Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2175 - Sex-Related Disparities Observed in Acute Pancreatitis-Associated ARF/ARDS Mortality: A CDC WONDER Analysis (2018-2023)
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Rohan Raj, MBBS (he/him/his)
Memorial Hospital at Gulfport
Gulfport, MS
Presenting Author(s)
Rohan Raj, MBBS1, Naga Vamsi Krishna Machineni, MD2, Pavana Appala, MBBS3, Megha Joshi, MBBS4, Sonali Dash, BS5, Tarika Walia, MBBS6, Tejeswara Rao Pydi, MBBS7, Siri Gottipati, 8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9
1Memorial Hospital at Gulfport, Gulfport, MS; 2Appalachian Regional Healthcare, Harlan, KY; 3Kasturba Medical College, Cumming, GA; 4Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, NY; 5Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD; 6Raikhi Hospital Patiala, Patiala, Punjab, India; 7Osmania medical college, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 8Glenelg High School, Glenelg, MD; 9Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis complicated by acute respiratory failure (ARF) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is associated with high mortality. However, recent population-level trends and sex-related disparities in mortality from this condition remain poorly characterized, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) for acute pancreatitis-associated ARF/ARDS in the United States using CDC WONDER data from 2018 to 2023. Trends were evaluated for the total population and stratified by sex. Both linear and segmented regression models were applied to assess annual percent change (APC) and to identify inflection points in mortality trends.
Results: Six years of data comprising 6,881 deaths related to ARF/ARDS in the setting of acute pancreatitis were analyzed. For the overall population, the AAMR was 0.47 per 100,000, with a significant upward trend (APC +5.7%, p=0.042). Mortality rates remained stable at 0.4 per 100,000 during 2018–2019, then increased to 0.5 per 100,000 from 2020–2023, with a clear inflection point identified in 2020. Males exhibited higher mortality (AAMR 0.60 per 100,000) than females (AAMR 0.37 per 100,000), representing a 62% disparity. Males showed a more variable trajectory, with a peak in 2020–2021 (0.7 per 100,000) and a subsequent decline, while females demonstrated a consistent stepwise increase from 0.3 to 0.4 per 100,000 (APC +7.6%, p=0.042). Segmented regression confirmed 2020 as a significant breakpoint across all groups.
Discussion: Males exhibit 62% higher mortality rates than females (0.60 vs. 0.37 per 100,000). Mortality from acute pancreatitis-associated ARF/ARDS increased abruptly in 2020 and remained elevated, with pronounced sex-based disparities—particularly a greater relative increase among females. These findings highlight 2020 as a critical transition year, likely reflecting pandemic-related healthcare disruptions, and underscore the need for targeted interventions and continued surveillance of at-risk populations.
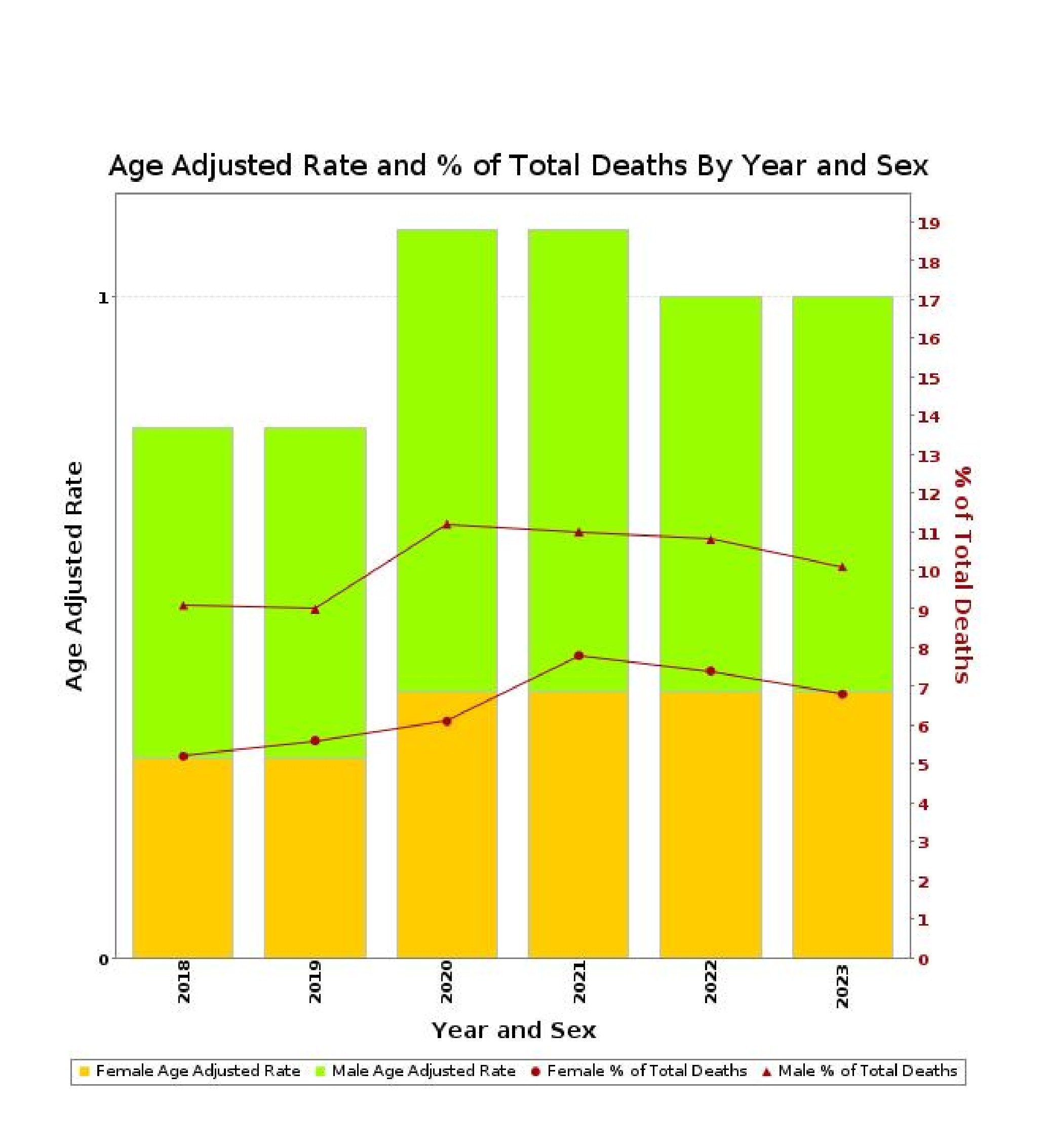
Figure: Figure 1. Age-adjusted mortality rates and percentage of total deaths by sex from 2018 to 2023. Yellow and green bars represent female and male age-adjusted mortality rates, respectively. Red dots and triangles denote the percentage of total deaths for females and males.
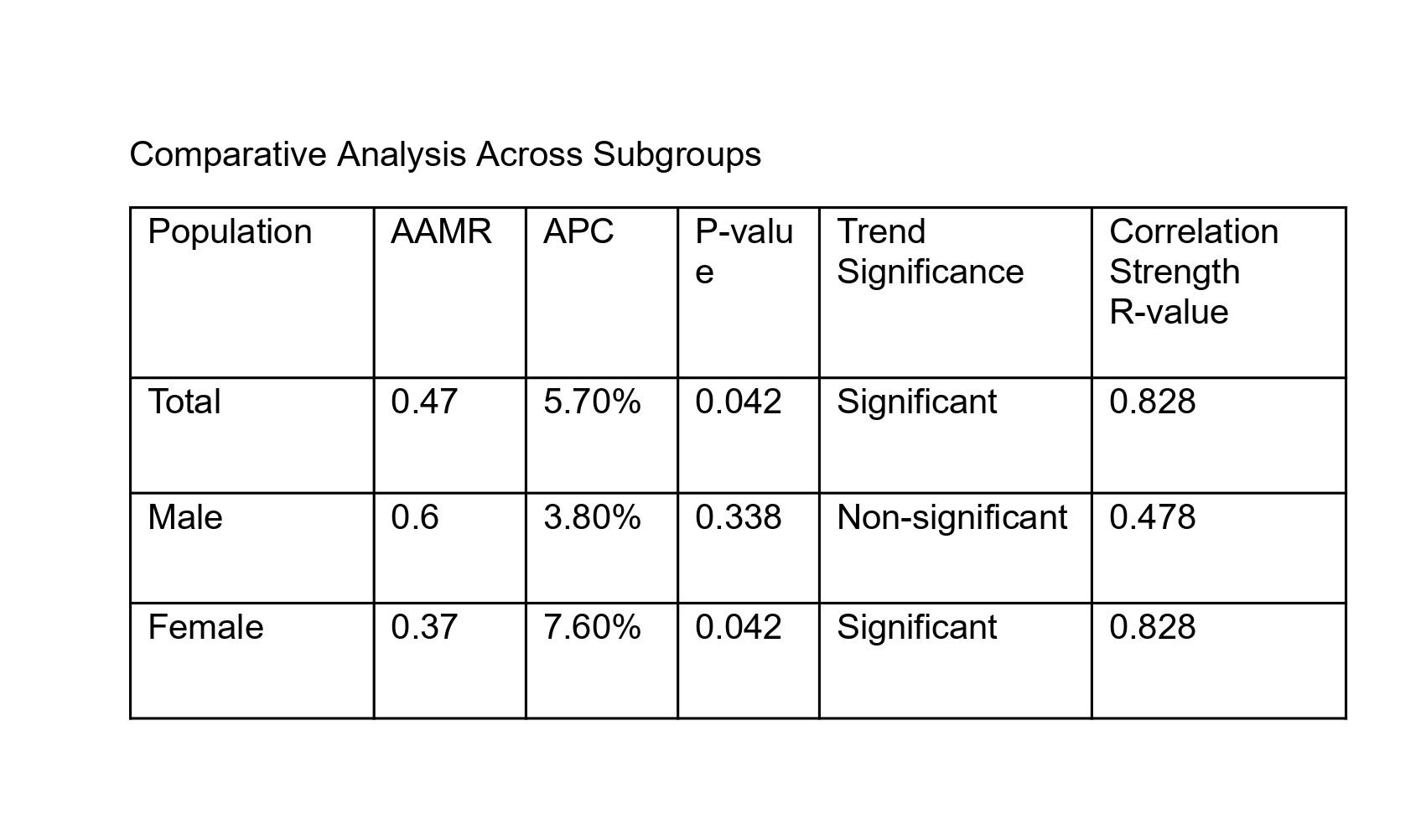
Figure: Figure 2. Comparative trend analysis across subgroups showing age-adjusted mortality rate (AAMR), annual percent change (APC), statistical significance (P-value), trend significance, and correlation strength (R-value) for the total population and by sex.
Disclosures:
Rohan Raj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naga Vamsi Krishna Machineni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pavana Appala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Megha Joshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sonali Dash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarika Walia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tejeswara Rao Pydi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Siri Gottipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Raj, MBBS1, Naga Vamsi Krishna Machineni, MD2, Pavana Appala, MBBS3, Megha Joshi, MBBS4, Sonali Dash, BS5, Tarika Walia, MBBS6, Tejeswara Rao Pydi, MBBS7, Siri Gottipati, 8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9. P2175 - Sex-Related Disparities Observed in Acute Pancreatitis-Associated ARF/ARDS Mortality: A CDC WONDER Analysis (2018-2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Memorial Hospital at Gulfport, Gulfport, MS; 2Appalachian Regional Healthcare, Harlan, KY; 3Kasturba Medical College, Cumming, GA; 4Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, NY; 5Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD; 6Raikhi Hospital Patiala, Patiala, Punjab, India; 7Osmania medical college, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 8Glenelg High School, Glenelg, MD; 9Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis complicated by acute respiratory failure (ARF) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is associated with high mortality. However, recent population-level trends and sex-related disparities in mortality from this condition remain poorly characterized, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) for acute pancreatitis-associated ARF/ARDS in the United States using CDC WONDER data from 2018 to 2023. Trends were evaluated for the total population and stratified by sex. Both linear and segmented regression models were applied to assess annual percent change (APC) and to identify inflection points in mortality trends.
Results: Six years of data comprising 6,881 deaths related to ARF/ARDS in the setting of acute pancreatitis were analyzed. For the overall population, the AAMR was 0.47 per 100,000, with a significant upward trend (APC +5.7%, p=0.042). Mortality rates remained stable at 0.4 per 100,000 during 2018–2019, then increased to 0.5 per 100,000 from 2020–2023, with a clear inflection point identified in 2020. Males exhibited higher mortality (AAMR 0.60 per 100,000) than females (AAMR 0.37 per 100,000), representing a 62% disparity. Males showed a more variable trajectory, with a peak in 2020–2021 (0.7 per 100,000) and a subsequent decline, while females demonstrated a consistent stepwise increase from 0.3 to 0.4 per 100,000 (APC +7.6%, p=0.042). Segmented regression confirmed 2020 as a significant breakpoint across all groups.
Discussion: Males exhibit 62% higher mortality rates than females (0.60 vs. 0.37 per 100,000). Mortality from acute pancreatitis-associated ARF/ARDS increased abruptly in 2020 and remained elevated, with pronounced sex-based disparities—particularly a greater relative increase among females. These findings highlight 2020 as a critical transition year, likely reflecting pandemic-related healthcare disruptions, and underscore the need for targeted interventions and continued surveillance of at-risk populations.

Figure: Figure 1. Age-adjusted mortality rates and percentage of total deaths by sex from 2018 to 2023. Yellow and green bars represent female and male age-adjusted mortality rates, respectively. Red dots and triangles denote the percentage of total deaths for females and males.

Figure: Figure 2. Comparative trend analysis across subgroups showing age-adjusted mortality rate (AAMR), annual percent change (APC), statistical significance (P-value), trend significance, and correlation strength (R-value) for the total population and by sex.
Disclosures:
Rohan Raj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naga Vamsi Krishna Machineni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pavana Appala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Megha Joshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sonali Dash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tarika Walia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tejeswara Rao Pydi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Siri Gottipati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Raj, MBBS1, Naga Vamsi Krishna Machineni, MD2, Pavana Appala, MBBS3, Megha Joshi, MBBS4, Sonali Dash, BS5, Tarika Walia, MBBS6, Tejeswara Rao Pydi, MBBS7, Siri Gottipati, 8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9. P2175 - Sex-Related Disparities Observed in Acute Pancreatitis-Associated ARF/ARDS Mortality: A CDC WONDER Analysis (2018-2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
