Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3192 - Effects of Subcutaneous Guselkumab Induction and Maintenance on Histologic Outcomes in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease in GRAVITI, a Phase 3 Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Treat-Through Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG
Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Geert R. D’Haens, MD, PhD1, Ailsa Hart, BA, BMBCh, PhD2, Remo Panaccione, MD3, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MACG4, Qian Cao, MD, PhD5, Mobolaji Olurinde, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD6, Patrick Branigan, BS6, Wilbert van Duijnhoven, MSc7, Nat A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD8, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD9, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG10
1Department of Gastroenterology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, Netherlands; 2London North-West University Healthcare NHS Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 3Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unit, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, Calgary, AB, Canada; 4Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 5Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China; 6Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 7Johnson & Johnson, Antwerp, Antwerpen, Belgium; 8Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 9Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 10Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS) is a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor that was efficacious in double-blind, placebo-controlled, treat-through trials in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD) using IV induction and SC maintenance (GALAXI 2 & 3) or SC induction and maintenance (GRAVITI). Assessment of histologic disease activity is becoming increasingly important as a measure of treatment efficacy. Here we report histologic outcomes at Weeks (W) 12 & 48 from GRAVITI.
Methods: Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 400mg SC q4w→200mg SC q4w, GUS 400mg SC q4w→100mg SC q8w, or PBO. Biopsies were obtained from the most affected area (or if no disease activity present, normal-appearing mucosa) in 5 segments: terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and rectum. Histologic response, histologic remission, and the composite endpoints of histo-endoscopic response and histo-endoscopic remission were evaluated using Robarts Histopathology Index (RHI), Global Histologic Activity Score (GHAS), and Geboes scoring. Histologic response was assessed in pts with baseline histologic disease; histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission were assessed in the full analysis set (definitions in table legend). Pts who met rescue criteria at W16 were considered non-responders at W48. Histologic endpoints in GRAVITI were exploratory and not controlled for multiple comparisons; p-values are nominal.
Results: Of the 347 pts in the full analysis set, 273 (78.7%) had baseline histologic disease per RHI score. SC induction with GUS (400mg SC at W0, W4, & W8) resulted in greater rates of histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission compared to placebo at W12 (Table). At W48, greater proportions of pts receiving GUS 100mg SC q8w or GUS 200mg SC q4w maintenance also achieved histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission compared to PBO. Comparable outcomes were observed using GHAS or Geboes scoring criteria.
Discussion: Compared to PBO, pts with moderately to severely active CD receiving SC induction and maintenance treatment with GUS achieved greater rates of histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission through W48. These results support the use of histologic and composite histologic and endoscopic endpoints as a measure of CD activity, and the efficacy of SC guselkumab in CD.
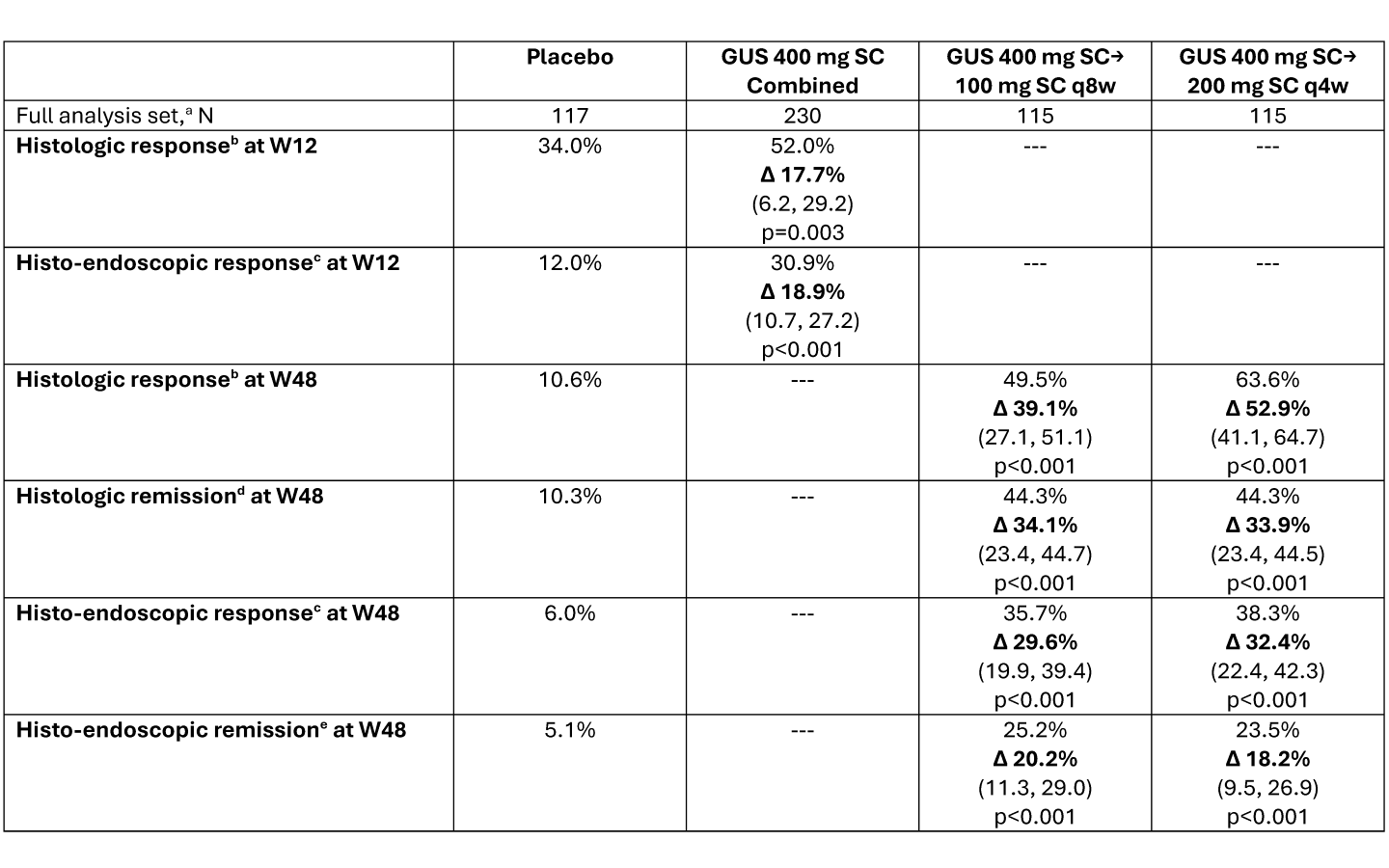
Figure: Data presented as percentage of participants attaining the endpoint, with adjusted treatment difference (Δ), (95% confidence interval), and nominal p-value versus placebo. Adjusted treatment differences, 95% CIs, and p-values were based on the common risk difference by use of Mantel-Haenszel stratum weights and the Sato variance estimator, using stratification factors of baseline CDAI score (≤300 or >300), baseline SES-CD (≤12 or >12), and prior history of inadequate response or intolerance to biologics (Yes or No).
Participants who had a CD-related surgery (with the exception of minor procedures such as drainage of a superficial abscess or seton placement, etc.), had a prohibited change in CD medication, discontinued study intervention for any reason (other than COVID-19 related reasons [excluding COVID-19 infection] or regional crisis), or met rescue criteria (only applicable after Week 16) were considered not to have met the endpoint at the designated timepoint. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis had their observed data used, if available. After accounting for the aforementioned data handling rules, participants who were missing data pertaining to an endpoint at a designated timepoint were considered not to have achieved the endpoint.
DEFINITIONS: a. Full analysis set: all randomized participants who received ≥1 dose of study medication.
b. Histologic response: ≥50% reduction in RHI score from baseline or a score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils and neutrophils in epithelium must be equal to 0, with no ulcers or erosions. Assessed in participants in the full analysis set with baseline histologic disease, defined as RHI score > 0 for any of Items 2-4 of RHI (lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in epithelium, or erosions or ulcerations); N = placebo (94), GUS 400mg SC Combined (179), GUS 400mg SC→100mg SC q8w (91), GUS 400mg SC→200mg SC q4w (88).
c. Histo-endoscopic response: ≥50% reduction in RHI score from baseline or a score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils and neutrophils in epithelium must be equal to 0, with no ulcers or erosions AND ≥50% improvement from baseline in SES-CD or SES-CD ≤ 2. Assessed in the full analysis set.
d. Histologic remission: RHI score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in the epithelium and erosions or ulcerations equal to 0. Assessed in the full analysis set.
e. Histo-endoscopic remission: RHI score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in the epithelium and erosions or ulcerations equal to 0 AND SES-CD ≤ 4 and at least a 2-point reduction from baseline and no subscore greater than 1 in any individual component. Assessed in the full analysis set.
Disclosures:
Geert D’Haens: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Agomab – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AMT – Consultant. Anaptys Bio – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Exeliom – Consultant. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Glaxo Smith Kline – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Gossamerbio – Consultant. Immunic – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Kaleido – Consultant. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Origo – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Polpharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Procise Diagnostics – Consultant. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Seres Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Tillotts – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ailsa Hart: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Falk – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Galapagos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. GSK – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Lecturer. MSD – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer.
Remo Panaccione: Abbott – Consultant. AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Abivax – Consultant. Alimentiv – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Biogen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Celltrion – Consultant. Cosmos Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eisai – Consultant. Elan Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAMP Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Merck & Co., Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Mirador – Consultant. Mylan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Odyssey – Consultant. Oppilan Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Pandion Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pendopharm G.I. Solutions – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Satisfai Health – Consultant. Shire Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant. Tillots – Consultant. Trellus Health – Consultant. UCB – Consultant. Union Biopharma – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Flavio Steinwurz: Abbvie – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Amgen – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Celltrion – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Ferring – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Pfizer – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Sandoz – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Takeda – Consultant, Speaker, researcher.
Qian Cao: Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Mobolaji Olurinde: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Leonardo Salese: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Patrick Branigan: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Wilbert van Duijnhoven: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nat Terry: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie GK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Boston Scientific Corporation – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Honararium. EA Pharma Co. Ltd. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. JIMRO Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Lilly – Consultant. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd – Consultant. Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Zeria Pharmaceutical Co – Grant/Research Support.
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, speaking fees. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab Therapeutics – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Company – Consultant, speaking fees. Enthera – Consultant. Enveda Biosciences – Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Fzatat – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen R&D – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Stock Options.
Geert R. D’Haens, MD, PhD1, Ailsa Hart, BA, BMBCh, PhD2, Remo Panaccione, MD3, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MACG4, Qian Cao, MD, PhD5, Mobolaji Olurinde, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD6, Patrick Branigan, BS6, Wilbert van Duijnhoven, MSc7, Nat A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD8, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD9, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG10. P3192 - Effects of Subcutaneous Guselkumab Induction and Maintenance on Histologic Outcomes in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease in GRAVITI, a Phase 3 Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Treat-Through Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Geert R. D’Haens, MD, PhD1, Ailsa Hart, BA, BMBCh, PhD2, Remo Panaccione, MD3, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MACG4, Qian Cao, MD, PhD5, Mobolaji Olurinde, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD6, Patrick Branigan, BS6, Wilbert van Duijnhoven, MSc7, Nat A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD8, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD9, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG10
1Department of Gastroenterology, Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, Netherlands; 2London North-West University Healthcare NHS Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 3Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unit, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, Calgary, AB, Canada; 4Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, São Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil; 5Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China; 6Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 7Johnson & Johnson, Antwerp, Antwerpen, Belgium; 8Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 9Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 10Dr. Henry D. Janowitz Division of Gastroenterology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, New York, NY
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS) is a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor that was efficacious in double-blind, placebo-controlled, treat-through trials in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD) using IV induction and SC maintenance (GALAXI 2 & 3) or SC induction and maintenance (GRAVITI). Assessment of histologic disease activity is becoming increasingly important as a measure of treatment efficacy. Here we report histologic outcomes at Weeks (W) 12 & 48 from GRAVITI.
Methods: Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 400mg SC q4w→200mg SC q4w, GUS 400mg SC q4w→100mg SC q8w, or PBO. Biopsies were obtained from the most affected area (or if no disease activity present, normal-appearing mucosa) in 5 segments: terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and rectum. Histologic response, histologic remission, and the composite endpoints of histo-endoscopic response and histo-endoscopic remission were evaluated using Robarts Histopathology Index (RHI), Global Histologic Activity Score (GHAS), and Geboes scoring. Histologic response was assessed in pts with baseline histologic disease; histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission were assessed in the full analysis set (definitions in table legend). Pts who met rescue criteria at W16 were considered non-responders at W48. Histologic endpoints in GRAVITI were exploratory and not controlled for multiple comparisons; p-values are nominal.
Results: Of the 347 pts in the full analysis set, 273 (78.7%) had baseline histologic disease per RHI score. SC induction with GUS (400mg SC at W0, W4, & W8) resulted in greater rates of histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission compared to placebo at W12 (Table). At W48, greater proportions of pts receiving GUS 100mg SC q8w or GUS 200mg SC q4w maintenance also achieved histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission compared to PBO. Comparable outcomes were observed using GHAS or Geboes scoring criteria.
Discussion: Compared to PBO, pts with moderately to severely active CD receiving SC induction and maintenance treatment with GUS achieved greater rates of histologic response, histologic remission, histo-endoscopic response, and histo-endoscopic remission through W48. These results support the use of histologic and composite histologic and endoscopic endpoints as a measure of CD activity, and the efficacy of SC guselkumab in CD.

Figure: Data presented as percentage of participants attaining the endpoint, with adjusted treatment difference (Δ), (95% confidence interval), and nominal p-value versus placebo. Adjusted treatment differences, 95% CIs, and p-values were based on the common risk difference by use of Mantel-Haenszel stratum weights and the Sato variance estimator, using stratification factors of baseline CDAI score (≤300 or >300), baseline SES-CD (≤12 or >12), and prior history of inadequate response or intolerance to biologics (Yes or No).
Participants who had a CD-related surgery (with the exception of minor procedures such as drainage of a superficial abscess or seton placement, etc.), had a prohibited change in CD medication, discontinued study intervention for any reason (other than COVID-19 related reasons [excluding COVID-19 infection] or regional crisis), or met rescue criteria (only applicable after Week 16) were considered not to have met the endpoint at the designated timepoint. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis had their observed data used, if available. After accounting for the aforementioned data handling rules, participants who were missing data pertaining to an endpoint at a designated timepoint were considered not to have achieved the endpoint.
DEFINITIONS: a. Full analysis set: all randomized participants who received ≥1 dose of study medication.
b. Histologic response: ≥50% reduction in RHI score from baseline or a score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils and neutrophils in epithelium must be equal to 0, with no ulcers or erosions. Assessed in participants in the full analysis set with baseline histologic disease, defined as RHI score > 0 for any of Items 2-4 of RHI (lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in epithelium, or erosions or ulcerations); N = placebo (94), GUS 400mg SC Combined (179), GUS 400mg SC→100mg SC q8w (91), GUS 400mg SC→200mg SC q4w (88).
c. Histo-endoscopic response: ≥50% reduction in RHI score from baseline or a score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils and neutrophils in epithelium must be equal to 0, with no ulcers or erosions AND ≥50% improvement from baseline in SES-CD or SES-CD ≤ 2. Assessed in the full analysis set.
d. Histologic remission: RHI score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in the epithelium and erosions or ulcerations equal to 0. Assessed in the full analysis set.
e. Histo-endoscopic remission: RHI score ≤ 3 with sub-scores of lamina propria neutrophils, neutrophils in the epithelium and erosions or ulcerations equal to 0 AND SES-CD ≤ 4 and at least a 2-point reduction from baseline and no subscore greater than 1 in any individual component. Assessed in the full analysis set.
Disclosures:
Geert D’Haens: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Agomab – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AMT – Consultant. Anaptys Bio – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Exeliom – Consultant. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Glaxo Smith Kline – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Gossamerbio – Consultant. Immunic – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Kaleido – Consultant. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Origo – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Polpharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Procise Diagnostics – Consultant. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Seres Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Tillotts – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Ailsa Hart: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Falk – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Galapagos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. GSK – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Lecturer. MSD – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecturer.
Remo Panaccione: Abbott – Consultant. AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Abivax – Consultant. Alimentiv – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Biogen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Celltrion – Consultant. Cosmos Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eisai – Consultant. Elan Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAMP Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Merck & Co., Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Mirador – Consultant. Mylan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Odyssey – Consultant. Oppilan Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Pandion Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pendopharm G.I. Solutions – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Satisfai Health – Consultant. Shire Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker's fees. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant. Tillots – Consultant. Trellus Health – Consultant. UCB – Consultant. Union Biopharma – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Flavio Steinwurz: Abbvie – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Amgen – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Celltrion – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Ferring – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Pfizer – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Sandoz – Consultant, Speaker, researcher. Takeda – Consultant, Speaker, researcher.
Qian Cao: Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Mobolaji Olurinde: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Leonardo Salese: Johnson & Johnson – Employee.
Patrick Branigan: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Wilbert van Duijnhoven: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nat Terry: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie GK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Boston Scientific Corporation – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Honararium. EA Pharma Co. Ltd. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. JIMRO Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Lilly – Consultant. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd – Consultant. Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Zeria Pharmaceutical Co – Grant/Research Support.
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, speaking fees. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab Therapeutics – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Company – Consultant, speaking fees. Enthera – Consultant. Enveda Biosciences – Consultant. Equillium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Fzatat – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen R&D – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaking fees. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biosciences – Consultant, Stock Options.
Geert R. D’Haens, MD, PhD1, Ailsa Hart, BA, BMBCh, PhD2, Remo Panaccione, MD3, Flavio Steinwurz, MD, MACG4, Qian Cao, MD, PhD5, Mobolaji Olurinde, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD6, Patrick Branigan, BS6, Wilbert van Duijnhoven, MSc7, Nat A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD8, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD9, Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, FACG10. P3192 - Effects of Subcutaneous Guselkumab Induction and Maintenance on Histologic Outcomes in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease in GRAVITI, a Phase 3 Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Treat-Through Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

