Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Practice Management
P6191 - Pre-Charting Reinvented: Real-World Evaluation of a Gastroenterology-Specific AI Tool to Improve Care Quality and Physician Efficiency
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Omeed Alipour, MD
Santa Clara Valley Medical Center
San Jose, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Outstanding Research Award in the Practice Management Category
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Omeed Alipour, MD1, Ganesh Krishnan, MSc2, Chandan Kaur, MBA, MSc2, Richard Manfready, MD3
1Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA; 2Acucare AI, San Francisco, CA; 3Cedar Valley Digestive Health Center, Waterloo, IA
Introduction: Pre-charting longitudinal electronic health record (EHR) data is a critical but time intensive task in gastroenterology (GI), accounting for up to 30% of specialist time. Patients with chronic GI disease often have fragmented records across diverse care settings, increasing the burden of manual review. To address this, we developed and evaluated a gastroenterology-specific AI system (Prax) that automates chart review and generates clinically relevant summaries to support pre-visit planning and point-of-care decision-making.
Methods: We evaluated Prax (AcucareAI, San Francisco) for generating GI pre-chart summaries. A de-identified EHR dataset (n=39) included clinical notes, imaging, procedures, phone encounters, and inpatient/outpatient documentation. The cohort comprised 30 established GI patients ( >1 year, ≥5 encounters) and 9 new referrals (≥6 months, ≥3 encounters). Prax-generated summaries were compared to physician-generated references using precision, recall, F1-score, and ROUGE-2. Gastroenterologists assessed summary relevance, completeness, and clinical utility through structured review.
Results: Prax summaries achieved a precision of 0.50, recall of 0.60, F1-score of 0.54, and ROUGE-2 of 0.20 compared to physician-generated references. In structured review, manual charting took 14±4.9 minutes versus 4±1.3 minutes for reviewing the summary, plus 3±1.7 minutes for supplemental chart review, a 50% time reduction. Physicians rated the summaries 4 out of 5 for informing the patient's current state and follow-up needs, reflecting improvement over manual review. Detail level was rated “2” (just right), indicating appropriate information density. The tool subjectively reduced cognitive load and improved pre-visit clinical insight.
Discussion: Prax showed modest ROUGE-2 (0.20) and F1 (0.54) scores, but its higher recall (0.60) reflects strong sensitivity to clinically relevant information. Physician review deemed Prax summaries as more informative than manual review, particularly for follow-up planning and clinical synthesis. This highlights limitations of standard natural language processing (NLP) metrics and significance of expert review. Prax captured key contextual details such as diagnostic timelines and follow-up prompts, absent from reference summaries, lowering scores despite improving completeness. Results underscore high value in AI based pre-charting and the need for GI-specific NLP validation frameworks to evaluate clinical completeness, accuracy, and utility.
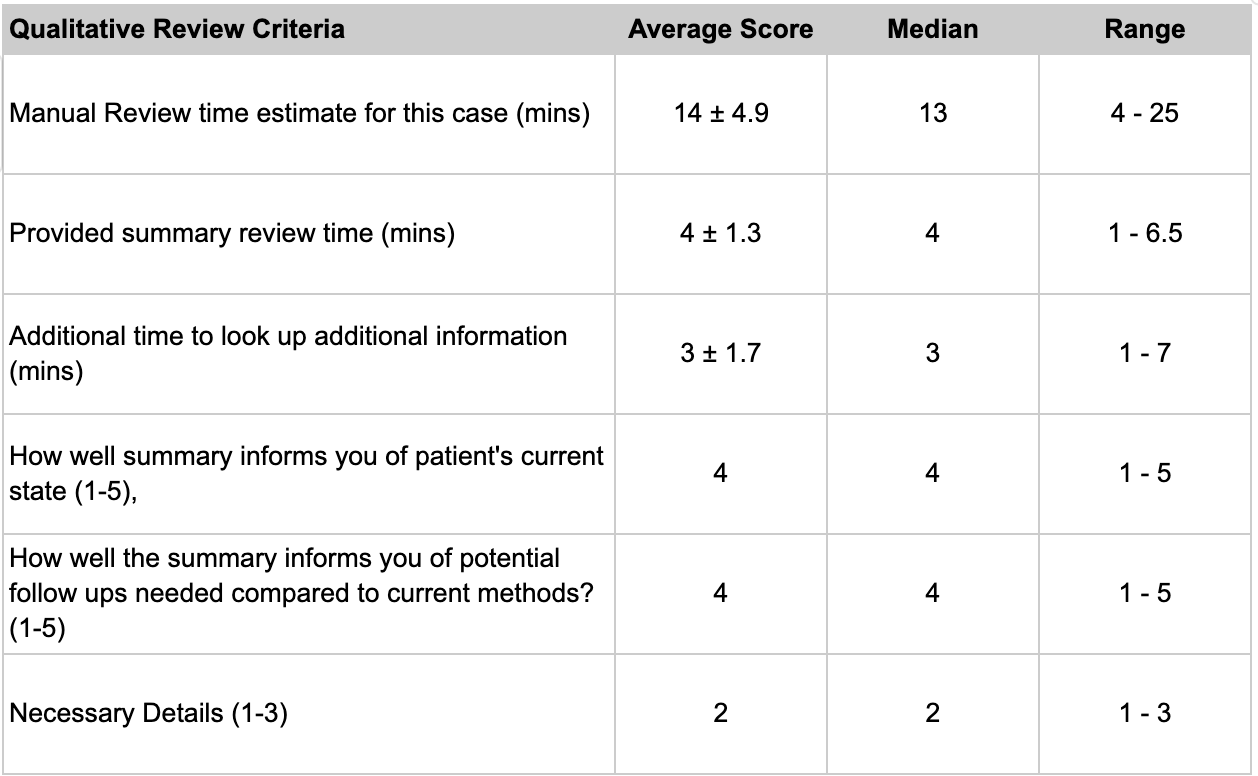
Figure: Quantitative Metrics Utilizing Prax
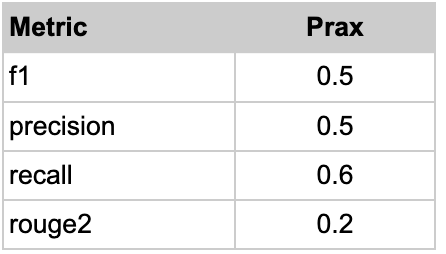
Figure: Qualitative Review Findings Utilizing Prax
Disclosures:
Omeed Alipour: Acucare AI – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ganesh Krishnan: Acucare AI – Owner/Ownership Interest.
Chandan Kaur: Acucare AI – Owner/Ownership Interest.
Richard Manfready: Acucare AI – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Omeed Alipour, MD1, Ganesh Krishnan, MSc2, Chandan Kaur, MBA, MSc2, Richard Manfready, MD3. P6191 - Pre-Charting Reinvented: Real-World Evaluation of a Gastroenterology-Specific AI Tool to Improve Care Quality and Physician Efficiency, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Omeed Alipour, MD1, Ganesh Krishnan, MSc2, Chandan Kaur, MBA, MSc2, Richard Manfready, MD3
1Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA; 2Acucare AI, San Francisco, CA; 3Cedar Valley Digestive Health Center, Waterloo, IA
Introduction: Pre-charting longitudinal electronic health record (EHR) data is a critical but time intensive task in gastroenterology (GI), accounting for up to 30% of specialist time. Patients with chronic GI disease often have fragmented records across diverse care settings, increasing the burden of manual review. To address this, we developed and evaluated a gastroenterology-specific AI system (Prax) that automates chart review and generates clinically relevant summaries to support pre-visit planning and point-of-care decision-making.
Methods: We evaluated Prax (AcucareAI, San Francisco) for generating GI pre-chart summaries. A de-identified EHR dataset (n=39) included clinical notes, imaging, procedures, phone encounters, and inpatient/outpatient documentation. The cohort comprised 30 established GI patients ( >1 year, ≥5 encounters) and 9 new referrals (≥6 months, ≥3 encounters). Prax-generated summaries were compared to physician-generated references using precision, recall, F1-score, and ROUGE-2. Gastroenterologists assessed summary relevance, completeness, and clinical utility through structured review.
Results: Prax summaries achieved a precision of 0.50, recall of 0.60, F1-score of 0.54, and ROUGE-2 of 0.20 compared to physician-generated references. In structured review, manual charting took 14±4.9 minutes versus 4±1.3 minutes for reviewing the summary, plus 3±1.7 minutes for supplemental chart review, a 50% time reduction. Physicians rated the summaries 4 out of 5 for informing the patient's current state and follow-up needs, reflecting improvement over manual review. Detail level was rated “2” (just right), indicating appropriate information density. The tool subjectively reduced cognitive load and improved pre-visit clinical insight.
Discussion: Prax showed modest ROUGE-2 (0.20) and F1 (0.54) scores, but its higher recall (0.60) reflects strong sensitivity to clinically relevant information. Physician review deemed Prax summaries as more informative than manual review, particularly for follow-up planning and clinical synthesis. This highlights limitations of standard natural language processing (NLP) metrics and significance of expert review. Prax captured key contextual details such as diagnostic timelines and follow-up prompts, absent from reference summaries, lowering scores despite improving completeness. Results underscore high value in AI based pre-charting and the need for GI-specific NLP validation frameworks to evaluate clinical completeness, accuracy, and utility.

Figure: Quantitative Metrics Utilizing Prax

Figure: Qualitative Review Findings Utilizing Prax
Disclosures:
Omeed Alipour: Acucare AI – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ganesh Krishnan: Acucare AI – Owner/Ownership Interest.
Chandan Kaur: Acucare AI – Owner/Ownership Interest.
Richard Manfready: Acucare AI – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Omeed Alipour, MD1, Ganesh Krishnan, MSc2, Chandan Kaur, MBA, MSc2, Richard Manfready, MD3. P6191 - Pre-Charting Reinvented: Real-World Evaluation of a Gastroenterology-Specific AI Tool to Improve Care Quality and Physician Efficiency, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

