Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2830 - When Swallowing Becomes a Clue: Dysphagia Unveils an Ectopic Parathyroid Adenoma
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD (she/her/hers)
UAB Montgomery
Montgomery, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD, Yousif Elmofti, MD, FACG
UAB Montgomery, Montgomery, AL
Introduction: Dysphagia is an uncommon but potentially important symptom in individuals with ectopic parathyroid adenomas (EPA). Parathyroid adenomas which are usually found near the thyroid can arise in atypical locations outside the neck—such as the mediastinum, or in rare cases, the soft palate or within the vagus nerve—they are referred to as EPA.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient is a 81 year old female who presented with stroke like symptoms, work up was done in which CT angio neck showed incidental finding of heterogeneous enhancing soft tissue mass measuring 2.6 x 2.0 cm identified posterior to the trachea (figure 1). She was evaluated by ENT and Cardiothoracic surgery who recommend outpatient evaluation. 5 months later, the patient presented with dysphagia to solid foods and intermittently tolerating liquid diet. Labs showed calcium 12.1 mg/dl, albumin 2.9 g/dl, vitamin D 25 OH 64 ng/ml, parathyroid hormone 141.45 pg/ml. CT chest with contrast was done which showed enlargement of the retro tracheal mass measuring 3.0 x 2.3 cm causing compression on esophagus. Thyroid Ultrasound is negative. NM parathyroid scan showed persistent activity within the right superior chest mass corresponding to hyper enhancing mass within the tracheoesophageal groove which is parathyroid adenoma (figure 2). ENT and Cardiothoracic surgery evaluated the patient and recommended transfer to higher level of care as she will be at high risk for surgery with multiple comorbidities. She was started on cinacalcet for primary hyperparathyroidism after which her calcium levels improved.
Discussion: Parathyroid glands arise from the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches and migrate to the thyroid's posterior surface. Disruptions in this process can cause ectopic parathyroid tissue along the migration path or in adjacent areas. EPAs lead to the development of primary hyperparathyroidism and hypercalcemia. They can cause dysphagia through mechanical compression or neuromuscular dysfunction related to hypercalcemia. Timely identification of this uncommon presentation is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. The sestamibi scan can be used for identifying abnormal parathyroid glands. Recognizing EPAs can help surgeons prevent unsuccessful neck explorations and better plan for a minimally invasive surgical resection.
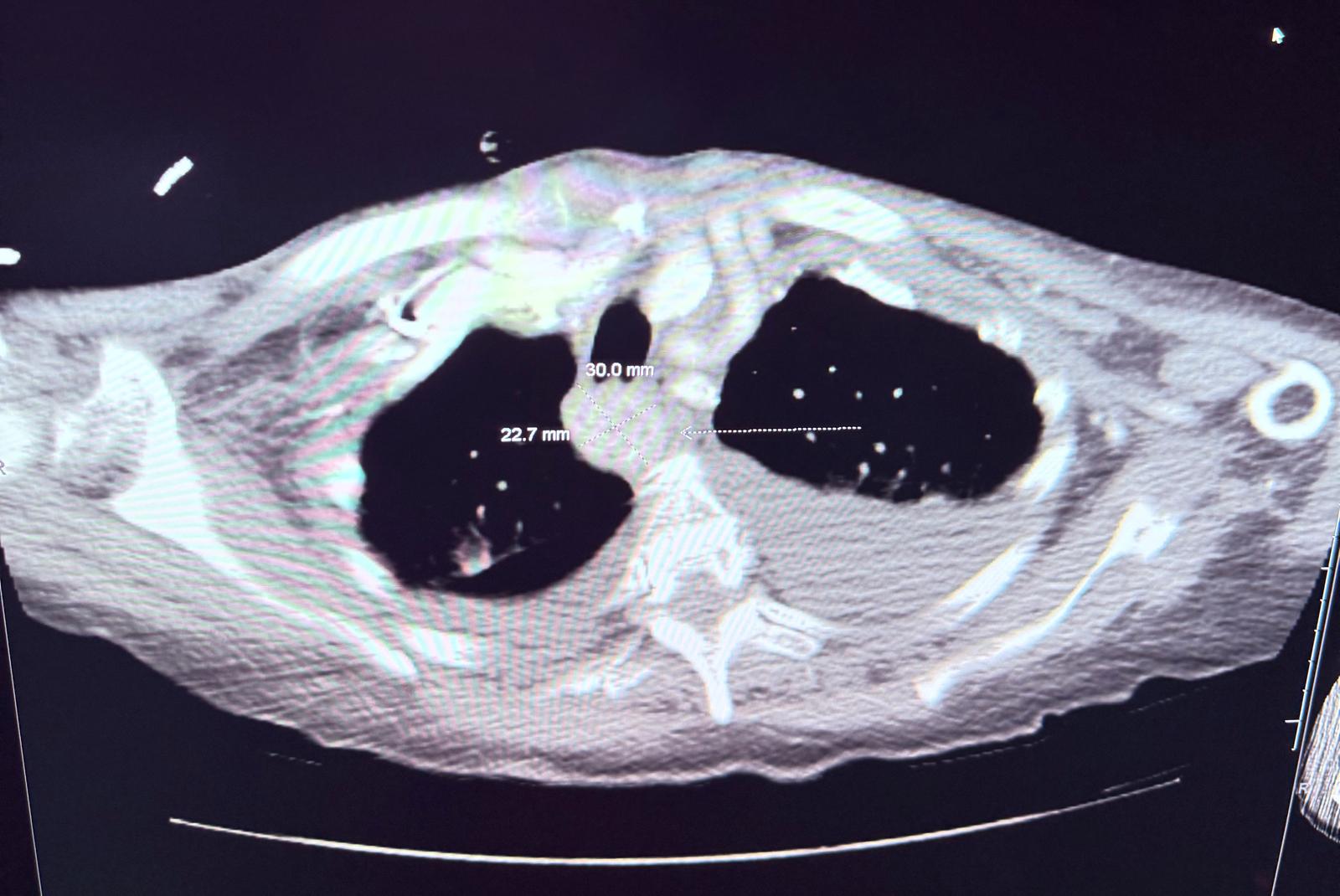
Figure: Figure 1
Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yousif Elmofti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD, Yousif Elmofti, MD, FACG. P2830 - When Swallowing Becomes a Clue: Dysphagia Unveils an Ectopic Parathyroid Adenoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
UAB Montgomery, Montgomery, AL
Introduction: Dysphagia is an uncommon but potentially important symptom in individuals with ectopic parathyroid adenomas (EPA). Parathyroid adenomas which are usually found near the thyroid can arise in atypical locations outside the neck—such as the mediastinum, or in rare cases, the soft palate or within the vagus nerve—they are referred to as EPA.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient is a 81 year old female who presented with stroke like symptoms, work up was done in which CT angio neck showed incidental finding of heterogeneous enhancing soft tissue mass measuring 2.6 x 2.0 cm identified posterior to the trachea (figure 1). She was evaluated by ENT and Cardiothoracic surgery who recommend outpatient evaluation. 5 months later, the patient presented with dysphagia to solid foods and intermittently tolerating liquid diet. Labs showed calcium 12.1 mg/dl, albumin 2.9 g/dl, vitamin D 25 OH 64 ng/ml, parathyroid hormone 141.45 pg/ml. CT chest with contrast was done which showed enlargement of the retro tracheal mass measuring 3.0 x 2.3 cm causing compression on esophagus. Thyroid Ultrasound is negative. NM parathyroid scan showed persistent activity within the right superior chest mass corresponding to hyper enhancing mass within the tracheoesophageal groove which is parathyroid adenoma (figure 2). ENT and Cardiothoracic surgery evaluated the patient and recommended transfer to higher level of care as she will be at high risk for surgery with multiple comorbidities. She was started on cinacalcet for primary hyperparathyroidism after which her calcium levels improved.
Discussion: Parathyroid glands arise from the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches and migrate to the thyroid's posterior surface. Disruptions in this process can cause ectopic parathyroid tissue along the migration path or in adjacent areas. EPAs lead to the development of primary hyperparathyroidism and hypercalcemia. They can cause dysphagia through mechanical compression or neuromuscular dysfunction related to hypercalcemia. Timely identification of this uncommon presentation is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. The sestamibi scan can be used for identifying abnormal parathyroid glands. Recognizing EPAs can help surgeons prevent unsuccessful neck explorations and better plan for a minimally invasive surgical resection.

Figure: Figure 1

Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yousif Elmofti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD, Yousif Elmofti, MD, FACG. P2830 - When Swallowing Becomes a Clue: Dysphagia Unveils an Ectopic Parathyroid Adenoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
