Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3391 - Acute Fibrostenotic and Fistulizing Ileal Crohn’s Disease: Timing of Biologic Therapy in the Setting of Obstruction and Infection
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Wael T. Mohamed, MD (he/him/his)
University of Kansas School of Medicine
Wichita, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Wael T. Mohamed, MD1, Mohamed A. Omar, MD1, Kyle Rowe, MD1, Nathan Tofteland, MD1, William J.. Salyers, MD, MPH2
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine - Wichita, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic relapsing inflammatory disorder with highly variable phenotypes. Patients with stricturing and/or fistulizing disease are at increased risk for surgery and long-term disability. Biologic therapies, especially anti-TNF agents, are effective in altering disease progression when initiated early. However, acute complications such as obstruction or suspected infection may delay therapy, complicating management.
Case Description/
Methods: A 30-year-old biologic-naïve female with stricturing ileal CD diagnosed in 2020 (baseline fecal calprotectin 5,000 μg/g) presented with worsening abdominal pain while on prednisone 40 mg daily pending biologic approval. Labs showed leukocytosis (WBC 20,000/μL) and CRP 30.2 mg/L. CT abdomen/pelvis revealed small bowel obstruction at the terminal ileum with circumferential thickening and an adjacent enhancing collection with punctate air, suggestive of early fistula formation. A second fluid collection between the bladder and uterus was suspicious for phlegmon or early abscess.
Surgical evaluation recommended conservative management. A nasogastric tube was placed, and IV antibiotics and methylprednisolone were initiated. The patient clinically improved and was transitioned to oral prednisone and a regular diet. CRP improved to 14.6 mg/L; fecal calprotectin decreased to 222 μg/g. Colonoscopy was deferred due to obstruction. Small bowel follow-through was unremarkable. TPMT testing confirmed normal metabolism.
Vedolizumab was denied by insurance. Given suspicion for evolving fistulizing disease, infliximab with azathioprine was selected. Biologic initiation was deferred for 2 weeks to allow infection control.
Discussion: This case highlights the complexity of initiating biologic therapy in CD complicated by obstruction and possible infection. Imaging played a crucial role when endoscopy was contraindicated. Early identification of fistulizing disease is critical, and anti-TNF combination therapy remains the standard in this setting. Multidisciplinary coordination with surgery, infectious disease, and pharmacy facilitated safe initiation of appropriate long-term treatment.
Timely recognition and treatment of early fistulizing CD are essential. When infection or obstruction precludes immediate therapy, a cautious, coordinated approach allows for stabilization and optimized treatment outcomes.
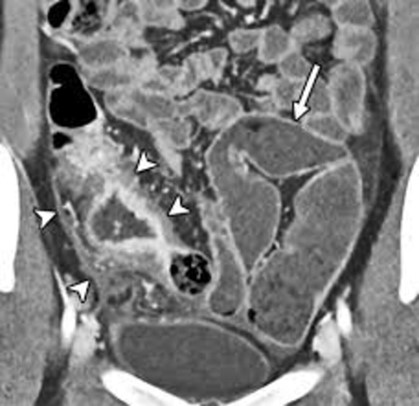
Figure: • Multifocal ileal strictures over 15 cm of the ileum. Pre-stenotic bowel wall dilatation to 4 cm.
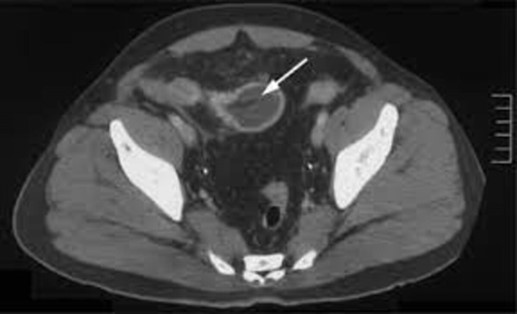
Figure: Transition point is in the RLQ at the terminal ileum, demonstrating circumferential mural thickening & surrounding inflammatory changes.
Disclosures:
Wael Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Omar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rowe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nathan Tofteland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William Salyers indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wael T. Mohamed, MD1, Mohamed A. Omar, MD1, Kyle Rowe, MD1, Nathan Tofteland, MD1, William J.. Salyers, MD, MPH2. P3391 - Acute Fibrostenotic and Fistulizing Ileal Crohn’s Disease: Timing of Biologic Therapy in the Setting of Obstruction and Infection, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine - Wichita, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic relapsing inflammatory disorder with highly variable phenotypes. Patients with stricturing and/or fistulizing disease are at increased risk for surgery and long-term disability. Biologic therapies, especially anti-TNF agents, are effective in altering disease progression when initiated early. However, acute complications such as obstruction or suspected infection may delay therapy, complicating management.
Case Description/
Methods: A 30-year-old biologic-naïve female with stricturing ileal CD diagnosed in 2020 (baseline fecal calprotectin 5,000 μg/g) presented with worsening abdominal pain while on prednisone 40 mg daily pending biologic approval. Labs showed leukocytosis (WBC 20,000/μL) and CRP 30.2 mg/L. CT abdomen/pelvis revealed small bowel obstruction at the terminal ileum with circumferential thickening and an adjacent enhancing collection with punctate air, suggestive of early fistula formation. A second fluid collection between the bladder and uterus was suspicious for phlegmon or early abscess.
Surgical evaluation recommended conservative management. A nasogastric tube was placed, and IV antibiotics and methylprednisolone were initiated. The patient clinically improved and was transitioned to oral prednisone and a regular diet. CRP improved to 14.6 mg/L; fecal calprotectin decreased to 222 μg/g. Colonoscopy was deferred due to obstruction. Small bowel follow-through was unremarkable. TPMT testing confirmed normal metabolism.
Vedolizumab was denied by insurance. Given suspicion for evolving fistulizing disease, infliximab with azathioprine was selected. Biologic initiation was deferred for 2 weeks to allow infection control.
Discussion: This case highlights the complexity of initiating biologic therapy in CD complicated by obstruction and possible infection. Imaging played a crucial role when endoscopy was contraindicated. Early identification of fistulizing disease is critical, and anti-TNF combination therapy remains the standard in this setting. Multidisciplinary coordination with surgery, infectious disease, and pharmacy facilitated safe initiation of appropriate long-term treatment.
Timely recognition and treatment of early fistulizing CD are essential. When infection or obstruction precludes immediate therapy, a cautious, coordinated approach allows for stabilization and optimized treatment outcomes.

Figure: • Multifocal ileal strictures over 15 cm of the ileum. Pre-stenotic bowel wall dilatation to 4 cm.

Figure: Transition point is in the RLQ at the terminal ileum, demonstrating circumferential mural thickening & surrounding inflammatory changes.
Disclosures:
Wael Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Omar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyle Rowe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nathan Tofteland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William Salyers indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wael T. Mohamed, MD1, Mohamed A. Omar, MD1, Kyle Rowe, MD1, Nathan Tofteland, MD1, William J.. Salyers, MD, MPH2. P3391 - Acute Fibrostenotic and Fistulizing Ileal Crohn’s Disease: Timing of Biologic Therapy in the Setting of Obstruction and Infection, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
