Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3534 - Trends in Utilization and Outcomes After Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies: An MBSAQIP Database Analysis From 2016-2023
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Sevag Hamamah, DO
Scripps Mercy Hospital
San Diego, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Sevag Hamamah, DO1, Jamil Samaan, MD2, Rabindra Watson, MD2
1Scripps Mercy Hospital, San Diego, CA; 2Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Endoscopic bariatric therapies (EBTs), including endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) placement, are minimally invasive therapy options for obesity management. Despite their widespread adoption, national data on yearly trends in utilization and trends in postoperative outcomes are limited. In this study, we used a bariatric surgery registry to assess trends in EBT utilization and 30-day outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 1,627,034 patients from 2016 to 2023 using the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP) database. Utilization rates are expressed as percent of total bariatric surgeries and procedures performed per year for both ESG and IGB. 30-day postoperative outcomes were assessed and reported as percentages across the 8-year study period. Postoperative outcomes included 30-day emergency department visits, readmissions, reoperations, and interventions. Linear regression analysis was performed to assess the statistical significance of trends. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: We identified 5,757 patients who underwent ESG and 4,555 who underwent IGB. ESG utilization increased through 2020, peaking at 0.46% of total bariatric surgery cases, before declining to 0.27% in 2023 (p=0.57). IGB use steadily declined from 0.54% to 0.11% of total bariatric surgery cases (p=0.001), with ESG surpassing IGB in 2018. ESG was associated with significant reductions in 30-day reoperations (3.83% to 0.86%, p=0.044) and interventions (5.91% to 0.86%, p=0.002), while ED visits and readmission rates remained stable over the 8-year study period. In contrast, IGB showed a significant increase in ED visits over time (3.28% to 9.61%, p=0.033), with no statistically significant change in 30-day readmissions, reoperations, and interventions.
Discussion: This large national analysis demonstrates divergent trends in the utilization and postoperative outcomes of ESG and IGB. Our analysis is limited by the lack of additional data to investigate potential etiologies for the observed trends such as glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist use and data beyond 30 days. Our findings reflect shifting practice patterns and support further prospective evaluation of EBT modalities to optimize patient selection and long‐term outcomes.
AI Disclosure: ChatGPT was used to assist with language editing during the preparation of this abstract. The authors reviewed and approved the final content.
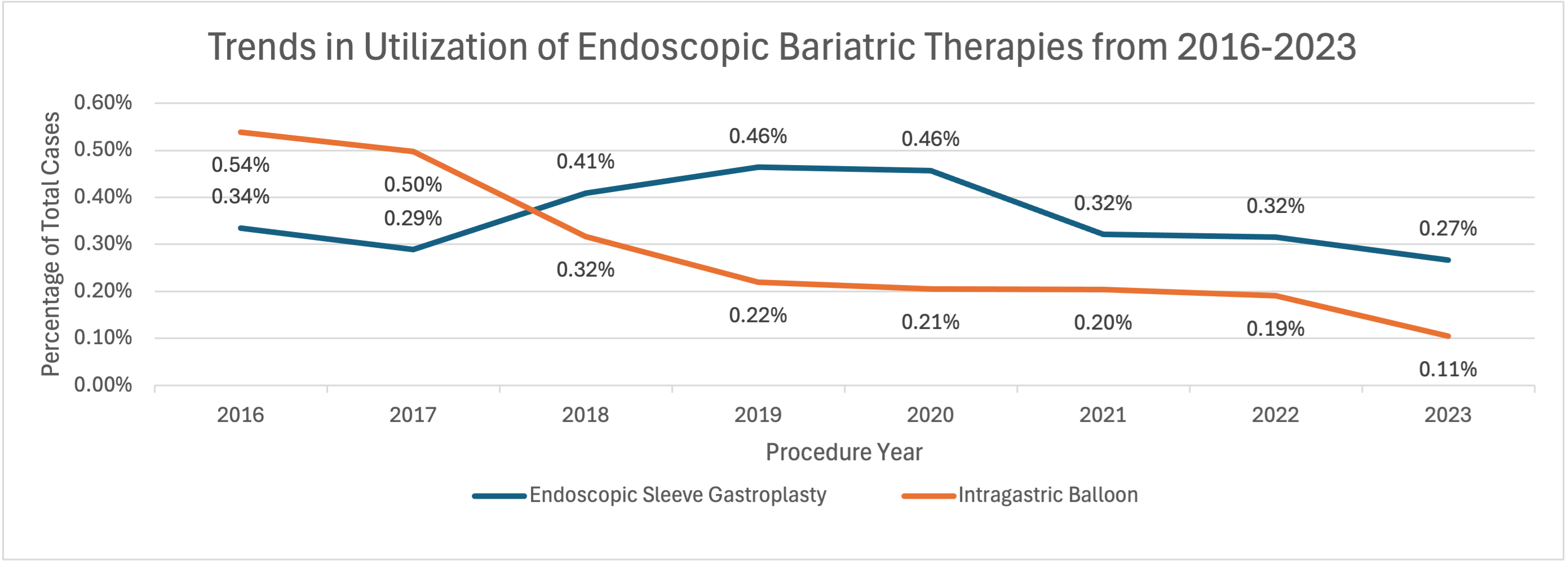
Figure: Figure 1. Trends in utilization of endoscopic bariatric therapies from 2016 to 2023. Annual case volumes of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) are shown as percentages of total bariatric surgery or procedure cases by calendar year. p-values: ESG = 0.57; IGB = 0.001.
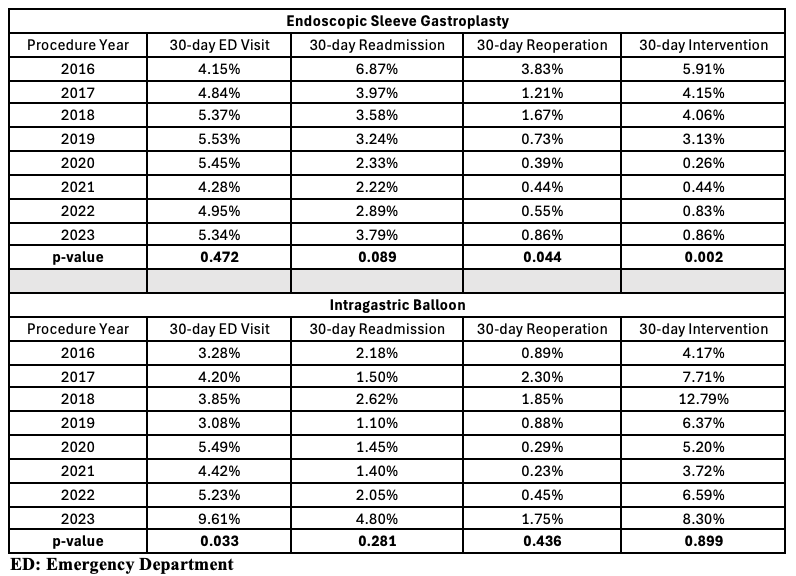
Figure: Table 1. Trends in 30-day emergency department visits, readmissions, reoperations, and interventions following endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) from 2016 to 2023. Each outcome is reported as a percentage of the total number of ESG or IGB cases performed in a given calendar year.
Disclosures:
Sevag Hamamah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jamil Samaan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabindra Watson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sevag Hamamah, DO1, Jamil Samaan, MD2, Rabindra Watson, MD2. P3534 - Trends in Utilization and Outcomes After Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies: An MBSAQIP Database Analysis From 2016-2023, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Scripps Mercy Hospital, San Diego, CA; 2Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Endoscopic bariatric therapies (EBTs), including endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) placement, are minimally invasive therapy options for obesity management. Despite their widespread adoption, national data on yearly trends in utilization and trends in postoperative outcomes are limited. In this study, we used a bariatric surgery registry to assess trends in EBT utilization and 30-day outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 1,627,034 patients from 2016 to 2023 using the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement Program (MBSAQIP) database. Utilization rates are expressed as percent of total bariatric surgeries and procedures performed per year for both ESG and IGB. 30-day postoperative outcomes were assessed and reported as percentages across the 8-year study period. Postoperative outcomes included 30-day emergency department visits, readmissions, reoperations, and interventions. Linear regression analysis was performed to assess the statistical significance of trends. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: We identified 5,757 patients who underwent ESG and 4,555 who underwent IGB. ESG utilization increased through 2020, peaking at 0.46% of total bariatric surgery cases, before declining to 0.27% in 2023 (p=0.57). IGB use steadily declined from 0.54% to 0.11% of total bariatric surgery cases (p=0.001), with ESG surpassing IGB in 2018. ESG was associated with significant reductions in 30-day reoperations (3.83% to 0.86%, p=0.044) and interventions (5.91% to 0.86%, p=0.002), while ED visits and readmission rates remained stable over the 8-year study period. In contrast, IGB showed a significant increase in ED visits over time (3.28% to 9.61%, p=0.033), with no statistically significant change in 30-day readmissions, reoperations, and interventions.
Discussion: This large national analysis demonstrates divergent trends in the utilization and postoperative outcomes of ESG and IGB. Our analysis is limited by the lack of additional data to investigate potential etiologies for the observed trends such as glucagon-like peptide 1 agonist use and data beyond 30 days. Our findings reflect shifting practice patterns and support further prospective evaluation of EBT modalities to optimize patient selection and long‐term outcomes.
AI Disclosure: ChatGPT was used to assist with language editing during the preparation of this abstract. The authors reviewed and approved the final content.

Figure: Figure 1. Trends in utilization of endoscopic bariatric therapies from 2016 to 2023. Annual case volumes of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) are shown as percentages of total bariatric surgery or procedure cases by calendar year. p-values: ESG = 0.57; IGB = 0.001.

Figure: Table 1. Trends in 30-day emergency department visits, readmissions, reoperations, and interventions following endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) and intragastric balloon (IGB) from 2016 to 2023. Each outcome is reported as a percentage of the total number of ESG or IGB cases performed in a given calendar year.
Disclosures:
Sevag Hamamah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jamil Samaan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rabindra Watson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sevag Hamamah, DO1, Jamil Samaan, MD2, Rabindra Watson, MD2. P3534 - Trends in Utilization and Outcomes After Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies: An MBSAQIP Database Analysis From 2016-2023, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
