Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3603 - Vagal Nerve Injury as a Complication of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Brendan Kemple, MD (he/him/his)
Augusta University Medical Center
Augusta, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Brendan Kemple, MD1, Raguraj Chandradevan, MD2, Phuong Nguyen, MD2, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MD2
1Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 2Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: GERD is one of the most common presenting complaints in gastroenterology. Surgical management is commonly reserved for refractory GERD. Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF), a new technique rising in frequency as an endoscopic intervention for refractory cases. Vagal nerve injury is a known complication of intra-abdominal surgeries, including Nissen Fundoplication. Here we present a case concerning for vagal nerve injury due to TIF.
Case Description/
Methods: A 70 year old male patient with a history of TIF performed 3 months ago and remote cholecystectomy presented to the hospital for diarrhea and intermittent epigastric pain. His bowel movements had been normal prior to the TIF procedure. His last colonoscopy in 2023 only showed one large polyp. The laboratory parameters demonstrated a TSH of 5.97, a pancreatic elastase of 369 and unremarkable tissue transglutaminase antibody, IgA and transglutaminase IgAs. He has reportedly tried antacids, PPIs, antibiotics, antiemetics, cholestyramine, loperamide and bulking agents without relief. He underwent EGD with biopsy which demonstrated evidence of the prior TIF procedure, a prolapsed hiatal hernia & erythema of the gastric antrum. The gastric biopsies demonstrated reactive gastropathy with focal intestinal metaplasia. The duodenal biopsies showed focal foveolar metaplasia. Stool PCR resulted negative for infectious causes. Blood VIP, gastrin and glucagon levels were normal. An abdominal CT imaging was unremarkable. Gastric emptying studies were normal. He is currently pending glucose breath testing, and endoscopy with for aspirate culture and disaccharidase assays. He is currently taking pantoprazole 40mg daily.
Discussion: GERD remains a highly prevalent disease process in the United States. TIF is a promising intervention that often decreases symptom burden and reduces long term dependence on PPIs. Commonly reported side effects of TIF include bleeding, perforation, and pneumothorax. Our patient presented with typical symptoms of vagal nerve injury including diarrhea and epigastric pain. Considering the temporal relationship of this patient’s symptoms and the TIF, a procedural complication must be considered including injury to the vagus nerve. Vagal nerve injury should be counseled as a potential side effect of TIF due to the significant impact it can have on patient’s livelihood.
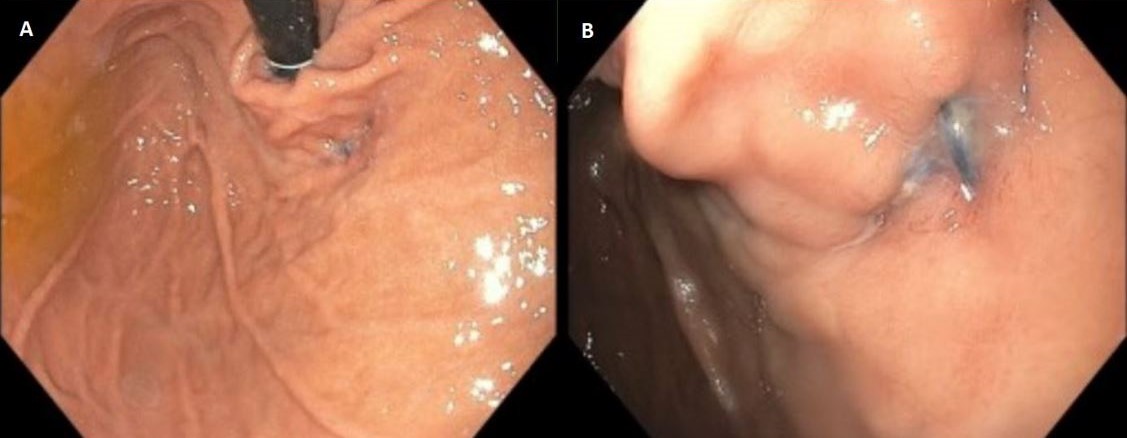
Figure: Figure 1: A) Retroflexion during esophagogastroduodenoscopy demonstrating the prior transoral incisionless fundoplication B) The intact sutures of the prior transoral incisionless fundoplication
Disclosures:
Brendan Kemple indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raguraj Chandradevan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phuong Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Subbaramiah Sridhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brendan Kemple, MD1, Raguraj Chandradevan, MD2, Phuong Nguyen, MD2, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MD2. P3603 - Vagal Nerve Injury as a Complication of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 2Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: GERD is one of the most common presenting complaints in gastroenterology. Surgical management is commonly reserved for refractory GERD. Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF), a new technique rising in frequency as an endoscopic intervention for refractory cases. Vagal nerve injury is a known complication of intra-abdominal surgeries, including Nissen Fundoplication. Here we present a case concerning for vagal nerve injury due to TIF.
Case Description/
Methods: A 70 year old male patient with a history of TIF performed 3 months ago and remote cholecystectomy presented to the hospital for diarrhea and intermittent epigastric pain. His bowel movements had been normal prior to the TIF procedure. His last colonoscopy in 2023 only showed one large polyp. The laboratory parameters demonstrated a TSH of 5.97, a pancreatic elastase of 369 and unremarkable tissue transglutaminase antibody, IgA and transglutaminase IgAs. He has reportedly tried antacids, PPIs, antibiotics, antiemetics, cholestyramine, loperamide and bulking agents without relief. He underwent EGD with biopsy which demonstrated evidence of the prior TIF procedure, a prolapsed hiatal hernia & erythema of the gastric antrum. The gastric biopsies demonstrated reactive gastropathy with focal intestinal metaplasia. The duodenal biopsies showed focal foveolar metaplasia. Stool PCR resulted negative for infectious causes. Blood VIP, gastrin and glucagon levels were normal. An abdominal CT imaging was unremarkable. Gastric emptying studies were normal. He is currently pending glucose breath testing, and endoscopy with for aspirate culture and disaccharidase assays. He is currently taking pantoprazole 40mg daily.
Discussion: GERD remains a highly prevalent disease process in the United States. TIF is a promising intervention that often decreases symptom burden and reduces long term dependence on PPIs. Commonly reported side effects of TIF include bleeding, perforation, and pneumothorax. Our patient presented with typical symptoms of vagal nerve injury including diarrhea and epigastric pain. Considering the temporal relationship of this patient’s symptoms and the TIF, a procedural complication must be considered including injury to the vagus nerve. Vagal nerve injury should be counseled as a potential side effect of TIF due to the significant impact it can have on patient’s livelihood.

Figure: Figure 1: A) Retroflexion during esophagogastroduodenoscopy demonstrating the prior transoral incisionless fundoplication B) The intact sutures of the prior transoral incisionless fundoplication
Disclosures:
Brendan Kemple indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raguraj Chandradevan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phuong Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Subbaramiah Sridhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brendan Kemple, MD1, Raguraj Chandradevan, MD2, Phuong Nguyen, MD2, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MD2. P3603 - Vagal Nerve Injury as a Complication of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

