Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3536 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing for Glycemic and Metabolic Improvement in Insulin-Resistant Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Observational Studies
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Umar Farooque, MBBS (he/him/his)
Health Education England, East of England, United Kingdom
Luton, England, United Kingdom
Presenting Author(s)
Umar Farooque, MBBS1, Aimen Khan Burki, MD2, Hadiah Ashraf, MBBS3, Meer Murtaza, MBBS4, Muhammad Akhlaq, MBBS5, Muhammad Umais, MBBS6, Samiullah Shaikh, MBBS7, Aaron George G. Abouganem, MD8, Afeera Bashir, MBBS9, Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG10
1Health Education England, East of England, United Kingdom, Luton, England, United Kingdom; 2University of Bologna, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 3Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Shahpur Chakar, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Lady Reading Hospital Peshawar, Timergara, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Liaquat University of Medical and health Sciences, Jamshoro, Pakistan, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Ciudad de la Salud, Panama City, Panama, Panama; 9Dr. Ruth K M Pfau Civil Hospital, Karachi, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10NYU Grossman School of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York, NY
Introduction: Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure designed to improve glucose metabolism by ablating the duodenal mucosa. While both randomized and non-randomized studies suggest metabolic benefits, the evidence base remains limited and inconsistent. This meta-analysis evaluates the impact of DMR on glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and broader metabolic parameters in insulin-resistant overweight patients.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane from inception to March 2025. Eligible studies included both randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational therapeutic trials assessing DMR in insulin-resistant and overweight adults. Primary outcomes were changes in HbA1c, HOMA-IR, and weight. Secondary outcomes included ALT, AST, HDL, systolic blood pressure (SBP), fasting glucose, and fasting insulin. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model.
Results: Four studies (two RCTs and two observational trials) with a total of 143 participants met the inclusion criteria. DMR significantly reduced HbA1c in patients with diabetes (–1.18%, 95% CI: –1.37 to –1.00) and showed a non-significant reduction in the overall population (–0.80%, 95% CI: –1.81 to 0.20) at 24 weeks (Figure 1). HOMA-IR improved significantly (–1.14, 95% CI: –2.22 to –0.06), and body weight decreased by –2.50 kg (95% CI: –2.54 to –2.46) at 24 weeks (Figure 2). Directionally favorable but statistically non-significant changes were observed in ALT (–9.87 U/L), AST (–2.78 U/L), SBP (–3.83 mmHg), HDL (+6.90 mg/dL), fasting plasma glucose (–29.66 mg/dL), and fasting plasma insulin (–9.64 amol/L). Adverse events were rare and generally mild. Unpooled outcomes, including C-peptide, liver fat, and hormonal AUC metrics, also showed favorable trends.
Discussion: DMR significantly improves glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and body weight in insulin-resistant patients, particularly those with type 2 diabetes. Although secondary metabolic markers demonstrated promising trends, they did not reach statistical significance. The procedure appears safe, with minimal and manageable adverse events. These findings underscore DMR’s potential as a therapeutic option for metabolic disease. Larger, high-quality multicenter RCTs are warranted to confirm its long-term efficacy and safety.
ChatGPT (OpenAI) was used for language clarity and grammar refinement. All scientific content, data, and analysis are original and solely by the authors
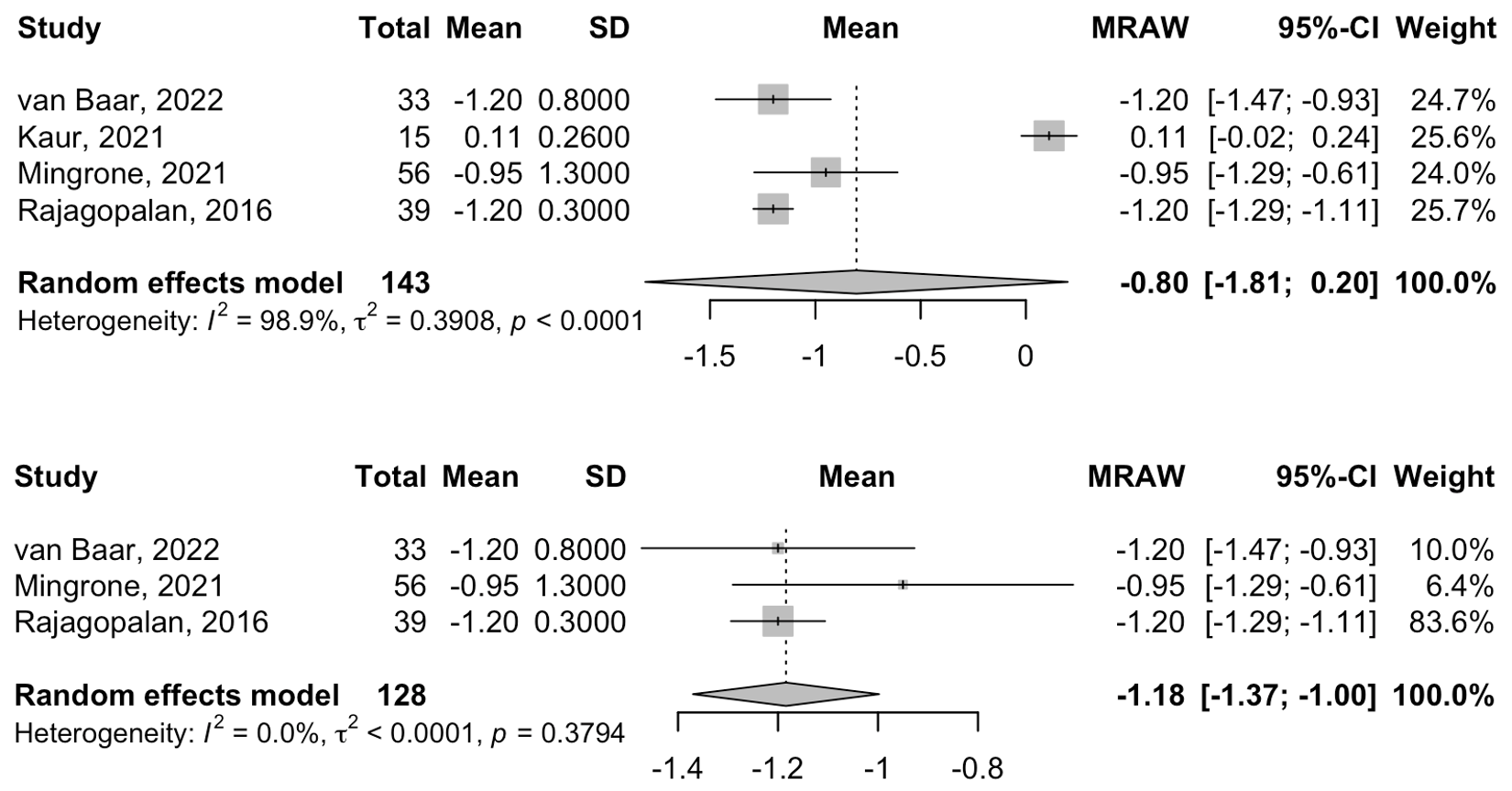
Figure: Figure 1. Forest plot showing the reduction in HbA1c (%) at 24-week follow-up following Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) intervention in: (top) all patients with insulin resistance, and (bottom) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
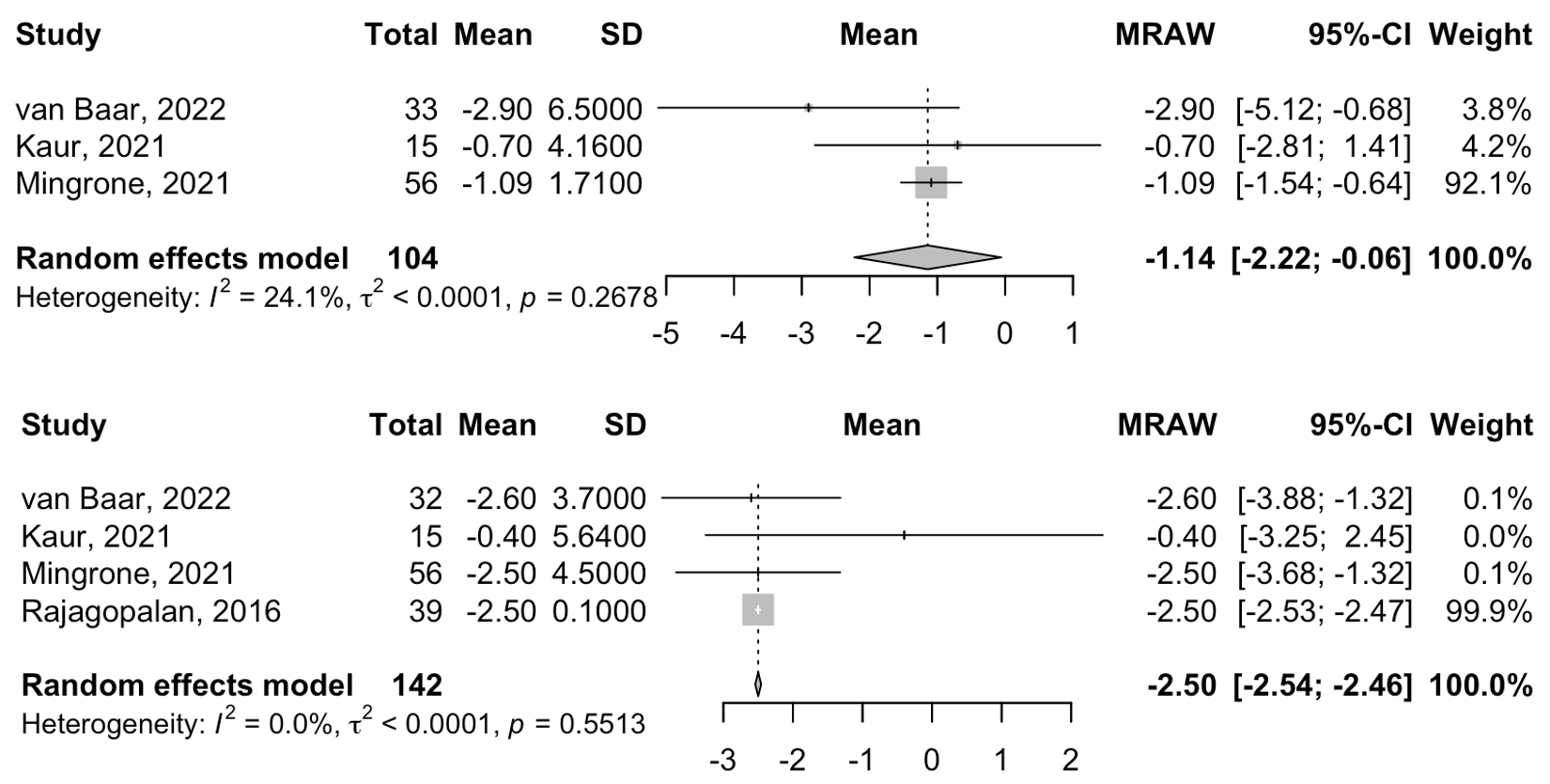
Figure: Figure 2. Forest plot showing the reduction at 24-week follow-up following Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) intervention in all patients: (top) HOMA-IR, and (bottom) body weight (kg)
Disclosures:
Umar Farooque indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aimen Khan Burki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hadiah Ashraf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meer Murtaza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Akhlaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Umais indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiullah Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron George Abouganem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Afeera Bashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aasma Shaukat: Freenome inc – Consultant.
Umar Farooque, MBBS1, Aimen Khan Burki, MD2, Hadiah Ashraf, MBBS3, Meer Murtaza, MBBS4, Muhammad Akhlaq, MBBS5, Muhammad Umais, MBBS6, Samiullah Shaikh, MBBS7, Aaron George G. Abouganem, MD8, Afeera Bashir, MBBS9, Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG10. P3536 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing for Glycemic and Metabolic Improvement in Insulin-Resistant Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Observational Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Health Education England, East of England, United Kingdom, Luton, England, United Kingdom; 2University of Bologna, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 3Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Liaquat University of Medical and Health Science, Shahpur Chakar, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Lady Reading Hospital Peshawar, Timergara, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Liaquat University of Medical and health Sciences, Jamshoro, Pakistan, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Ciudad de la Salud, Panama City, Panama, Panama; 9Dr. Ruth K M Pfau Civil Hospital, Karachi, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10NYU Grossman School of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York, NY
Introduction: Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR) is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure designed to improve glucose metabolism by ablating the duodenal mucosa. While both randomized and non-randomized studies suggest metabolic benefits, the evidence base remains limited and inconsistent. This meta-analysis evaluates the impact of DMR on glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and broader metabolic parameters in insulin-resistant overweight patients.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane from inception to March 2025. Eligible studies included both randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational therapeutic trials assessing DMR in insulin-resistant and overweight adults. Primary outcomes were changes in HbA1c, HOMA-IR, and weight. Secondary outcomes included ALT, AST, HDL, systolic blood pressure (SBP), fasting glucose, and fasting insulin. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model.
Results: Four studies (two RCTs and two observational trials) with a total of 143 participants met the inclusion criteria. DMR significantly reduced HbA1c in patients with diabetes (–1.18%, 95% CI: –1.37 to –1.00) and showed a non-significant reduction in the overall population (–0.80%, 95% CI: –1.81 to 0.20) at 24 weeks (Figure 1). HOMA-IR improved significantly (–1.14, 95% CI: –2.22 to –0.06), and body weight decreased by –2.50 kg (95% CI: –2.54 to –2.46) at 24 weeks (Figure 2). Directionally favorable but statistically non-significant changes were observed in ALT (–9.87 U/L), AST (–2.78 U/L), SBP (–3.83 mmHg), HDL (+6.90 mg/dL), fasting plasma glucose (–29.66 mg/dL), and fasting plasma insulin (–9.64 amol/L). Adverse events were rare and generally mild. Unpooled outcomes, including C-peptide, liver fat, and hormonal AUC metrics, also showed favorable trends.
Discussion: DMR significantly improves glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and body weight in insulin-resistant patients, particularly those with type 2 diabetes. Although secondary metabolic markers demonstrated promising trends, they did not reach statistical significance. The procedure appears safe, with minimal and manageable adverse events. These findings underscore DMR’s potential as a therapeutic option for metabolic disease. Larger, high-quality multicenter RCTs are warranted to confirm its long-term efficacy and safety.
ChatGPT (OpenAI) was used for language clarity and grammar refinement. All scientific content, data, and analysis are original and solely by the authors

Figure: Figure 1. Forest plot showing the reduction in HbA1c (%) at 24-week follow-up following Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) intervention in: (top) all patients with insulin resistance, and (bottom) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.

Figure: Figure 2. Forest plot showing the reduction at 24-week follow-up following Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) intervention in all patients: (top) HOMA-IR, and (bottom) body weight (kg)
Disclosures:
Umar Farooque indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aimen Khan Burki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hadiah Ashraf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Meer Murtaza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Akhlaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Umais indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samiullah Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron George Abouganem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Afeera Bashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aasma Shaukat: Freenome inc – Consultant.
Umar Farooque, MBBS1, Aimen Khan Burki, MD2, Hadiah Ashraf, MBBS3, Meer Murtaza, MBBS4, Muhammad Akhlaq, MBBS5, Muhammad Umais, MBBS6, Samiullah Shaikh, MBBS7, Aaron George G. Abouganem, MD8, Afeera Bashir, MBBS9, Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, FACG10. P3536 - Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing for Glycemic and Metabolic Improvement in Insulin-Resistant Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Observational Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
