Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3227 - Comparative Efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Maintenance Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mulham Alom, MD
Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine
Springfield, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Bisher Sawaf, MD1, Mulham Alom, MD2, Mohammad Al Hayek, MD3, Muhammed Elhadi, MD4, Ahmad Kasem, MSc5, Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS6, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD7, Shahem Abbarh, MD8, Amine Rakab, MD9, Miguel Regueiro, MD10, Yaseen Alastal, MD11
1University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 2Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 3Damascus University, Dimashq, Dimashq, Syria; 4College of Medicine, Korea University, Seongbuk, Seoul-t'ukpyolsi, Republic of Korea; 5David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 6Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sana'a, Hadramawt, Yemen; 7The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 8Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 9Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 10Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 11University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease requiring long-term treatment to maintain remission and prevent relapse. Biologic therapies targeting interleukin (IL)-12/23 and IL-23 pathways have emerged as effective options for patients with moderate to severe disease. However, direct comparisons between individual IL-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors are lacking in the current literature, making it challenging to determine their relative efficacy.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov for randomized clinical trials. A Bayesian network meta-analysis was conducted to compare the efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors for maintenance therapy in Crohn’s disease, allowing for indirect comparisons across interventions. Primary outcomes were clinical remission and corticosteroid-free clinical remission. Relative risks (RRs), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) probabilities were calculated to rank treatments according to their likelihood of being the most effective.
Results: A total of 2,281 patients were enrolled across five clinical trials during the maintenance phase. Among them, 659 were treated with ustekinumab, 63 with guselkumab, 396 with risankizumab, 579 with mirikizumab, and 496 received a placebo. Although no statistically significant differences were observed between the treatment groups and placebo during the maintenance period, SUCRA rankings indicated that guselkumab had the highest rate of clinical remission (73.6%). Risankizumab demonstrated the greatest corticosteroid-free clinical remission rate (RR: 2.37; 95% CI: 1.64–3.42, SUCRA: 88.8%) compared to placebo, and it also showed a statistically significant advantage over ustekinumab (RR: 1.51; 95% CI: 1.26–1.80).
Discussion: Although no statistically significant differences for clinical remission were observed between treatments or versus placebo, all IL-12/23– and IL–23–targeted therapies ranked higher than placebo for corticosteroid-free remission based on SUCRA analysis. Between the treatments, only risankizumab showed a statistically significant benefit over ustekinumab. These findings underscore the potential efficacy of these agents and the need for head-to-head trials to confirm their comparative performance.
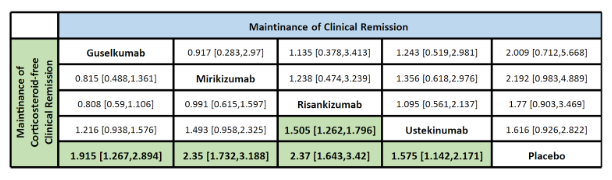
Figure: Table 1 - Maintenance of clinical remission & corticosteroid-free clinical remission
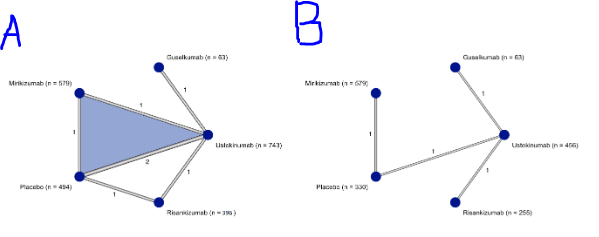
Figure: Figure 1A - Maintenance of Clinical Remission
Figure 1B - Maintenance of corticosteroid-free clinical remission
Disclosures:
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Al Hayek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammed Elhadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Kasem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Beshr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Regueiro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Celegene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf, MD1, Mulham Alom, MD2, Mohammad Al Hayek, MD3, Muhammed Elhadi, MD4, Ahmad Kasem, MSc5, Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS6, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD7, Shahem Abbarh, MD8, Amine Rakab, MD9, Miguel Regueiro, MD10, Yaseen Alastal, MD11. P3227 - Comparative Efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Maintenance Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 2Internal Medicine, Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, IL; 3Damascus University, Dimashq, Dimashq, Syria; 4College of Medicine, Korea University, Seongbuk, Seoul-t'ukpyolsi, Republic of Korea; 5David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 6Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sana'a, Hadramawt, Yemen; 7The University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 8Georgetown University MedStar Health, Baltimore, WA; 9Division of Medical Education, Weill Cornell Medicine, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 10Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 11University of Toledo, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease requiring long-term treatment to maintain remission and prevent relapse. Biologic therapies targeting interleukin (IL)-12/23 and IL-23 pathways have emerged as effective options for patients with moderate to severe disease. However, direct comparisons between individual IL-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors are lacking in the current literature, making it challenging to determine their relative efficacy.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov for randomized clinical trials. A Bayesian network meta-analysis was conducted to compare the efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 inhibitors for maintenance therapy in Crohn’s disease, allowing for indirect comparisons across interventions. Primary outcomes were clinical remission and corticosteroid-free clinical remission. Relative risks (RRs), 95% confidence intervals (CI), and surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) probabilities were calculated to rank treatments according to their likelihood of being the most effective.
Results: A total of 2,281 patients were enrolled across five clinical trials during the maintenance phase. Among them, 659 were treated with ustekinumab, 63 with guselkumab, 396 with risankizumab, 579 with mirikizumab, and 496 received a placebo. Although no statistically significant differences were observed between the treatment groups and placebo during the maintenance period, SUCRA rankings indicated that guselkumab had the highest rate of clinical remission (73.6%). Risankizumab demonstrated the greatest corticosteroid-free clinical remission rate (RR: 2.37; 95% CI: 1.64–3.42, SUCRA: 88.8%) compared to placebo, and it also showed a statistically significant advantage over ustekinumab (RR: 1.51; 95% CI: 1.26–1.80).
Discussion: Although no statistically significant differences for clinical remission were observed between treatments or versus placebo, all IL-12/23– and IL–23–targeted therapies ranked higher than placebo for corticosteroid-free remission based on SUCRA analysis. Between the treatments, only risankizumab showed a statistically significant benefit over ustekinumab. These findings underscore the potential efficacy of these agents and the need for head-to-head trials to confirm their comparative performance.

Figure: Table 1 - Maintenance of clinical remission & corticosteroid-free clinical remission

Figure: Figure 1A - Maintenance of Clinical Remission
Figure 1B - Maintenance of corticosteroid-free clinical remission
Disclosures:
Bisher Sawaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mulham Alom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Al Hayek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammed Elhadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Kasem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Beshr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yusuf Omar Hallak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahem Abbarh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amine Rakab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Regueiro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Celegene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bisher Sawaf, MD1, Mulham Alom, MD2, Mohammad Al Hayek, MD3, Muhammed Elhadi, MD4, Ahmad Kasem, MSc5, Mohammed S. Beshr, MBBS6, Yusuf Omar Hallak, MD7, Shahem Abbarh, MD8, Amine Rakab, MD9, Miguel Regueiro, MD10, Yaseen Alastal, MD11. P3227 - Comparative Efficacy of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Maintenance Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

