Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3164 - Real-World Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Vedolizumab Versus Adalimumab in Adult Crohn’s Disease: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Sameh Gomaa, MD
Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health
Phoenixville, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2
1Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health, Phoenixville, PA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Needham, MA
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic and debilitating disease with a waxing and waning nature. Biologics have been a mainstay of therapeutics with both Vedolizumab (VDZ) and adalimumab (ADB) showing superiority to placebo in inducing remission. Direct comparisons were only made in small scale trials and further meta-analysis showed conflicting results on clinical remission and steroid free remission. We aim to Utilize nation-wide data to compare between (VDZ) and (ADB).
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX database on adult patients >18 years of age with CD, initiated VDZ or ADB between 1/2015 and 12/2023. The Outcomes are the risk developing colorectal cancer (CRC) and fistulizing complications (FC). Time to switch to a different biologic, steroid use (SU), and developing (FC). Number of instances of Emergency room (ER) visits. Fecal calprotectin levels and CRP levels. Serious adverse events of sepsis, lymphoma or opportunistic infections. Propensity score matching (PSM) performed for demographics, prior medication use, confounding comorbidities. Results expressed in the form of risk difference (RD). Time to event endpoints using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models reported as hazard ratio (HR) and log-rank P values.
Results: After matching, the cohort included 13661 CD patients in VDZ and ADB groups. The RD of developing CRC and FC was not significant. VDZ was showed a higher hazard of switching to a different biologic (HR 1.27, 95 % CI 1.19–1.35; log-rank p < 0.0001) and systemic steroid use (HR 1.32, 95 % CI 1.291,1.367 ; log-rank p < 0.0001). There was a significant increase in the risk of developing lymphomas for VDZ (RD 0.644%, 95 % CI 0.381,0.907, P < 0.0001) and opportunistic infections ( RD 1.537%, 95% CI 0.576,2.499, P=0.0017). Instances of Emergency room (ER) visits. fecal calprotectin or CRP levels, sepsis rates were not significantly different.
Discussion: Our Study is the first of this magnitude comparing to popular biologics. ADB in comparison to VDZ showed more robustness as regards to steroid free remission and the likelihood of switching to a different biologic. ADB is also showing lower risk of adverse events in the form of lymphoma and opportunistic infections.
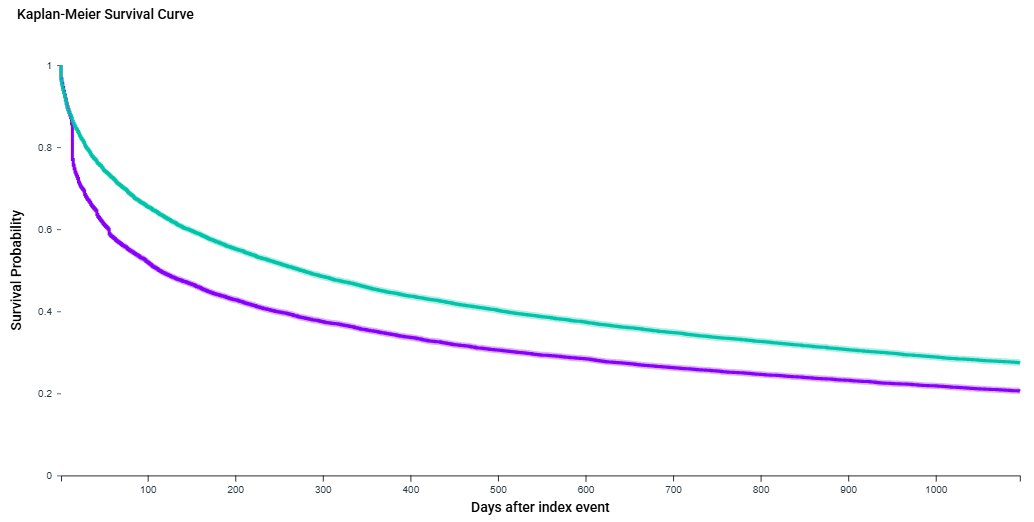
Figure: Steroid Free remission
Figure: Risk of Sepsis
Disclosures:
Sameh Gomaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Alabdul Razzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hatem Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eyad Abdulrazzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2. P3164 - Real-World Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Vedolizumab Versus Adalimumab in Adult Crohn’s Disease: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Phoenixville Hospital - Tower Health, Phoenixville, PA; 2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Needham, MA
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic and debilitating disease with a waxing and waning nature. Biologics have been a mainstay of therapeutics with both Vedolizumab (VDZ) and adalimumab (ADB) showing superiority to placebo in inducing remission. Direct comparisons were only made in small scale trials and further meta-analysis showed conflicting results on clinical remission and steroid free remission. We aim to Utilize nation-wide data to compare between (VDZ) and (ADB).
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX database on adult patients >18 years of age with CD, initiated VDZ or ADB between 1/2015 and 12/2023. The Outcomes are the risk developing colorectal cancer (CRC) and fistulizing complications (FC). Time to switch to a different biologic, steroid use (SU), and developing (FC). Number of instances of Emergency room (ER) visits. Fecal calprotectin levels and CRP levels. Serious adverse events of sepsis, lymphoma or opportunistic infections. Propensity score matching (PSM) performed for demographics, prior medication use, confounding comorbidities. Results expressed in the form of risk difference (RD). Time to event endpoints using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models reported as hazard ratio (HR) and log-rank P values.
Results: After matching, the cohort included 13661 CD patients in VDZ and ADB groups. The RD of developing CRC and FC was not significant. VDZ was showed a higher hazard of switching to a different biologic (HR 1.27, 95 % CI 1.19–1.35; log-rank p < 0.0001) and systemic steroid use (HR 1.32, 95 % CI 1.291,1.367 ; log-rank p < 0.0001). There was a significant increase in the risk of developing lymphomas for VDZ (RD 0.644%, 95 % CI 0.381,0.907, P < 0.0001) and opportunistic infections ( RD 1.537%, 95% CI 0.576,2.499, P=0.0017). Instances of Emergency room (ER) visits. fecal calprotectin or CRP levels, sepsis rates were not significantly different.
Discussion: Our Study is the first of this magnitude comparing to popular biologics. ADB in comparison to VDZ showed more robustness as regards to steroid free remission and the likelihood of switching to a different biologic. ADB is also showing lower risk of adverse events in the form of lymphoma and opportunistic infections.

Figure: Steroid Free remission

Figure: Risk of Sepsis
Disclosures:
Sameh Gomaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Alabdul Razzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hatem Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eyad Abdulrazzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameh Gomaa, MD1, Imad Alabdul Razzak, MD1, Hatem Ahmed, MD1, Eyad Abdulrazzak, MBBS2. P3164 - Real-World Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Vedolizumab Versus Adalimumab in Adult Crohn’s Disease: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
