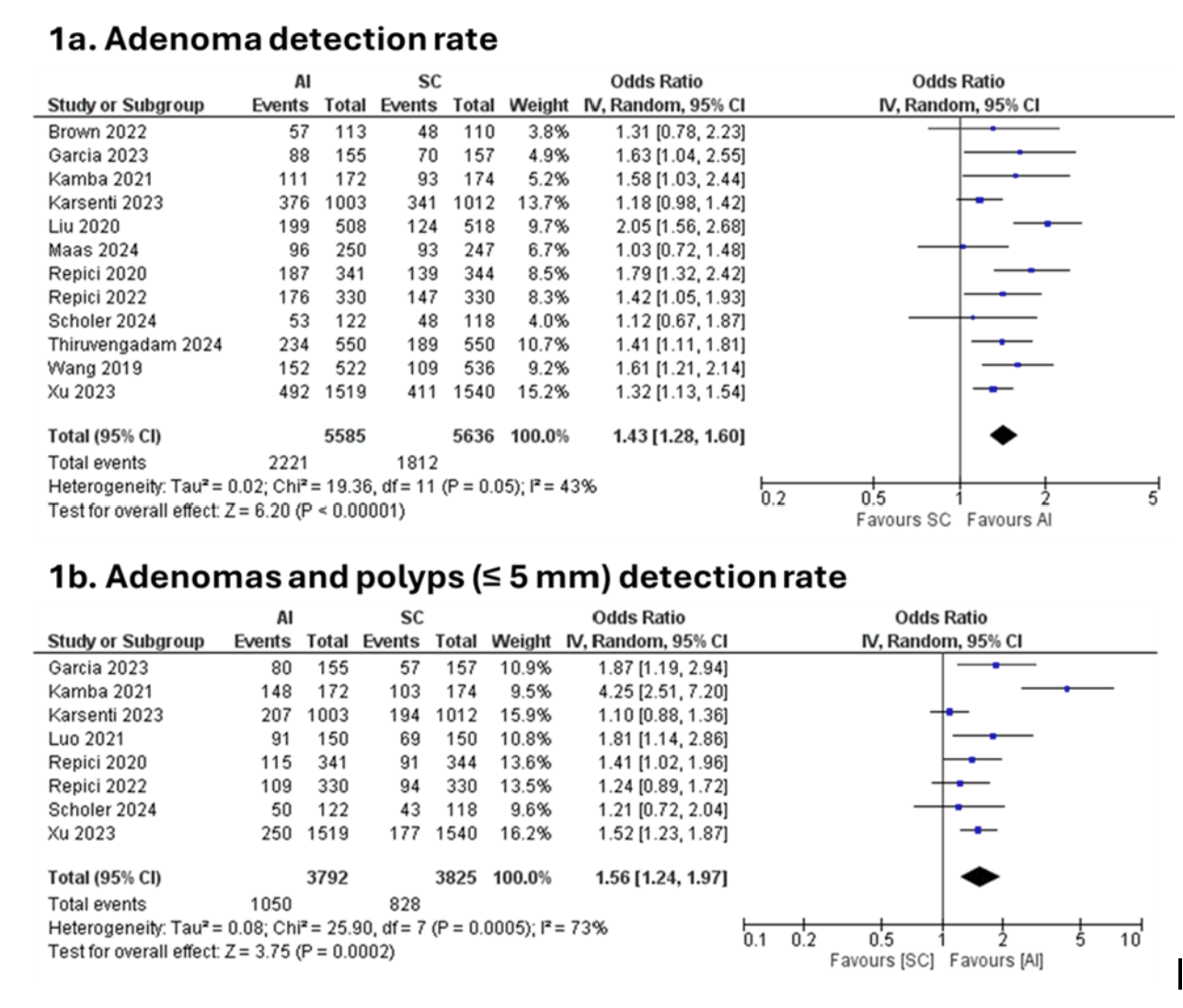
Figure: Figure 1: Colonoscopy with AI assisted vs standard. 1a. Adenoma detection rate, 1b. adenoma and polyp with size ≤ 5 mm detection rate.
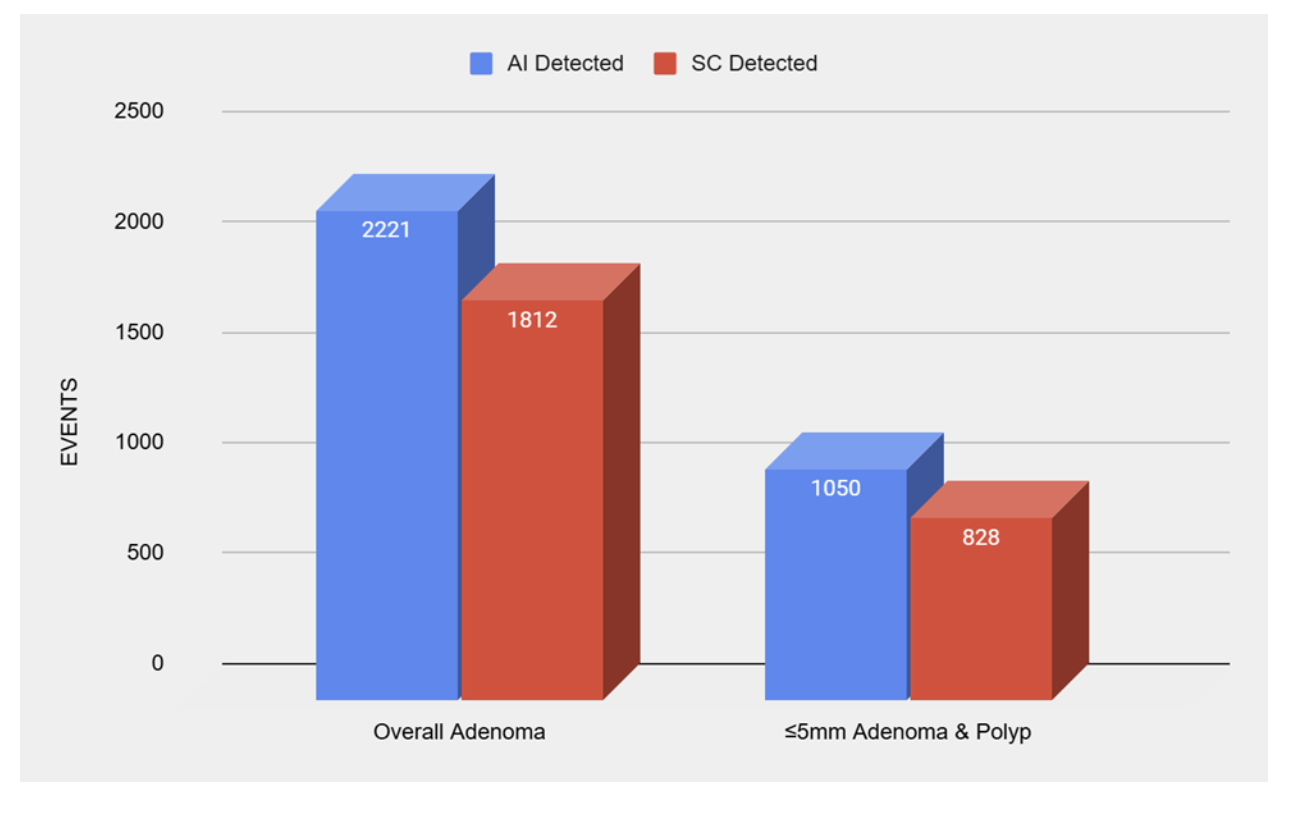
Figure: Figure 2: Column chart showing comparison in detection rate of adenoma and small adenoma and polyp (≤5mm) between AI (Artificial Intelligence) assisted and Standard Colonoscopy.
Disclosures:
Prince Shah-Riar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samia Sarker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumaiya Monjur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tathagato Das indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tasnim Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asif Zamir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Shah-Riar, MD1, Samia Sarker, MBBS2, Sumaiya Monjur, MBBS3, Tathagato Das, MBBS4, Tasnim Rahman, MBBS5, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG6. P4753 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Colonoscopy Increases Adenoma and Small Polyp Detection: A Meta-Analysis of 13 RCTs, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1DHR Health, Edinburg, Tx, McAllen, TX; 2Dhaka Medical College and Hospital, Houston, TX; 3Dhaka Medical College and Hospital, Spokane, WA; 4Jalalabad Ragib Rabeya Medical College, Sylhet, Bangladesh, Sylhet, Sylhet, Bangladesh; 5Wenzhou Medical University, Fort Collins, CO; 6DHR Health Gastroenterology, Edinburg, TX
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most commonly diagnosed malignancy and ranks third in cancer-related mortality in the United States. Early detection through colonoscopy is a cornerstone of CRC prevention. The adenoma detection rate (ADR) is a validated quality metric, with higher ADRs linked to decreased incidence of post-colonoscopy CRC. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising adjunct in endoscopy, capable of enhancing detection by reducing human error and highlighting subtle or overlooked lesions. While several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the utility of AI, a comprehensive meta-analytic comparison between AI-assisted and standard colonoscopy (SC), especially in detecting small adenomas (≤5 mm), remains lacking.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs published between 2019 and 2024. Databases searched included PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and PLOS One. Thirteen RCTs involving 11,521 patients were included (5,585 AI-assisted; 5,636 SC). Data were pooled using odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic. Subgroup analysis focused on the detection of diminutive lesions (≤5 mm).
Results: AI-assisted colonoscopy demonstrated a significantly higher overall ADR than SC (OR 1.43; 95% CI: 1.28–1.60; I² = 43%; P < 0.00001). In detecting small adenomas and polyps (≤5 mm), AI also showed superior performance (OR 1.56; 95% CI: 1.24–1.97; I² = 73%; P = 0.0002). These results reflect a robust and consistent benefit of AI integration across key outcome measures.
Discussion: AI-enhanced colonoscopy significantly improves the detection of adenomas, including diminutive lesions, compared to standard methods. These findings support the integration of AI into routine CRC screening protocols and justify continued research into AI-based diagnostic tools to advance precision endoscopy and reduce cancer burden.

Figure: Figure 1: Colonoscopy with AI assisted vs standard. 1a. Adenoma detection rate, 1b. adenoma and polyp with size ≤ 5 mm detection rate.

Figure: Figure 2: Column chart showing comparison in detection rate of adenoma and small adenoma and polyp (≤5mm) between AI (Artificial Intelligence) assisted and Standard Colonoscopy.
Disclosures:
Prince Shah-Riar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samia Sarker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumaiya Monjur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tathagato Das indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tasnim Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asif Zamir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Shah-Riar, MD1, Samia Sarker, MBBS2, Sumaiya Monjur, MBBS3, Tathagato Das, MBBS4, Tasnim Rahman, MBBS5, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG6. P4753 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Colonoscopy Increases Adenoma and Small Polyp Detection: A Meta-Analysis of 13 RCTs, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
