Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P6068 - Unmasking the Biliary Trap: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges of Cysto-Biliary Communication in Hepatic Hydatid Disease
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- RA
Rohan Aggarwal, MD (he/him/his)
Apollo Hospital
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Rohan Aggarwal, MD1, Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MD2, Sanjay Jain, MRCP1, Amol Sharma, MD, MSc, FACG3, Rigved Gupta, MS1, Surabhi Gupta, MD1, Prackriti Masand, MD4, Aishwarya Singh, MBBS1, Neerav Goel, MS1, Abhiraj Singh, MD1
1Apollo Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Apollo Hospital, Dothan, AL; 3Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 4MAX Superspecialty Hospital and Vaishali, New Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: Hepatic hydatid disease, caused by Echinococcus granulosus, often follows an indolent course but may lead to complication in up to 40% of patients. Cysto-biliary communication is the most common complication. Frank communication with intraductal migration of daughter cysts presents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge, especially in elderly or comorbid patients. These cases may mimic neoplasms or pyogenic abscesses, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment.
Case Description/
Methods: A 75-year-old woman with diabetes and hypertension presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain, vomiting, anorexia, and acute encephalopathy with global aphasia. Liver enzymes revealed cholestatic injury (elevated ALP and GGT). Ultrasound revealed a complex hepatic cyst; MRI showed an 11 x 8.6 x 8.5 cm T2-hyperintense lesion in the right lobe with internal daughter cysts, complex septations, and a tubular projection extending beyond the capsule – raising suspicion for cysto-biliary communication, confirmed on MRCP. Serology detected Echinococcus infection. Albendazole was initiated preoperatively. Exploratory laparotomy revealed an infected hydatid cyst adherent to the diaphragm with daughter cysts extending into the common bile duct. Cystopericystectomy, common bile duct clearance, and biliary stenting were performed. Neurologic function improved postoperatively and the patient remained well on follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights several clinical pearls. First, frank cysto-biliary communication with intraductal migration is rare and easily overlooked without high clinical suspicion. Second, advanced imaging, especially MRCP, is critical for detecting occult biliary communications and informing surgical planning. Third, radical surgical intervention remains the cornerstone of treatment in extensive cysto-biliary communication, with benzimidazole therapy playing and adjunctive role in perioperative management. Early anti-parasitic therapy reduces risk of intraoperative spillage and recurrence. Cysto-biliary communication in hepatic hydatidosis is under-recognized and frequently misdiagnosed. In elderly or immune-compromised patients, a multidisciplinary approach incorporating imaging, anti-parasitic therapy, and radical surgery is essential for optimal patient outcomes.
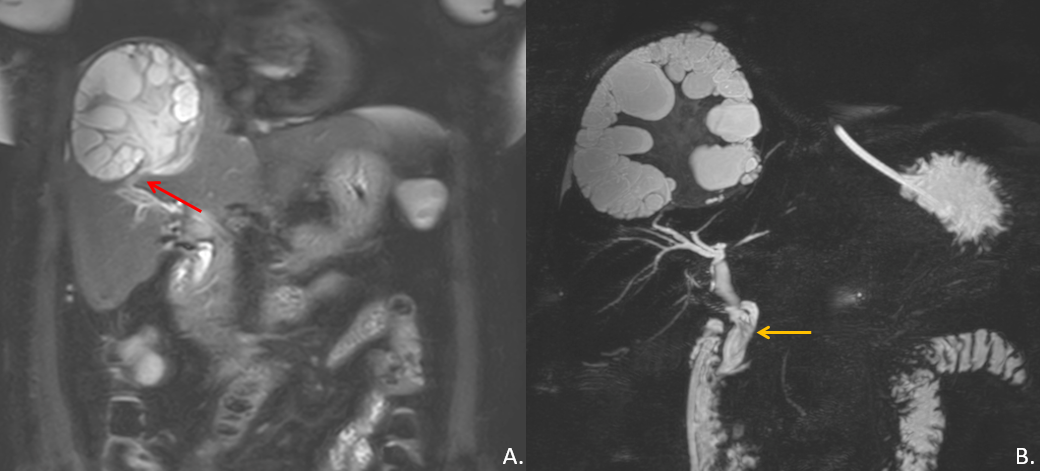
Figure: (A) Coronal T2-weighted MRI shows hydatid cyst in right lobe of liver with biliary communication (red arrow). (B) MRCP shows multiple curvilinear flow voids in the common bile duct (yellow arrow) representing hydatid parasitic worms.

Figure: A.Gross Pathology: Exploratory laparotomy reveals irregular, grey-white cystic fragments with thick fibrotic walls, focal calcification, and discoloration. Translucent gelatinous daughter cysts and germinal layers with hydatid sand are noted. Bile-staining on some fragments suggests cysto-biliary communication. No solid or hemorrhagic areas are seen. B.Histopathology - Low power: Shows hydatid cyst of Echinococcus granulosus origin with daughter cysts and thick eosinophilic laminated membrane. Protoscolices appear as basophilic dots. The pericyst exhibits granulomatous inflammation with giant cells, lymphocytes, and eosinophils. Surrounding stroma shows mild to moderate inflammation. C. Histopathology - High power: Highlights crescent-shaped, eosinophilic, chitinous hooks of E. granulosus protoscolices arranged in a diagnostic double row.
Disclosures:
Rohan Aggarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikarsh Bhardwaj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanjay Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amol Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rigved Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Surabhi Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prackriti Masand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aishwarya Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neerav Goel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhiraj Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Aggarwal, MD1, Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MD2, Sanjay Jain, MRCP1, Amol Sharma, MD, MSc, FACG3, Rigved Gupta, MS1, Surabhi Gupta, MD1, Prackriti Masand, MD4, Aishwarya Singh, MBBS1, Neerav Goel, MS1, Abhiraj Singh, MD1. P6068 - Unmasking the Biliary Trap: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges of Cysto-Biliary Communication in Hepatic Hydatid Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Apollo Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Apollo Hospital, Dothan, AL; 3Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 4MAX Superspecialty Hospital and Vaishali, New Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: Hepatic hydatid disease, caused by Echinococcus granulosus, often follows an indolent course but may lead to complication in up to 40% of patients. Cysto-biliary communication is the most common complication. Frank communication with intraductal migration of daughter cysts presents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge, especially in elderly or comorbid patients. These cases may mimic neoplasms or pyogenic abscesses, leading to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment.
Case Description/
Methods: A 75-year-old woman with diabetes and hypertension presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain, vomiting, anorexia, and acute encephalopathy with global aphasia. Liver enzymes revealed cholestatic injury (elevated ALP and GGT). Ultrasound revealed a complex hepatic cyst; MRI showed an 11 x 8.6 x 8.5 cm T2-hyperintense lesion in the right lobe with internal daughter cysts, complex septations, and a tubular projection extending beyond the capsule – raising suspicion for cysto-biliary communication, confirmed on MRCP. Serology detected Echinococcus infection. Albendazole was initiated preoperatively. Exploratory laparotomy revealed an infected hydatid cyst adherent to the diaphragm with daughter cysts extending into the common bile duct. Cystopericystectomy, common bile duct clearance, and biliary stenting were performed. Neurologic function improved postoperatively and the patient remained well on follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights several clinical pearls. First, frank cysto-biliary communication with intraductal migration is rare and easily overlooked without high clinical suspicion. Second, advanced imaging, especially MRCP, is critical for detecting occult biliary communications and informing surgical planning. Third, radical surgical intervention remains the cornerstone of treatment in extensive cysto-biliary communication, with benzimidazole therapy playing and adjunctive role in perioperative management. Early anti-parasitic therapy reduces risk of intraoperative spillage and recurrence. Cysto-biliary communication in hepatic hydatidosis is under-recognized and frequently misdiagnosed. In elderly or immune-compromised patients, a multidisciplinary approach incorporating imaging, anti-parasitic therapy, and radical surgery is essential for optimal patient outcomes.

Figure: (A) Coronal T2-weighted MRI shows hydatid cyst in right lobe of liver with biliary communication (red arrow). (B) MRCP shows multiple curvilinear flow voids in the common bile duct (yellow arrow) representing hydatid parasitic worms.

Figure: A.Gross Pathology: Exploratory laparotomy reveals irregular, grey-white cystic fragments with thick fibrotic walls, focal calcification, and discoloration. Translucent gelatinous daughter cysts and germinal layers with hydatid sand are noted. Bile-staining on some fragments suggests cysto-biliary communication. No solid or hemorrhagic areas are seen. B.Histopathology - Low power: Shows hydatid cyst of Echinococcus granulosus origin with daughter cysts and thick eosinophilic laminated membrane. Protoscolices appear as basophilic dots. The pericyst exhibits granulomatous inflammation with giant cells, lymphocytes, and eosinophils. Surrounding stroma shows mild to moderate inflammation. C. Histopathology - High power: Highlights crescent-shaped, eosinophilic, chitinous hooks of E. granulosus protoscolices arranged in a diagnostic double row.
Disclosures:
Rohan Aggarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikarsh Bhardwaj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanjay Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amol Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rigved Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Surabhi Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prackriti Masand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aishwarya Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neerav Goel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhiraj Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Aggarwal, MD1, Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MD2, Sanjay Jain, MRCP1, Amol Sharma, MD, MSc, FACG3, Rigved Gupta, MS1, Surabhi Gupta, MD1, Prackriti Masand, MD4, Aishwarya Singh, MBBS1, Neerav Goel, MS1, Abhiraj Singh, MD1. P6068 - Unmasking the Biliary Trap: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges of Cysto-Biliary Communication in Hepatic Hydatid Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
