Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3517 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Samreen Jawaid, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Samreen Jawaid, MD1, Ambar Godoy, MD2, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Daniela M. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD4, Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD5, Leandro Sierra, MD6, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 7, Renato Beas, MD8, Dalton A. Norwood, MD9, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD10
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 3Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 4Universidad Autónoma de Honduras, Tegucigalpa, Francisco Morazan, Honduras; 5Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Lima, Peru; 6Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 7Ruth Lilly Medical Library, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 8Washington University in St Louis, St. Louis, MO; 9University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL; 10Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Prolonged exposure to obesogenic diets leads to functional alterations in the duodenal mucosa causing intestinal malabsorption, insulin resistance and subsequent type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Duodenal mucosal resection (DMR) is a novel, minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that thermally ablates duodenal mucosa, thereby limiting nutrient-mucosa signaling and exerting metabolic benefits. This meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of DMR on glycemic and hepatic parameters in patients with T2DM.
Methods: We used the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Clinicaltrials.gov databases to identify studies, from inception to present. We included original studies that evaluated REVITA DMR procedure (Fractyl Laboratories, Lexington, MA, United States) amongst patients from age 28-75 years, withBMI > 25, HbA1c > 7.5, and on at least one oral antidiabetic agent. The primary outcomes were changes in metabolic parameters; HbA1c, weight, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), measured at 3-, 6-, and 12-months post-procedure.
Results: Among 130 titles identified, 23 were full text reviewed, and 5 studies fulfilling the criteria were screened for final analysis. All 5 studies reported changes in HbA1C, whereas 3 reported weight changes and HOMA-IR. Baseline characteristics of included studies are shown in Table 1. DMR significantly reduced HbA1c at 6 months (−1.21% [95% CI: −1.58 to −0.84]) and 12 months (−0.74% [−0.96 to −0.52]). HOMA-IR also decreased significantly at 6 months (−1.55 [−2.36 to −0.73]), with sustained reductions at 12 months. Weight change was not statistically significant, with a pooled mean difference of −1.60 kg [−4.63 to 1.43] at 6 months and −1.86 kg [−4.99 to 1.28] at 12 months. These findings suggest DMR improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity through 12 months, with minimal effect on weight. (Figure 1)
Discussion: Current data suggests that DMR emerges as an effective procedure and a promising intervention for glycemic control in T2DM with suboptimal medical therapy. Metabolic effects with drops in HbA1c and weight were seen as early as 3 months with effects sustained up to 12 months. A significant drop of at least 1% in A1c was seen at 6 months. Further mechanistic studies are warranted to assess the long-term safety, metabolic durability, and potential application to DMR.
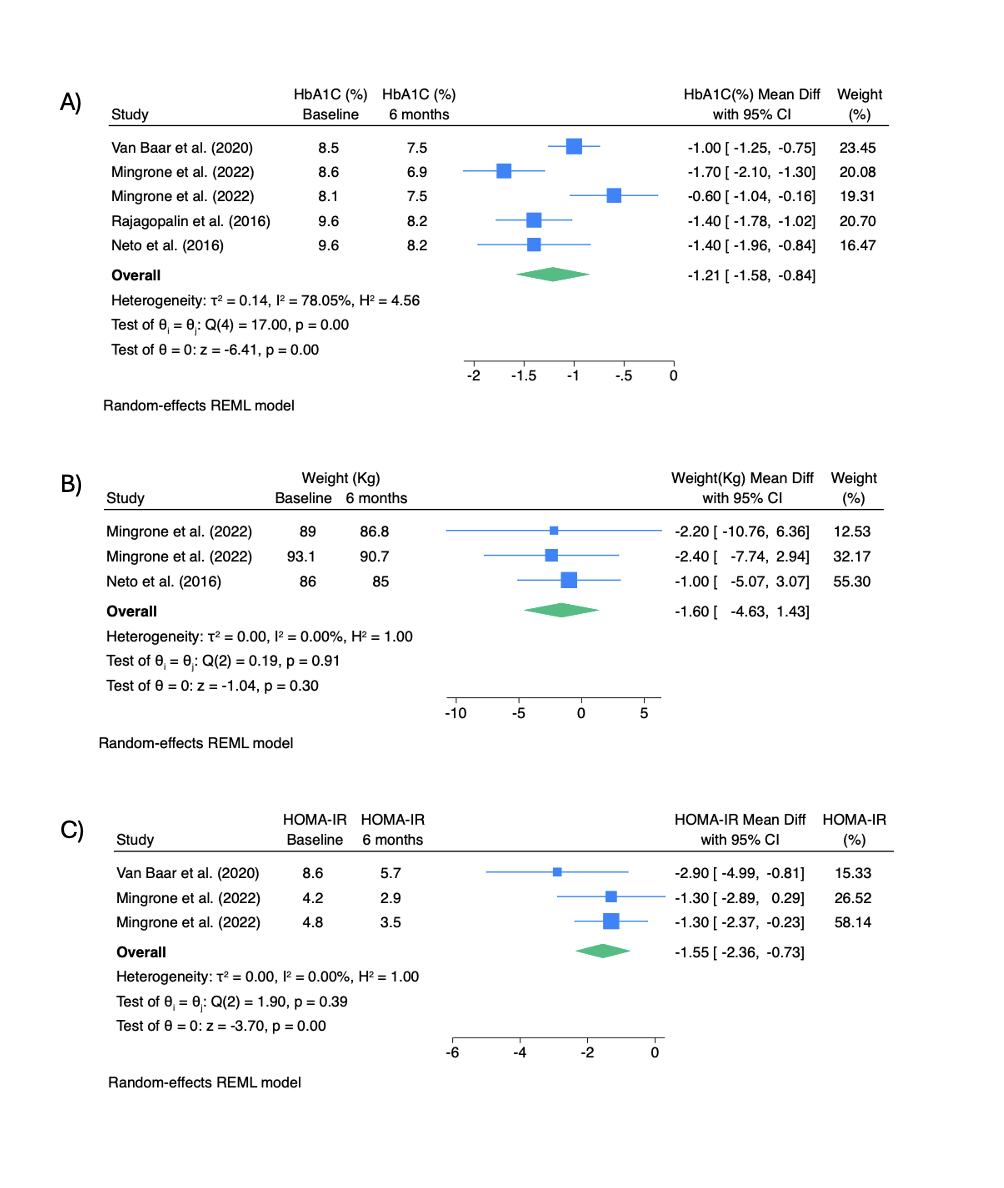
Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics of included studies.
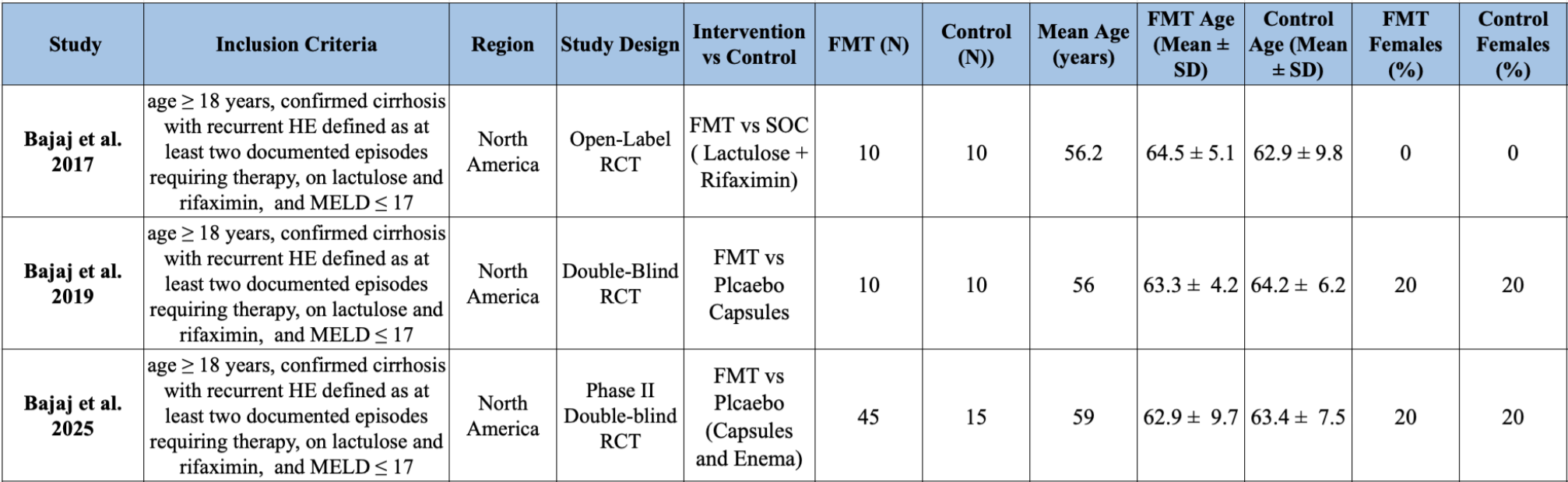
Figure: Figure 1: Forest plots demonstrating the effects of duodenal mucosal resurfacing at 6 months on (A) HbA1c (%), (B) body weight (kg), and (C) HOMA-IR, based on random-effects REML models.
Disclosures:
Samreen Jawaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ambar Godoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniela M. Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leandro Sierra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mirian Ramirez-Rojas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Renato Beas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalton Norwood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eleazar Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Jawaid, MD1, Ambar Godoy, MD2, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Daniela M. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD4, Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD5, Leandro Sierra, MD6, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 7, Renato Beas, MD8, Dalton A. Norwood, MD9, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD10. P3517 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 3Cook County Health and Hospital Systems, Chicago, IL; 4Universidad Autónoma de Honduras, Tegucigalpa, Francisco Morazan, Honduras; 5Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), Lima, Lima, Peru; 6Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 7Ruth Lilly Medical Library, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 8Washington University in St Louis, St. Louis, MO; 9University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL; 10Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Introduction: Prolonged exposure to obesogenic diets leads to functional alterations in the duodenal mucosa causing intestinal malabsorption, insulin resistance and subsequent type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Duodenal mucosal resection (DMR) is a novel, minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that thermally ablates duodenal mucosa, thereby limiting nutrient-mucosa signaling and exerting metabolic benefits. This meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of DMR on glycemic and hepatic parameters in patients with T2DM.
Methods: We used the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Clinicaltrials.gov databases to identify studies, from inception to present. We included original studies that evaluated REVITA DMR procedure (Fractyl Laboratories, Lexington, MA, United States) amongst patients from age 28-75 years, withBMI > 25, HbA1c > 7.5, and on at least one oral antidiabetic agent. The primary outcomes were changes in metabolic parameters; HbA1c, weight, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), measured at 3-, 6-, and 12-months post-procedure.
Results: Among 130 titles identified, 23 were full text reviewed, and 5 studies fulfilling the criteria were screened for final analysis. All 5 studies reported changes in HbA1C, whereas 3 reported weight changes and HOMA-IR. Baseline characteristics of included studies are shown in Table 1. DMR significantly reduced HbA1c at 6 months (−1.21% [95% CI: −1.58 to −0.84]) and 12 months (−0.74% [−0.96 to −0.52]). HOMA-IR also decreased significantly at 6 months (−1.55 [−2.36 to −0.73]), with sustained reductions at 12 months. Weight change was not statistically significant, with a pooled mean difference of −1.60 kg [−4.63 to 1.43] at 6 months and −1.86 kg [−4.99 to 1.28] at 12 months. These findings suggest DMR improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity through 12 months, with minimal effect on weight. (Figure 1)
Discussion: Current data suggests that DMR emerges as an effective procedure and a promising intervention for glycemic control in T2DM with suboptimal medical therapy. Metabolic effects with drops in HbA1c and weight were seen as early as 3 months with effects sustained up to 12 months. A significant drop of at least 1% in A1c was seen at 6 months. Further mechanistic studies are warranted to assess the long-term safety, metabolic durability, and potential application to DMR.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics of included studies.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plots demonstrating the effects of duodenal mucosal resurfacing at 6 months on (A) HbA1c (%), (B) body weight (kg), and (C) HOMA-IR, based on random-effects REML models.
Disclosures:
Samreen Jawaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ambar Godoy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Guifarro Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniela M. Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leandro Sierra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mirian Ramirez-Rojas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Renato Beas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalton Norwood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eleazar Montalvan-Sanchez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samreen Jawaid, MD1, Ambar Godoy, MD2, Daniel Guifarro Rivera, MD3, Daniela M. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD4, Fortunato S. Principe-Meneses, MD5, Leandro Sierra, MD6, Mirian Ramirez-Rojas, 7, Renato Beas, MD8, Dalton A. Norwood, MD9, Eleazar E.. Montalvan-Sanchez, MD10. P3517 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

