Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3170 - Comparative Effectiveness of Risankizumab (Skyrizi) vs Vedolizumab (Entyvio) in Crohn’s Disease Patients With Fistulizing Phenotype With and Without Prior Biologic Exposure: A Real-World Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Rakahn Haddadin, MD
HCA Healthcare MountainView Hospital
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Rakahn Haddadin, MD1, Aakriti Soni, MD2, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD3
1HCA Healthcare MountainView Hospital, Las Vegas, NV; 2HCA Houston Healthcare Kingwood, Kingwood, TX; 3Houston Regional Gastroenterology Institute and University of Houston, Sugar Land, TX
Introduction: Risankizumab and Vedolizumab are FDA-approved biologics used in the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD). Data remains limited regarding their comparative effectiveness in patients with fistulizing CD, particularly when stratified by prior anti-TNFα exposure. This study evaluates real-world outcomes in patients with and without prior biologic exposure treated with either Risankizumab or Vedolizumab.
Methods: Using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, two retrospective cohort analyses were performed on patients with Crohn’s disease of the large intestine with fistula (ICD-10: K50.113) who were initiated on Risankizumab or Vedolizumab. Patients were stratified based on prior biologic use: either no prior exposure (naïve) or prior exposure to anti-TNFα agents (Infliximab, Adalimumab, or Golimumab). Propensity score matching was applied to adjust baseline characteristics. Outcomes assessed over a 2-year period included colectomy, use of IV/oral steroids, extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs), infections (TB/CMV/PJP), and fistula-related procedures.
Results: After matching, 164 patients per cohort were analyzed in the no-prior biologic group (Table 1), and 251 per cohort in the prior biologic group (Table 2). In both strata, no significant differences were found in rates of colectomy, IV/oral steroid use, DVT/PE, requirement of seton procedure, or infections. However, Risankizumab-treated patients had significantly higher rates of EIMs in both biologic-naïve (51.8% vs. 40.2%, OR 1.60, p=0.035) and biologic-experienced (56.2% vs. 47.0%, OR 1.45, p=0.040) groups. Botulinum injections were observed exclusively in Vedolizumab-treated patients in the naïve and experienced groups, respectively (p< 0.01).
Discussion: In patients with fistulizing CD, Risankizumab and Vedolizumab demonstrated comparable rates of colectomy, corticosteroid use, and major adverse events, regardless of prior biologic exposure. However, higher rates of EIMs were noted in Risankizumab-treated patients across both cohorts. While this may reflect differences in disease phenotype or severity, further research is needed to elucidate potential mechanisms. These findings support the need for individualized therapy selection and underscore the utility of real-world data in informing treatment strategies for complex CD phenotypes.
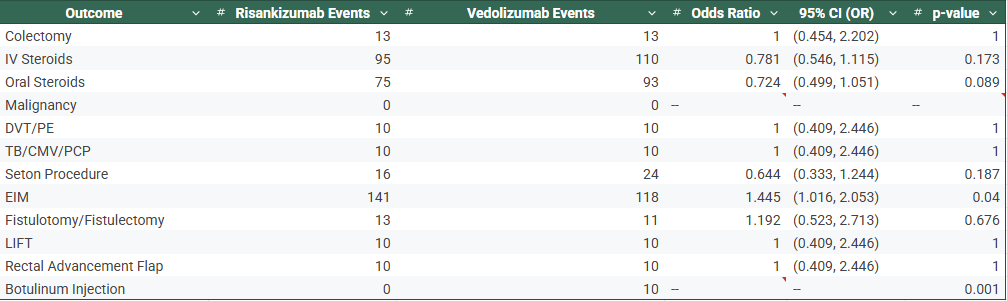
Figure: Table 1: Risankizumab vs Vedolizumab– With No Previous Biologic Exposure
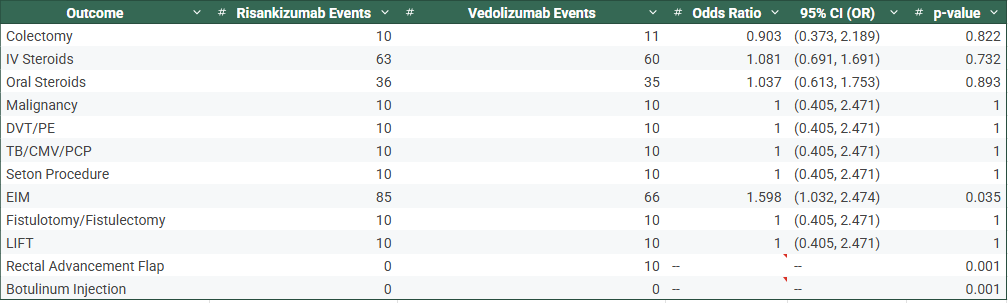
Figure: Table 2: Risankizumab vs Vedolizumab– With Previous Biologic Exposure
Disclosures:
Rakahn Haddadin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aakriti Soni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sushovan Guha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rakahn Haddadin, MD1, Aakriti Soni, MD2, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD3. P3170 - Comparative Effectiveness of Risankizumab (Skyrizi) vs Vedolizumab (Entyvio) in Crohn’s Disease Patients With Fistulizing Phenotype With and Without Prior Biologic Exposure: A Real-World Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1HCA Healthcare MountainView Hospital, Las Vegas, NV; 2HCA Houston Healthcare Kingwood, Kingwood, TX; 3Houston Regional Gastroenterology Institute and University of Houston, Sugar Land, TX
Introduction: Risankizumab and Vedolizumab are FDA-approved biologics used in the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD). Data remains limited regarding their comparative effectiveness in patients with fistulizing CD, particularly when stratified by prior anti-TNFα exposure. This study evaluates real-world outcomes in patients with and without prior biologic exposure treated with either Risankizumab or Vedolizumab.
Methods: Using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, two retrospective cohort analyses were performed on patients with Crohn’s disease of the large intestine with fistula (ICD-10: K50.113) who were initiated on Risankizumab or Vedolizumab. Patients were stratified based on prior biologic use: either no prior exposure (naïve) or prior exposure to anti-TNFα agents (Infliximab, Adalimumab, or Golimumab). Propensity score matching was applied to adjust baseline characteristics. Outcomes assessed over a 2-year period included colectomy, use of IV/oral steroids, extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs), infections (TB/CMV/PJP), and fistula-related procedures.
Results: After matching, 164 patients per cohort were analyzed in the no-prior biologic group (Table 1), and 251 per cohort in the prior biologic group (Table 2). In both strata, no significant differences were found in rates of colectomy, IV/oral steroid use, DVT/PE, requirement of seton procedure, or infections. However, Risankizumab-treated patients had significantly higher rates of EIMs in both biologic-naïve (51.8% vs. 40.2%, OR 1.60, p=0.035) and biologic-experienced (56.2% vs. 47.0%, OR 1.45, p=0.040) groups. Botulinum injections were observed exclusively in Vedolizumab-treated patients in the naïve and experienced groups, respectively (p< 0.01).
Discussion: In patients with fistulizing CD, Risankizumab and Vedolizumab demonstrated comparable rates of colectomy, corticosteroid use, and major adverse events, regardless of prior biologic exposure. However, higher rates of EIMs were noted in Risankizumab-treated patients across both cohorts. While this may reflect differences in disease phenotype or severity, further research is needed to elucidate potential mechanisms. These findings support the need for individualized therapy selection and underscore the utility of real-world data in informing treatment strategies for complex CD phenotypes.

Figure: Table 1: Risankizumab vs Vedolizumab– With No Previous Biologic Exposure

Figure: Table 2: Risankizumab vs Vedolizumab– With Previous Biologic Exposure
Disclosures:
Rakahn Haddadin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aakriti Soni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sushovan Guha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rakahn Haddadin, MD1, Aakriti Soni, MD2, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD3. P3170 - Comparative Effectiveness of Risankizumab (Skyrizi) vs Vedolizumab (Entyvio) in Crohn’s Disease Patients With Fistulizing Phenotype With and Without Prior Biologic Exposure: A Real-World Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
