Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3389 - Rapid Development of Malignancy in the Context of Crohn’s Disease: A Case of Ileocecal Valve Tumor Following Treatment With Risankizumab
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- ST
Sobaan Taj, MD
AdventHealth
Orlando, Florida
Presenting Author(s)
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Sobaan Taj, MD2, Ilan Aharoni, MD3
1AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel condition treated increasingly with biologic agents, including IL-23 inhibitors like risankizumab. While these therapies have improved disease control, their long-term safety—particularly concerning malignancy risk—remains under investigation. Interdigitating dendritic cell sarcoma (IDCS) is an extremely rare neoplasm of antigen-presenting cells, typically aggressive and seldom reported in the gastrointestinal tract. We present a rare case of IDCS in the ileocecal valve of a young woman with CD shortly after starting risankizumab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 27-year-old female with ileocolonic CD, diagnosed in 2017, had previously achieved remission with infliximab. In early 2023, she developed an ileocecal valve (ICV) stricture with mucosal inflammation. Biopsy showed inflammatory changes. Following complications from a hepatic abscess, infliximab was discontinued and she was transitioned to risankizumab in April 2024. Her symptoms initially improved.
In November 2024, a surveillance colonoscopy revealed a partially obstructing mass at the ICV. Biopsy showed a high-grade epithelioid and spindle cell neoplasm with focal S-100 positivity and negative results for other sarcoma and carcinoma markers (Figure 1). She underwent a right hemicolectomy in January 2025. Final pathology revealed a 0.5 cm mucosal spindle cell tumor consistent with IDCS, positive for S-100, CD4, CD163, and SMA (Figure 2). The tumor's small size and confinement to the mucosa suggested an indolent clinical course. The patient remains stable on follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights a rare malignancy in a young patient with CD treated with risankizumab. IDCS is an aggressive tumor derived from dendritic antigen-presenting cells, rarely seen in the gastrointestinal tract. The rapid onset of tumor development following risankizumab initiation raises concern for a potential, though unproven, association. IL-23 blockade may alter immune surveillance mechanisms, potentially contributing to tumorigenesis, particularly in the context of chronic intestinal inflammation.
While biologics are generally well tolerated, clinicians must remain vigilant for rare but serious adverse events, including malignancies. This case underscores the need for routine surveillance in high-risk patients and further study into the oncologic safety of newer biologic therapies in inflammatory bowel disease.
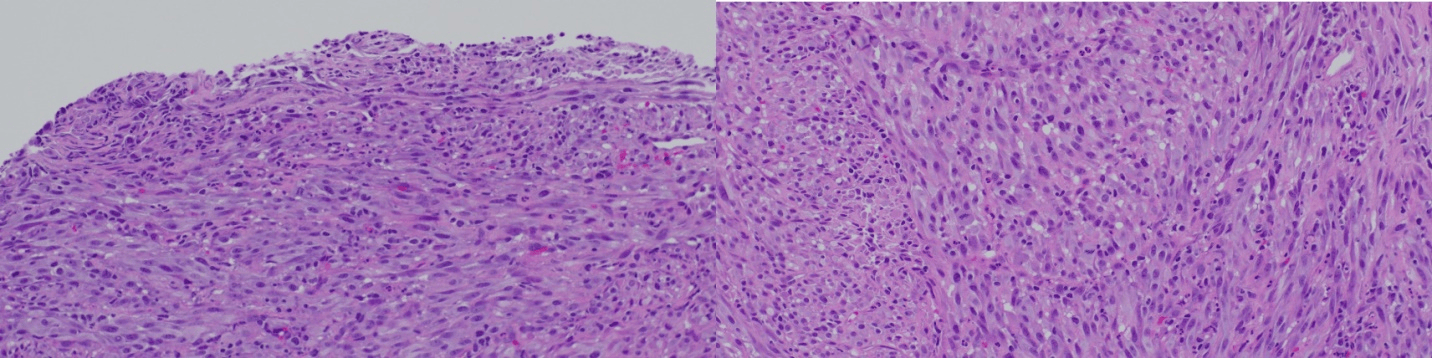
Figure: Figure 1: Histological sections from biopsy of tumor in colon showing epithelioid and spindle cell carcinoma
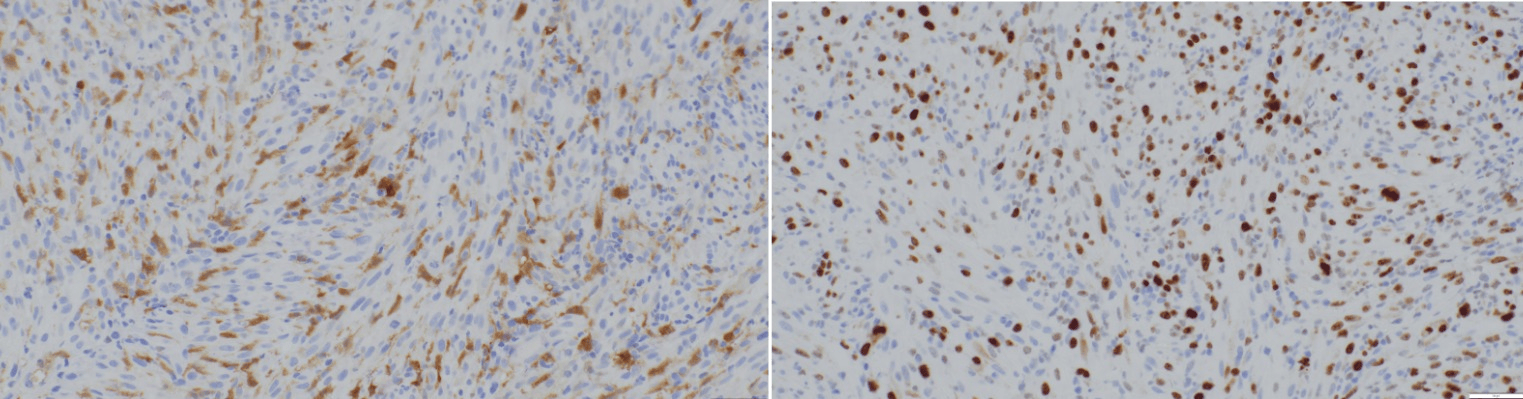
Figure: Figure 2: Immunohistochemistry of specimen from tumor site demonstrating focal S100 expression
Disclosures:
Nouman Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sobaan Taj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ilan Aharoni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Sobaan Taj, MD2, Ilan Aharoni, MD3. P3389 - Rapid Development of Malignancy in the Context of Crohn’s Disease: A Case of Ileocecal Valve Tumor Following Treatment With Risankizumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel condition treated increasingly with biologic agents, including IL-23 inhibitors like risankizumab. While these therapies have improved disease control, their long-term safety—particularly concerning malignancy risk—remains under investigation. Interdigitating dendritic cell sarcoma (IDCS) is an extremely rare neoplasm of antigen-presenting cells, typically aggressive and seldom reported in the gastrointestinal tract. We present a rare case of IDCS in the ileocecal valve of a young woman with CD shortly after starting risankizumab.
Case Description/
Methods: A 27-year-old female with ileocolonic CD, diagnosed in 2017, had previously achieved remission with infliximab. In early 2023, she developed an ileocecal valve (ICV) stricture with mucosal inflammation. Biopsy showed inflammatory changes. Following complications from a hepatic abscess, infliximab was discontinued and she was transitioned to risankizumab in April 2024. Her symptoms initially improved.
In November 2024, a surveillance colonoscopy revealed a partially obstructing mass at the ICV. Biopsy showed a high-grade epithelioid and spindle cell neoplasm with focal S-100 positivity and negative results for other sarcoma and carcinoma markers (Figure 1). She underwent a right hemicolectomy in January 2025. Final pathology revealed a 0.5 cm mucosal spindle cell tumor consistent with IDCS, positive for S-100, CD4, CD163, and SMA (Figure 2). The tumor's small size and confinement to the mucosa suggested an indolent clinical course. The patient remains stable on follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights a rare malignancy in a young patient with CD treated with risankizumab. IDCS is an aggressive tumor derived from dendritic antigen-presenting cells, rarely seen in the gastrointestinal tract. The rapid onset of tumor development following risankizumab initiation raises concern for a potential, though unproven, association. IL-23 blockade may alter immune surveillance mechanisms, potentially contributing to tumorigenesis, particularly in the context of chronic intestinal inflammation.
While biologics are generally well tolerated, clinicians must remain vigilant for rare but serious adverse events, including malignancies. This case underscores the need for routine surveillance in high-risk patients and further study into the oncologic safety of newer biologic therapies in inflammatory bowel disease.

Figure: Figure 1: Histological sections from biopsy of tumor in colon showing epithelioid and spindle cell carcinoma

Figure: Figure 2: Immunohistochemistry of specimen from tumor site demonstrating focal S100 expression
Disclosures:
Nouman Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sobaan Taj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ilan Aharoni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Sobaan Taj, MD2, Ilan Aharoni, MD3. P3389 - Rapid Development of Malignancy in the Context of Crohn’s Disease: A Case of Ileocecal Valve Tumor Following Treatment With Risankizumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
