Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3381 - Aseptic Abscess Syndrome Causing Repeat Liver Abscess in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Lauren Healey, DO (she/her/hers)
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Lauren Healey, DO1, Hobie L. Hughes, DO2, Shausha Farooq, MD1, Katherine Glosemeyer, MD1
1University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2Thomas Hospital, Fairhope, AL
Introduction: Aseptic abscess syndrome (AAS) is a rare inflammatory disorder that can be associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). AAS is characterized by circumscribed, PMN-rich, sterile lesions. The literature on AAS is limited.
Case Description/
Methods: 18-year-old female with ulcerative colitis and one prior liver abscess who presented for follow-up on a liver ultrasound suggestive of a new liver abscess. The patient was previously hospitalized in July for a liver abscess measuring 5.8 x 4.7 x 5.9 cm. The abscess was drained, and she completed 3 weeks of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole for antimicrobial therapy. Her body fluid cultures from the abscess remained negative. She presented for a follow-up liver ultrasound, where a new collection measuring 7.5 x 6.8 x 3.5 cm was noted. She denied any acute complaints on evaluation. She was previously on infliximab-dyyb infusions; however, she had missed several doses secondary to loss of insurance. Labs were significant for a white blood cell count of 4.97, alkaline phosphatase of 86, ALT < 10 and AST 18, all within normal limits. C-reactive protein was 1.2, and Erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 98. Stool entamoeba histolytica was negative. Giardia antigen, cryptosporidium antigen, stool cultures were all negative. Stool calprotectin was 2260. MRI during her admission showed findings compatible with abscess interposed between the lateral aspect of the liver and abdominal wall measuring approximately 5.2 x 2.4 x 6.3 cm. She underwent percutaneous drainage with interventional radiology that yielded purulent drainage. Her drain output remained minimal at less than 50cc throughout her hospitalization. Fungal, acid-fast bacilli, and bacterial culture from the abscess remained negative. She was initially started on Piperacillin-Tazobactam and metronidazole for coverage of an intra-abdominal abscess, however these were discontinued following negative cultures. She re-started her infliximab-dyyb therapy with no abscess recurrence at 3 months.
Discussion: Aseptic abscess syndrome is a manifestation of systemic inflammatory conditions and is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnosis is made through aspiration of the abscess which typically yields sterile collections of neutrophils. Abscesses can occur in a variety of organs including the spleen, skin, liver, lymph nodes, and lungs. Because many patients with IBD are on immunosuppression, each abscess should be considered infectious until proven otherwise.
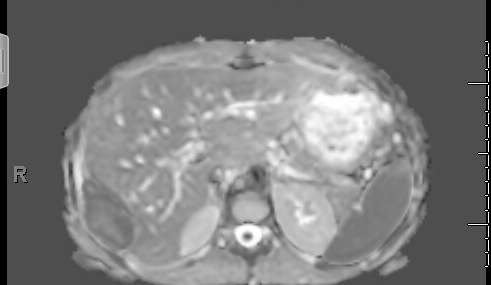
Figure: Loculated fluid collection measuring 5.2x2.4x6.3 cm
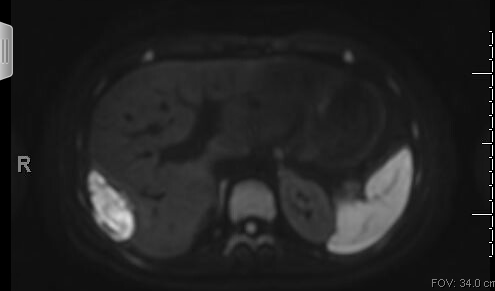
Figure: Loculated fluid collection measuring 5.2x2.4x6.3 cm
Disclosures:
Lauren Healey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hobie Hughes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shausha Farooq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katherine Glosemeyer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lauren Healey, DO1, Hobie L. Hughes, DO2, Shausha Farooq, MD1, Katherine Glosemeyer, MD1. P3381 - Aseptic Abscess Syndrome Causing Repeat Liver Abscess in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2Thomas Hospital, Fairhope, AL
Introduction: Aseptic abscess syndrome (AAS) is a rare inflammatory disorder that can be associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). AAS is characterized by circumscribed, PMN-rich, sterile lesions. The literature on AAS is limited.
Case Description/
Methods: 18-year-old female with ulcerative colitis and one prior liver abscess who presented for follow-up on a liver ultrasound suggestive of a new liver abscess. The patient was previously hospitalized in July for a liver abscess measuring 5.8 x 4.7 x 5.9 cm. The abscess was drained, and she completed 3 weeks of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole for antimicrobial therapy. Her body fluid cultures from the abscess remained negative. She presented for a follow-up liver ultrasound, where a new collection measuring 7.5 x 6.8 x 3.5 cm was noted. She denied any acute complaints on evaluation. She was previously on infliximab-dyyb infusions; however, she had missed several doses secondary to loss of insurance. Labs were significant for a white blood cell count of 4.97, alkaline phosphatase of 86, ALT < 10 and AST 18, all within normal limits. C-reactive protein was 1.2, and Erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 98. Stool entamoeba histolytica was negative. Giardia antigen, cryptosporidium antigen, stool cultures were all negative. Stool calprotectin was 2260. MRI during her admission showed findings compatible with abscess interposed between the lateral aspect of the liver and abdominal wall measuring approximately 5.2 x 2.4 x 6.3 cm. She underwent percutaneous drainage with interventional radiology that yielded purulent drainage. Her drain output remained minimal at less than 50cc throughout her hospitalization. Fungal, acid-fast bacilli, and bacterial culture from the abscess remained negative. She was initially started on Piperacillin-Tazobactam and metronidazole for coverage of an intra-abdominal abscess, however these were discontinued following negative cultures. She re-started her infliximab-dyyb therapy with no abscess recurrence at 3 months.
Discussion: Aseptic abscess syndrome is a manifestation of systemic inflammatory conditions and is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnosis is made through aspiration of the abscess which typically yields sterile collections of neutrophils. Abscesses can occur in a variety of organs including the spleen, skin, liver, lymph nodes, and lungs. Because many patients with IBD are on immunosuppression, each abscess should be considered infectious until proven otherwise.

Figure: Loculated fluid collection measuring 5.2x2.4x6.3 cm

Figure: Loculated fluid collection measuring 5.2x2.4x6.3 cm
Disclosures:
Lauren Healey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hobie Hughes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shausha Farooq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katherine Glosemeyer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lauren Healey, DO1, Hobie L. Hughes, DO2, Shausha Farooq, MD1, Katherine Glosemeyer, MD1. P3381 - Aseptic Abscess Syndrome Causing Repeat Liver Abscess in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
