Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Stomach and Spleen
P6312 - Evaluating Large Language Models for the Interpretation of ACG Guidelines on Premalignant Gastric Conditions: A Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT and DeepSeek
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- GS
Gina Singh, BA
Univeristy of Missouri-Kansas City
Kansas City, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Amna Zaheer, 1, Zahra Ali, 2, Shajadi Patan, MD3, Deepti Bala. Kallam, MD4, Uswah Imran Shaikh, MBBS1, Jamuna Shrestha, MD5, Fabeha Zafar, MD6, Vidhi Wadhwani, MBBS7, Muhammad Farrukh Siddiqui, MBBS1, Gina Singh, BA8, Shaliza Panjwani, MBBS9, Syed Mohsin Raza Bukhari, MBBS10, Shahan Javed, 11, Munazza Anwer, MBBS, FCPS12
1Liaquat National Hospital and Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 2Bolan Medical College, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 3Mid America Cancer Care, Kansas City, MO; 4USMD Hospital Arlington, Coppell, TX; 5Manipal College of Medical Sciences, Gorkha, Gandaki, Nepal; 6Department of Medicine, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 7Gujarat Cancer Society (GCS) Medical College, Hospital and Research Center, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8Univeristy of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO; 9Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10Nishtar Medical University and Hospital, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 11Alfaisal University, Riyadh, Ar Riyad, Saudi Arabia; 12Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Premalignant gastric conditions, such as intestinal metaplasia and atrophic gastritis present a high risk for progression to gastric cancer if not managed according to evidence-based guidelines. The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guidelines published in 2025 provide recommendations on diagnosis, surveillance, and management of premalignant gastric conditions. With the growing use of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DeepSeek by patients for medical advice, it is important to assess their accuracy in interpreting these guidelines. This study compares ChatGPT and DeepSeek in how well their responses align with the ACG recommendations on premalignant gastric conditions.
Methods: We developed 40 questions based on ACG guidelines addressing diagnosis, surveillance, and management. These were input into ChatGPT and DeepSeek. Two board-certified oncologists independently rated each response on accuracy, clarity, coherence, relevance, and completeness using a 5-point Likert scale. Scores were analyzed for inter-rater reliability and compared between models.
Results: Inter-rater reliability was moderate but statistically significant (Pearson r = 0.443, p < 0.01). Overall, DeepSeek outperformed ChatGPT across all domains. Oncologist 1 scored DeepSeek 4.81 versus ChatGPT 4.62; Oncologist 2 scored DeepSeek 4.92 versus ChatGPT 4.61. For factual accuracy, DeepSeek scored 4.8 and 4.85, compared to ChatGPT’s 4.5 and 4.25. DeepSeek also performed better in clarity, coherence, relevance, and completeness (up to 4.95 vs. ChatGPT’s 4.35–4.88). The most marked difference in performance was observed in the surveillance domain, where DeepSeek scored 4.82 and 4.92, compared to ChatGPT’s 4.17 and 4.14. Both models maintained high coherence, though DeepSeek demonstrated greater clinical precision.
Discussion: DeepSeek’s superior performance likely stems from domain-specific training, suggesting its potential as a clinical decision support tool in gastroenterology. Limitations include use of static prompts, lack of real-world clinical validation, and evolving model behavior. While both models show utility, these findings support cautious adoption of domain-trained LLMs with continued validation, oversight, and patient safety at the forefront.
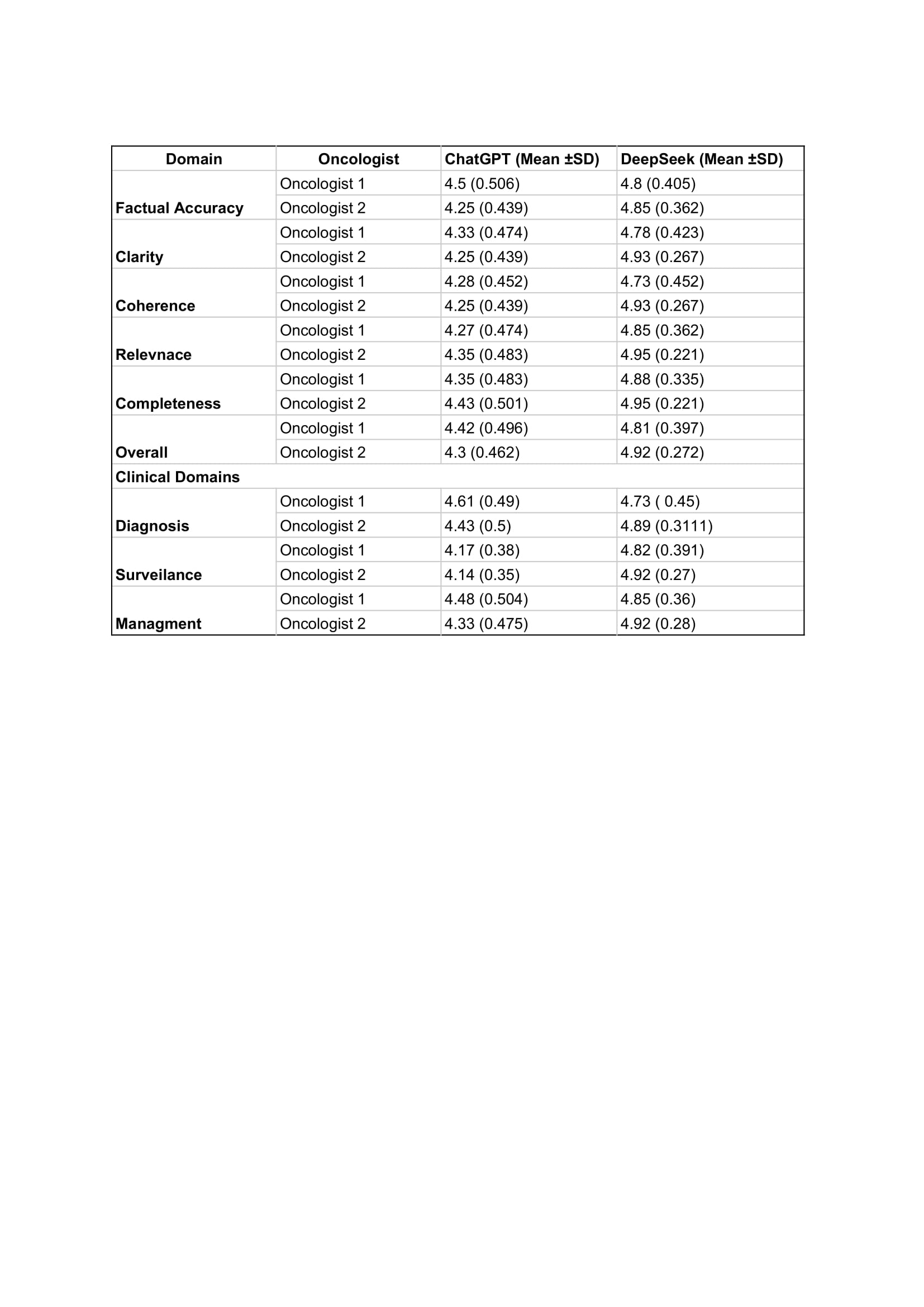
Figure: Category-wise analysis of AI performance across gastro-oncology domains.
Disclosures:
Amna Zaheer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zahra Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shajadi Patan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepti Kallam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Uswah Imran Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jamuna Shrestha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fabeha Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vidhi Wadhwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Farrukh Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gina Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaliza Panjwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Mohsin Raza Bukhari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahan Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Munazza Anwer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Zaheer, 1, Zahra Ali, 2, Shajadi Patan, MD3, Deepti Bala. Kallam, MD4, Uswah Imran Shaikh, MBBS1, Jamuna Shrestha, MD5, Fabeha Zafar, MD6, Vidhi Wadhwani, MBBS7, Muhammad Farrukh Siddiqui, MBBS1, Gina Singh, BA8, Shaliza Panjwani, MBBS9, Syed Mohsin Raza Bukhari, MBBS10, Shahan Javed, 11, Munazza Anwer, MBBS, FCPS12. P6312 - Evaluating Large Language Models for the Interpretation of ACG Guidelines on Premalignant Gastric Conditions: A Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT and DeepSeek, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Liaquat National Hospital and Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 2Bolan Medical College, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 3Mid America Cancer Care, Kansas City, MO; 4USMD Hospital Arlington, Coppell, TX; 5Manipal College of Medical Sciences, Gorkha, Gandaki, Nepal; 6Department of Medicine, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 7Gujarat Cancer Society (GCS) Medical College, Hospital and Research Center, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8Univeristy of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO; 9Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10Nishtar Medical University and Hospital, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 11Alfaisal University, Riyadh, Ar Riyad, Saudi Arabia; 12Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Premalignant gastric conditions, such as intestinal metaplasia and atrophic gastritis present a high risk for progression to gastric cancer if not managed according to evidence-based guidelines. The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guidelines published in 2025 provide recommendations on diagnosis, surveillance, and management of premalignant gastric conditions. With the growing use of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DeepSeek by patients for medical advice, it is important to assess their accuracy in interpreting these guidelines. This study compares ChatGPT and DeepSeek in how well their responses align with the ACG recommendations on premalignant gastric conditions.
Methods: We developed 40 questions based on ACG guidelines addressing diagnosis, surveillance, and management. These were input into ChatGPT and DeepSeek. Two board-certified oncologists independently rated each response on accuracy, clarity, coherence, relevance, and completeness using a 5-point Likert scale. Scores were analyzed for inter-rater reliability and compared between models.
Results: Inter-rater reliability was moderate but statistically significant (Pearson r = 0.443, p < 0.01). Overall, DeepSeek outperformed ChatGPT across all domains. Oncologist 1 scored DeepSeek 4.81 versus ChatGPT 4.62; Oncologist 2 scored DeepSeek 4.92 versus ChatGPT 4.61. For factual accuracy, DeepSeek scored 4.8 and 4.85, compared to ChatGPT’s 4.5 and 4.25. DeepSeek also performed better in clarity, coherence, relevance, and completeness (up to 4.95 vs. ChatGPT’s 4.35–4.88). The most marked difference in performance was observed in the surveillance domain, where DeepSeek scored 4.82 and 4.92, compared to ChatGPT’s 4.17 and 4.14. Both models maintained high coherence, though DeepSeek demonstrated greater clinical precision.
Discussion: DeepSeek’s superior performance likely stems from domain-specific training, suggesting its potential as a clinical decision support tool in gastroenterology. Limitations include use of static prompts, lack of real-world clinical validation, and evolving model behavior. While both models show utility, these findings support cautious adoption of domain-trained LLMs with continued validation, oversight, and patient safety at the forefront.

Figure: Category-wise analysis of AI performance across gastro-oncology domains.
Disclosures:
Amna Zaheer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zahra Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shajadi Patan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepti Kallam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Uswah Imran Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jamuna Shrestha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fabeha Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vidhi Wadhwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Farrukh Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gina Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaliza Panjwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Mohsin Raza Bukhari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahan Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Munazza Anwer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Zaheer, 1, Zahra Ali, 2, Shajadi Patan, MD3, Deepti Bala. Kallam, MD4, Uswah Imran Shaikh, MBBS1, Jamuna Shrestha, MD5, Fabeha Zafar, MD6, Vidhi Wadhwani, MBBS7, Muhammad Farrukh Siddiqui, MBBS1, Gina Singh, BA8, Shaliza Panjwani, MBBS9, Syed Mohsin Raza Bukhari, MBBS10, Shahan Javed, 11, Munazza Anwer, MBBS, FCPS12. P6312 - Evaluating Large Language Models for the Interpretation of ACG Guidelines on Premalignant Gastric Conditions: A Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT and DeepSeek, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
