Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Practice Management
P6193 - Development and Validation of an Electronic Health Record Machine Learning Model for Cumulative Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk Prediction
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Suraj K. Jaladanki, MD (he/him/his)
Mount Sinai Morningside, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Alyssa Y. Chen, MD, MPH1, Suraj K. Jaladanki, MD2, Pushkala Jayaraman, MS, PhD3, Ji Yoon Yoon, MD1, Chin Hur, MD, MPH4, Nicholas Tatonetti, MD5, Girish Nadkarni, MD1, Julian A. Abrams, MD, MS4, Ali Soroush, MD, MS1
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Mount Sinai Morningside, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, NY; 4Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cancers are predominantly diagnosed at advanced stages and disproportionately impact minority and immigrant populations. Existing cancer-specific prevention strategies underestimate the potential benefits of a unified endoscopic screening for all UGI cancers. We evaluated the viability of a novel UGI cancer risk assessment model using routinely collected electronic health record (EHR) variables.
Methods: We conducted a large-scale retrospective cohort study of adults 40-85 years old with at least one outpatient or inpatient encounter in the Mount Sinai Health System (MSHS) between 2011 and 2022. Patients with a cancer registry confirmed UGI cancer diagnosis within 1 year of their initial encounter or without histological confirmation were excluded. Routinely collected demographic, social, clinical and laboratory data were extracted from structured EHR fields. Time-dependent variables were extracted from the first encounter. Cox proportional hazards (CoxPH), logistic regression, and XGBoost models were developed for 3-, 5-, and 10-year risk horizons using an 80/20 train-validation split stratified by cancer diagnosis. In each model, features were selected based on univariate analysis, with significance defined as a p-value < 0.05. The best model was selected based on AUROC on the validation set. Performance metrics were calculated from the optimal risk percentile defined by the Youden index.
Results: Our final cohort consisted of 1,745,288 patients, of which 313 developed UGI cancer after a median follow-up time of 10 years. Cohort demographics are shown in Table 1. The best performing model was a CoxPH model and achieved an AUROC of 0.929 for a 5 year horizon (Table 2). The strongest predictors were PPI use, peptic ulcer disease, head and neck cancer, and male sex. At the optimal 92nd risk percentile, the model achieved a sensitivity of 81.8%, specificity of 92.4%, and number needed to screen of 754 patients.
Discussion: We internally validated a UGI cancer risk model that uses 15 readily available predictors from the initial patient encounter. The model demonstrated acceptable discrimination performance and has potential to inform unified screening strategies. Further work is needed to externally validate the model.
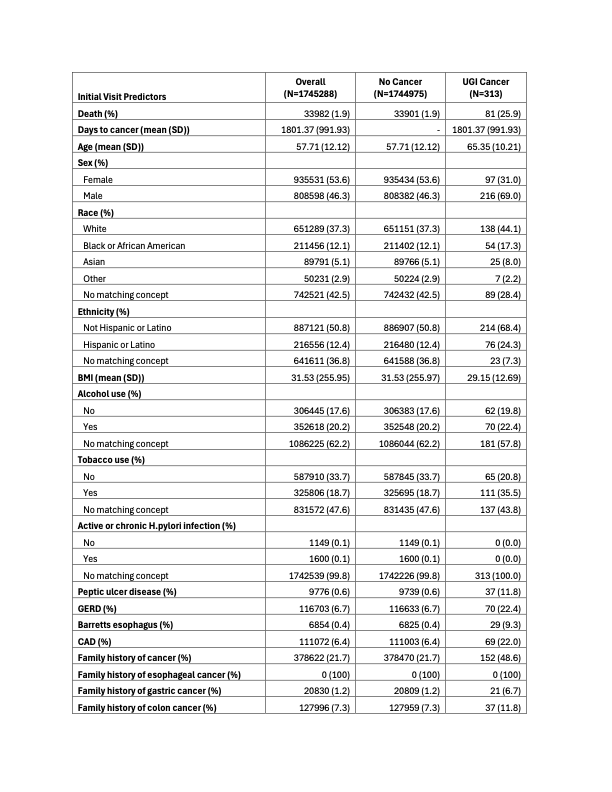
Figure: Table 1. Demographics Table
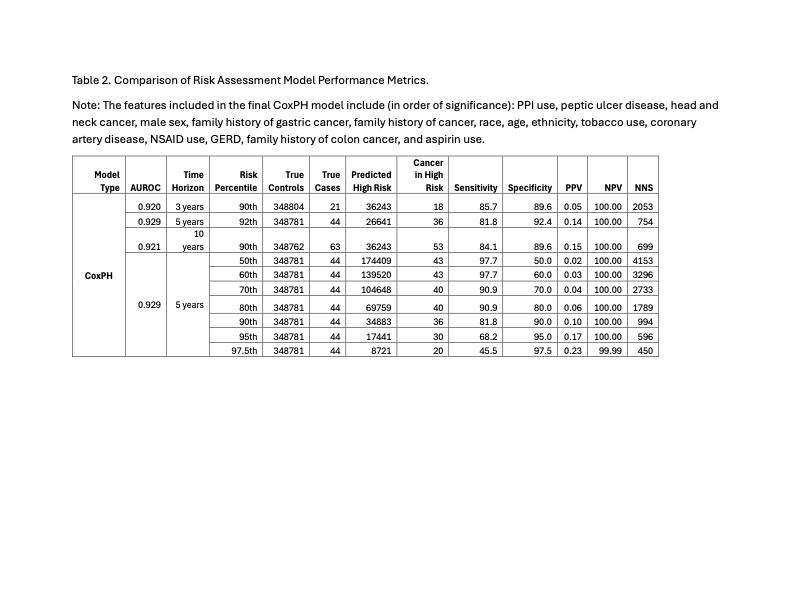
Figure: Table 2. Comparison of Risk Assessment Model Performance Metrics.
Note: The features included in the final CoxPH model include (in order of significance): PPI use, peptic ulcer disease, head and neck cancer, male sex, family history of gastric cancer, family history of cancer, race, age, ethnicity, tobacco use, coronary artery disease, NSAID use, GERD, family history of colon cancer, and aspirin use.
Disclosures:
Alyssa Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suraj Jaladanki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pushkala Jayaraman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ji Yoon Yoon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chin Hur: Cylinder Health – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Guardant Health – Consultant. Value Health Analytics – Consultant.
Nicholas Tatonetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Girish Nadkarni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julian Abrams: Cyted Health – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Consultant. Pentax Medical – Grant/Research Support.
Ali Soroush indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alyssa Y. Chen, MD, MPH1, Suraj K. Jaladanki, MD2, Pushkala Jayaraman, MS, PhD3, Ji Yoon Yoon, MD1, Chin Hur, MD, MPH4, Nicholas Tatonetti, MD5, Girish Nadkarni, MD1, Julian A. Abrams, MD, MS4, Ali Soroush, MD, MS1. P6193 - Development and Validation of an Electronic Health Record Machine Learning Model for Cumulative Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk Prediction, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Mount Sinai Morningside, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, NY; 4Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cancers are predominantly diagnosed at advanced stages and disproportionately impact minority and immigrant populations. Existing cancer-specific prevention strategies underestimate the potential benefits of a unified endoscopic screening for all UGI cancers. We evaluated the viability of a novel UGI cancer risk assessment model using routinely collected electronic health record (EHR) variables.
Methods: We conducted a large-scale retrospective cohort study of adults 40-85 years old with at least one outpatient or inpatient encounter in the Mount Sinai Health System (MSHS) between 2011 and 2022. Patients with a cancer registry confirmed UGI cancer diagnosis within 1 year of their initial encounter or without histological confirmation were excluded. Routinely collected demographic, social, clinical and laboratory data were extracted from structured EHR fields. Time-dependent variables were extracted from the first encounter. Cox proportional hazards (CoxPH), logistic regression, and XGBoost models were developed for 3-, 5-, and 10-year risk horizons using an 80/20 train-validation split stratified by cancer diagnosis. In each model, features were selected based on univariate analysis, with significance defined as a p-value < 0.05. The best model was selected based on AUROC on the validation set. Performance metrics were calculated from the optimal risk percentile defined by the Youden index.
Results: Our final cohort consisted of 1,745,288 patients, of which 313 developed UGI cancer after a median follow-up time of 10 years. Cohort demographics are shown in Table 1. The best performing model was a CoxPH model and achieved an AUROC of 0.929 for a 5 year horizon (Table 2). The strongest predictors were PPI use, peptic ulcer disease, head and neck cancer, and male sex. At the optimal 92nd risk percentile, the model achieved a sensitivity of 81.8%, specificity of 92.4%, and number needed to screen of 754 patients.
Discussion: We internally validated a UGI cancer risk model that uses 15 readily available predictors from the initial patient encounter. The model demonstrated acceptable discrimination performance and has potential to inform unified screening strategies. Further work is needed to externally validate the model.

Figure: Table 1. Demographics Table

Figure: Table 2. Comparison of Risk Assessment Model Performance Metrics.
Note: The features included in the final CoxPH model include (in order of significance): PPI use, peptic ulcer disease, head and neck cancer, male sex, family history of gastric cancer, family history of cancer, race, age, ethnicity, tobacco use, coronary artery disease, NSAID use, GERD, family history of colon cancer, and aspirin use.
Disclosures:
Alyssa Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suraj Jaladanki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pushkala Jayaraman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ji Yoon Yoon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chin Hur: Cylinder Health – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Guardant Health – Consultant. Value Health Analytics – Consultant.
Nicholas Tatonetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Girish Nadkarni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Julian Abrams: Cyted Health – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Consultant. Pentax Medical – Grant/Research Support.
Ali Soroush indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alyssa Y. Chen, MD, MPH1, Suraj K. Jaladanki, MD2, Pushkala Jayaraman, MS, PhD3, Ji Yoon Yoon, MD1, Chin Hur, MD, MPH4, Nicholas Tatonetti, MD5, Girish Nadkarni, MD1, Julian A. Abrams, MD, MS4, Ali Soroush, MD, MS1. P6193 - Development and Validation of an Electronic Health Record Machine Learning Model for Cumulative Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk Prediction, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
