Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3168 - Clinical Manifestation of Vasculitis, Treatment, and Outcome in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Literature
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Chanpreet Singh, MD (he/him/his)
South Texas Health System GME Consortium
McAllen, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Chanpreet Singh, MD1, Mourad M. Alsabbagh, MD2, Theodore G Pettle, MD3
1South Texas Health System GME Consortium, McAllen, TX; 2South Texas Health System, Edinburg, TX; 3South Texas Health System, McAllen, TX
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the large intestine and has systemic manifestations; the disease is described by a broad spectrum of extraintestinal manifestations. Of these, vasculitis is a relatively less investigated and probably an underdiagnosed dermatological upset. vasculitis is a small vessel vasculitis that results from deposition of an immune complex in the skin and leads to inflammation of and damage to these vessels.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature was conducted by searching the PubMed/MEDLINE database starting from January 2000 to 15 November 2024 to identify published cases and case series of patients with UC and vasculitis, in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. we analyzed 26 patients with concurrent UC and vasculitis.
Results: Palpable purpura (57.7%) followed by serous and/or hemorrhagic bullae (30.4%) and erythematous plaques (23.1%) are the most common clinical manifestations. In 38.1% of patients, the rash is painful, and the lower extremities are most commonly involved (73%). Vasculitis onset was observed more frequently after the diagnosis of UC (61.5%), and the majority of cases occurred during active disease (57.7%). These findings highlight the potential role of disease activity in triggering LCV, likely mediated by heightened systemic inflammation.
Combination therapy, including corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents, was the most common treatment approach (80.8%). Isolated corticosteroid use was sufficient in 15.4% of cases, while one patient required surgery (3.8%). The high recovery rate (96.2%) suggests that early recognition and prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Discussion: Our findings underscore the complexity of vasculitis as an extraintestinal manifestation of UC. Its strong association with active UC and systemic inflammation highlights the need for a multidisciplinary approach in managing affected patients. Early diagnosis and combination therapy are key to achieving favorable outcomes. This study is limited by missing data for some laboratory markers and the small sample size. Larger, prospective studies are warranted to better understand the pathophysiological mechanisms linking UC and LCV, refine diagnostic criteria, and optimize treatment protocols.
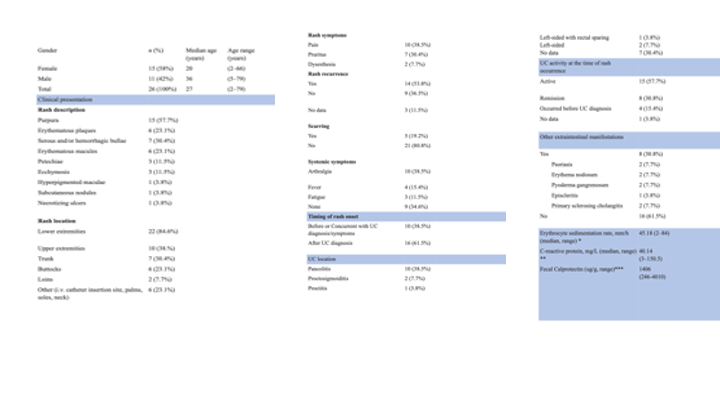
Figure: Demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants, including gender distribution, age range, lesion descriptions, and medical history factors such as tobacco exposure and cancer history.

Figure: Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients, including ANCA status, surgical history, malignancy types, treatment modalities, and recovery rates.
Disclosures:
Chanpreet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mourad M. Alsabbagh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Theodore G Pettle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chanpreet Singh, MD1, Mourad M. Alsabbagh, MD2, Theodore G Pettle, MD3. P3168 - Clinical Manifestation of Vasculitis, Treatment, and Outcome in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Literature, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1South Texas Health System GME Consortium, McAllen, TX; 2South Texas Health System, Edinburg, TX; 3South Texas Health System, McAllen, TX
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the large intestine and has systemic manifestations; the disease is described by a broad spectrum of extraintestinal manifestations. Of these, vasculitis is a relatively less investigated and probably an underdiagnosed dermatological upset. vasculitis is a small vessel vasculitis that results from deposition of an immune complex in the skin and leads to inflammation of and damage to these vessels.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature was conducted by searching the PubMed/MEDLINE database starting from January 2000 to 15 November 2024 to identify published cases and case series of patients with UC and vasculitis, in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. we analyzed 26 patients with concurrent UC and vasculitis.
Results: Palpable purpura (57.7%) followed by serous and/or hemorrhagic bullae (30.4%) and erythematous plaques (23.1%) are the most common clinical manifestations. In 38.1% of patients, the rash is painful, and the lower extremities are most commonly involved (73%). Vasculitis onset was observed more frequently after the diagnosis of UC (61.5%), and the majority of cases occurred during active disease (57.7%). These findings highlight the potential role of disease activity in triggering LCV, likely mediated by heightened systemic inflammation.
Combination therapy, including corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents, was the most common treatment approach (80.8%). Isolated corticosteroid use was sufficient in 15.4% of cases, while one patient required surgery (3.8%). The high recovery rate (96.2%) suggests that early recognition and prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Discussion: Our findings underscore the complexity of vasculitis as an extraintestinal manifestation of UC. Its strong association with active UC and systemic inflammation highlights the need for a multidisciplinary approach in managing affected patients. Early diagnosis and combination therapy are key to achieving favorable outcomes. This study is limited by missing data for some laboratory markers and the small sample size. Larger, prospective studies are warranted to better understand the pathophysiological mechanisms linking UC and LCV, refine diagnostic criteria, and optimize treatment protocols.

Figure: Demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants, including gender distribution, age range, lesion descriptions, and medical history factors such as tobacco exposure and cancer history.

Figure: Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients, including ANCA status, surgical history, malignancy types, treatment modalities, and recovery rates.
Disclosures:
Chanpreet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mourad M. Alsabbagh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Theodore G Pettle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chanpreet Singh, MD1, Mourad M. Alsabbagh, MD2, Theodore G Pettle, MD3. P3168 - Clinical Manifestation of Vasculitis, Treatment, and Outcome in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Literature, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
