Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P6154 - Beyond Imaging: A Rare Case of Hepatic Aspergillosis Diagnosed via EUS-Guided Liver Biopsy
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohamad Besher Adi, MD (he/him/his)
Ascension St. John Hospital
St. Clair Shores, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamad Besher Adi, MD1, Muhammad Ismail, MD2, Obaidah Adi, MBBS3, Abdullah Shaik, MD4, Gieth Alahdab, MD5, Bola Nashed, MD4, Mohammed Barawi, MD6
1Ascension St. John Hospital, St. Clair Shores, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Warren, MI; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Amarillo, TX; 4Ascension St. John Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Auburn Hills, MI; 6Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Hepatic aspergillosis is an uncommon yet potentially fatal opportunistic infection, typically affecting immunocompromised individuals. Diagnosis is often delayed due to vague symptoms and non-specific imaging. Endohepatology / Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with guided biopsy is an emerging tool for evaluating pathologies, particularly when conventional modalities are inconclusive. This case highlights the successful use of EUS-guided liver biopsy in diagnosing hepatic Aspergillus versicolor infection in a patient with ulcerative colitis and recent corticosteroid exposure.
Case Description/
Methods: A 57-year-old woman with a history of ulcerative colitis, recently tapered off corticosteroids, presented with fatigue, low-grade fever, anorexia, and diarrhea. Laboratory evaluation revealed leukocytosis, anemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase (391 U/L), AST (41 U/L), and CRP (256 mg/L). Stool studies were negative. Abdominal CT and MRCP demonstrated mild hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis but no discrete hepatic lesions. Due to persistent symptoms and liver test abnormalities, EUS was pursued for further evaluation.
EUS revealed subtle parenchymal changes in the liver, and fine-needle biopsy was performed. Histopathology showed caseating granulomas, and PCR testing confirmed Aspergillus versicolor. The patient was initiated on voriconazole therapy, resulting in marked clinical improvement.
Discussion: EUS is primarily used for pancreaticobiliary and rectal pathology, but its application in hepatic diagnostics is expanding. Compared to percutaneous or transjugular liver biopsy, EUS offers enhanced imaging resolution, real-time visualization, and precise sampling, even in the absence of focal lesions. This approach is especially valuable when other modalities are limited by anatomical or coagulation constraints. Hepatic aspergillosis is often diagnosed post-mortem due to its rarity and non-specific presentation. This case exemplifies the real-time diagnostic potential of EUS-guided biopsy in identifying a rare fungal infection ante-mortem.
EUS-guided liver biopsy can be a pivotal diagnostic tool for hepatic aspergillosis, particularly in immunocompromised patients with persistent liver abnormalities and inconclusive imaging. Its early application may facilitate timely antifungal therapy and improve clinical outcomes in rare but serious infections such as Aspergillus versicolor.
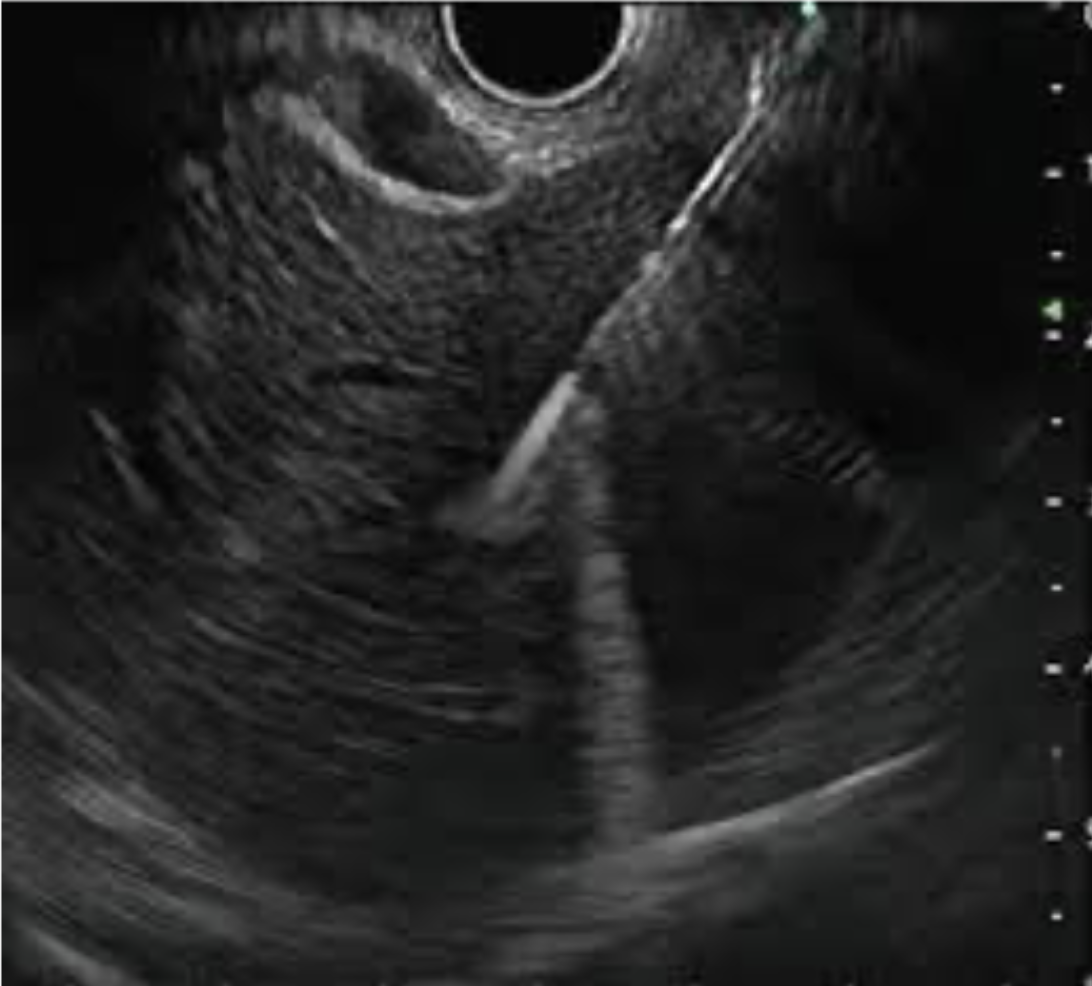
Figure: Figure 1, EUS with biopsy of the liver
Disclosures:
Mohamad Besher Adi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Obaidah Adi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Shaik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gieth Alahdab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bola Nashed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Barawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Besher Adi, MD1, Muhammad Ismail, MD2, Obaidah Adi, MBBS3, Abdullah Shaik, MD4, Gieth Alahdab, MD5, Bola Nashed, MD4, Mohammed Barawi, MD6. P6154 - Beyond Imaging: A Rare Case of Hepatic Aspergillosis Diagnosed via EUS-Guided Liver Biopsy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Ascension St. John Hospital, St. Clair Shores, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Warren, MI; 3Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Amarillo, TX; 4Ascension St. John Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Auburn Hills, MI; 6Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Hepatic aspergillosis is an uncommon yet potentially fatal opportunistic infection, typically affecting immunocompromised individuals. Diagnosis is often delayed due to vague symptoms and non-specific imaging. Endohepatology / Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with guided biopsy is an emerging tool for evaluating pathologies, particularly when conventional modalities are inconclusive. This case highlights the successful use of EUS-guided liver biopsy in diagnosing hepatic Aspergillus versicolor infection in a patient with ulcerative colitis and recent corticosteroid exposure.
Case Description/
Methods: A 57-year-old woman with a history of ulcerative colitis, recently tapered off corticosteroids, presented with fatigue, low-grade fever, anorexia, and diarrhea. Laboratory evaluation revealed leukocytosis, anemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase (391 U/L), AST (41 U/L), and CRP (256 mg/L). Stool studies were negative. Abdominal CT and MRCP demonstrated mild hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis but no discrete hepatic lesions. Due to persistent symptoms and liver test abnormalities, EUS was pursued for further evaluation.
EUS revealed subtle parenchymal changes in the liver, and fine-needle biopsy was performed. Histopathology showed caseating granulomas, and PCR testing confirmed Aspergillus versicolor. The patient was initiated on voriconazole therapy, resulting in marked clinical improvement.
Discussion: EUS is primarily used for pancreaticobiliary and rectal pathology, but its application in hepatic diagnostics is expanding. Compared to percutaneous or transjugular liver biopsy, EUS offers enhanced imaging resolution, real-time visualization, and precise sampling, even in the absence of focal lesions. This approach is especially valuable when other modalities are limited by anatomical or coagulation constraints. Hepatic aspergillosis is often diagnosed post-mortem due to its rarity and non-specific presentation. This case exemplifies the real-time diagnostic potential of EUS-guided biopsy in identifying a rare fungal infection ante-mortem.
EUS-guided liver biopsy can be a pivotal diagnostic tool for hepatic aspergillosis, particularly in immunocompromised patients with persistent liver abnormalities and inconclusive imaging. Its early application may facilitate timely antifungal therapy and improve clinical outcomes in rare but serious infections such as Aspergillus versicolor.

Figure: Figure 1, EUS with biopsy of the liver
Disclosures:
Mohamad Besher Adi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Obaidah Adi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Shaik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gieth Alahdab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bola Nashed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Barawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Besher Adi, MD1, Muhammad Ismail, MD2, Obaidah Adi, MBBS3, Abdullah Shaik, MD4, Gieth Alahdab, MD5, Bola Nashed, MD4, Mohammed Barawi, MD6. P6154 - Beyond Imaging: A Rare Case of Hepatic Aspergillosis Diagnosed via EUS-Guided Liver Biopsy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
