Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3335 - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Virtual Reality Support Tool in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Mild-to-Moderate Anxiety Is Feasible and Reduces Anxiety and Pain
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AG
Alvin George, MD (he/him/his)
University of Chicago Medicine, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Alvin George, MD1, Alexandra McDermott, BS1, Alyse Bedell, PhD2, Alexandra R.. Hannett, 1, Jessica Tanouye, 1, Rajsavi Anand, MD3, Omer Liran, MD, MSHS3, Allistair Clark, MA3, Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS3, David T. Rubin, MD4
1University of Chicago Medicine, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL; 2University of Chicago, Chicago, IL; 3Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 4University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Anxiety is prevalent in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based intervention for anxiety, but access to this and other psychotherapies is limited. We investigated the feasibility of an artificial intelligence (AI)-supported conversational avatar within a virtual reality (VR) environment to deliver mental health support to patients with CD or UC and mild-to-moderate anxiety.
Methods: The eXtended-reality Artificial Intelligence Assistant (XAIA, Cedars-Sinai, Los Angeles), a previously developed AI-enabled, mental health support program, was administered using a VR headset (Apple Vision Pro, Cupertino, CA). Patients following at the University of Chicago with CD or UC and a generalized anxiety disorder-7 (GAD-7) score of 5-14 were prospectively recruited. Participants engaged in a private 30-minute session with XAIA. Demographics were collected, and clinical disease activity was defined as Harvey Bradshaw Index >5 for CD or Simplified Clinical Colitis Activity Index >2 for UC. Participants completed Spielberg State Trait Anxiety Inventory and visual analog pain scales before and after the session. Following the VR experience, a semi-structured debrief interview was completed, and its transcription was reviewed for thematic content analysis.
Results: Among the 14 participants, 7 (50%) had CD, 13 (93%) were female, 9 (64%) identified as White, 12 (86%) never smoked, 6 (43%) were receiving medication for a mental health disorder, and 5 (36%) had a clinical diagnosis of depression (Table 1). Four patients (29%) had clinically active disease at the time of study participation. After completing one session with XAIA, participants noted improvement in total state-trait anxiety scores (96 vs 83, p=0.01) and in visual analog pain scores (mean 2.7 vs 2.1, p=0.03) (Figure 1). Thematic analysis demonstrated 196 first-level codes, and saturation was achieved (Figure 2). Adverse events only included mild discomfort due to the weight of the headset.
Discussion: The use of a self-administered mental health support tool using AI-enabled CBT in an immersive VR environment is feasible and well tolerated in patients with CD or UC and mild-to-moderate anxiety. Participants noted significant improvement in state trait anxiety and visual analog pain scores after one session, supporting further study of this tool for short- and longer-term benefit in patients with CD or UC.
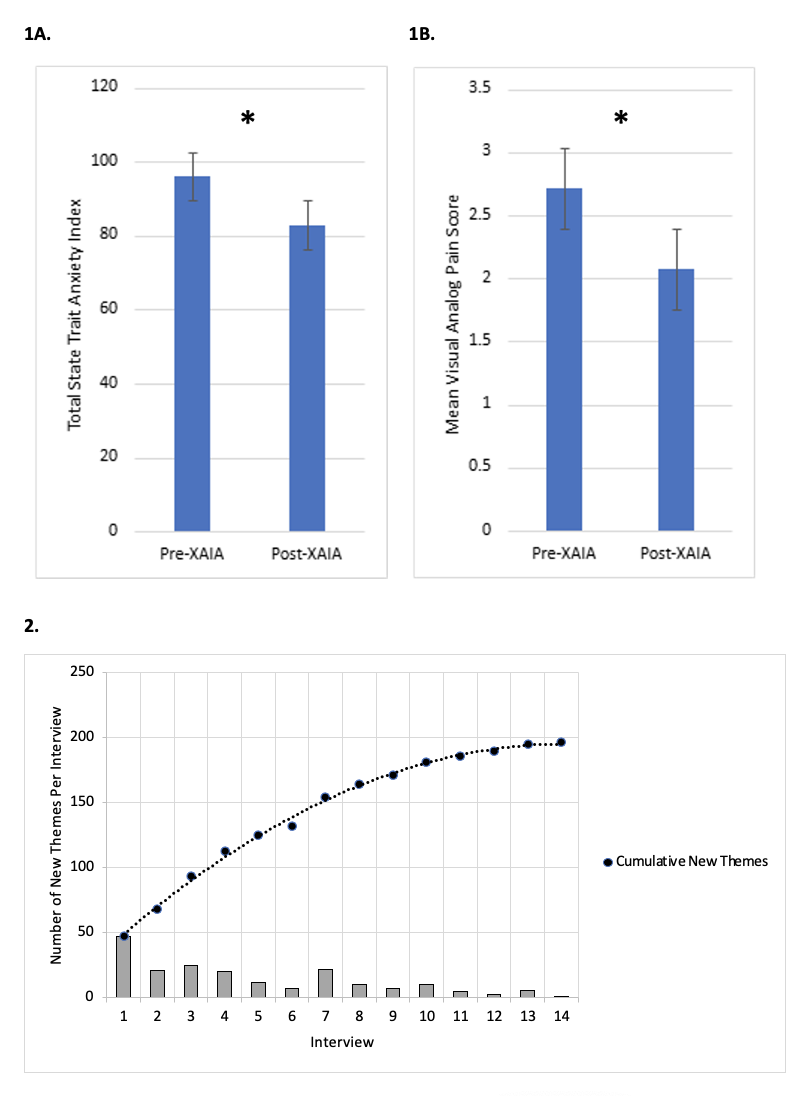
Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics (n=14)
Figure: Figure 1. Surveys completed before and after one session with XAIA reveal improvement in A) total state trait anxiety scores (p=0.01) and B) visual analog pain scores (p=0.03). Figure 2. Cumulative first-level codes over 14 participant interviews. An inflection point suggesting thematic saturation was noted at patient 9.
Disclosures:
Alvin George indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexandra McDermott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alyse Bedell indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexandra Hannett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessica Tanouye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajsavi Anand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Liran: Xaia – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Royalties, Stock-privately held company.
Allistair Clark indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brennan Spiegel: Exact Sciences – Consultant. Freenome – Consultant. Guardant Health – Consultant.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Abivax SA – Consultant. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker feees, Stock Options. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Bausch Health – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant. Cornerstones Health, Inc – Board of Directors membership. Douglas Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Co. – Consultant. Foresee, Genentech (Roche) Inc. – Consultant. Image Analysis Group – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Stock Options. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker fees. Throne – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Alvin George, MD1, Alexandra McDermott, BS1, Alyse Bedell, PhD2, Alexandra R.. Hannett, 1, Jessica Tanouye, 1, Rajsavi Anand, MD3, Omer Liran, MD, MSHS3, Allistair Clark, MA3, Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS3, David T. Rubin, MD4. P3335 - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Virtual Reality Support Tool in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Mild-to-Moderate Anxiety Is Feasible and Reduces Anxiety and Pain, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Chicago Medicine, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL; 2University of Chicago, Chicago, IL; 3Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 4University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Anxiety is prevalent in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based intervention for anxiety, but access to this and other psychotherapies is limited. We investigated the feasibility of an artificial intelligence (AI)-supported conversational avatar within a virtual reality (VR) environment to deliver mental health support to patients with CD or UC and mild-to-moderate anxiety.
Methods: The eXtended-reality Artificial Intelligence Assistant (XAIA, Cedars-Sinai, Los Angeles), a previously developed AI-enabled, mental health support program, was administered using a VR headset (Apple Vision Pro, Cupertino, CA). Patients following at the University of Chicago with CD or UC and a generalized anxiety disorder-7 (GAD-7) score of 5-14 were prospectively recruited. Participants engaged in a private 30-minute session with XAIA. Demographics were collected, and clinical disease activity was defined as Harvey Bradshaw Index >5 for CD or Simplified Clinical Colitis Activity Index >2 for UC. Participants completed Spielberg State Trait Anxiety Inventory and visual analog pain scales before and after the session. Following the VR experience, a semi-structured debrief interview was completed, and its transcription was reviewed for thematic content analysis.
Results: Among the 14 participants, 7 (50%) had CD, 13 (93%) were female, 9 (64%) identified as White, 12 (86%) never smoked, 6 (43%) were receiving medication for a mental health disorder, and 5 (36%) had a clinical diagnosis of depression (Table 1). Four patients (29%) had clinically active disease at the time of study participation. After completing one session with XAIA, participants noted improvement in total state-trait anxiety scores (96 vs 83, p=0.01) and in visual analog pain scores (mean 2.7 vs 2.1, p=0.03) (Figure 1). Thematic analysis demonstrated 196 first-level codes, and saturation was achieved (Figure 2). Adverse events only included mild discomfort due to the weight of the headset.
Discussion: The use of a self-administered mental health support tool using AI-enabled CBT in an immersive VR environment is feasible and well tolerated in patients with CD or UC and mild-to-moderate anxiety. Participants noted significant improvement in state trait anxiety and visual analog pain scores after one session, supporting further study of this tool for short- and longer-term benefit in patients with CD or UC.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics (n=14)

Figure: Figure 1. Surveys completed before and after one session with XAIA reveal improvement in A) total state trait anxiety scores (p=0.01) and B) visual analog pain scores (p=0.03). Figure 2. Cumulative first-level codes over 14 participant interviews. An inflection point suggesting thematic saturation was noted at patient 9.
Disclosures:
Alvin George indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexandra McDermott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alyse Bedell indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexandra Hannett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessica Tanouye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajsavi Anand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omer Liran: Xaia – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Royalties, Stock-privately held company.
Allistair Clark indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brennan Spiegel: Exact Sciences – Consultant. Freenome – Consultant. Guardant Health – Consultant.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Abivax SA – Consultant. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker feees, Stock Options. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Bausch Health – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant. Cornerstones Health, Inc – Board of Directors membership. Douglas Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Co. – Consultant. Foresee, Genentech (Roche) Inc. – Consultant. Image Analysis Group – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Stock Options. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker fees. Throne – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Alvin George, MD1, Alexandra McDermott, BS1, Alyse Bedell, PhD2, Alexandra R.. Hannett, 1, Jessica Tanouye, 1, Rajsavi Anand, MD3, Omer Liran, MD, MSHS3, Allistair Clark, MA3, Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS3, David T. Rubin, MD4. P3335 - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Virtual Reality Support Tool in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Mild-to-Moderate Anxiety Is Feasible and Reduces Anxiety and Pain, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
