Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P3070 - Association of Anxiety Disorders and Mortality Among Critically Ill Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Anjul Verma, MD (he/him/his)
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
Syracuse, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Anjul Verma, MD1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS2, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Gloria Erazo, MD1, Ooreoluwa Fasola, MD1, Bibek Saha, MD3, Rohit Goyal, MD4, Sameer Rao, MBBS5, Karan Sachdeva, MD6, Muhammad Saad, MD7, Vanya Rai, MBBS3, John Garza, PhD8, Kalyan Chakrala, DO1
1Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 2SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 4Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 5Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 6LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Midland, TX; 8Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center - Permian Basin, Odessa, TX
Introduction: Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) is a common and potentially life-threatening condition, with an annual incidence of 80 to 150 cases per 100,000 population and mortality rate of 2% to 10%. Anxiety disorders are prevalent, affecting up to 34% of individuals over their lifetime. Despite their high prevalence, the impact of anxiety disorders on critically ill patients hospitalized with UGIB remains unclear. Our study aims to explore the association between anxiety disorders and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients admitted with UGIB.
Methods: We conducted a population-based cohort study using deidentified, publicly available data on adults admitted to Texas acute care ICU units from 2016–2023 with a principal diagnosis of UGIB, identified using International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revisions, Clinical Modification codes selected from Clinical Classification Software Refined (CCSR) category DIG021: Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage. The primary exposure was anxiety disorders identified using CCSR category MBD005: Anxiety and fear-related disorders. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality, short-term mortality, and length of stay. Overlap propensity score weighting was applied with results expressed as adjusted risk ratio and 95% confidence interval.
Results: Among 79,900 hospitalizations for UGIB, 11.7% had anxiety disorders. These patients were younger (48.1% vs 58.7% aged ≥ 65 years, p < 0.0001) and and with lower Deyo comorbidity index (p < 0.0001). Anxiety disorders was associated with lower in-hospital (1.8% vs 3.1%) and short-term mortality (4.2% vs 6.0%). Adjusted analysis showed no association with in-hospital mortality (aRR 0.90, 95% CI 0.81–1.00), but remained associated with short-term mortality (aRR 0.80, 95% CI 0.68–0.93). Although mean length of stay was similar, anxiety disorders was associated with slightly longer adjusted length of stay (aRR 1.03, 95% CI 1.05–1.07).
Discussion: Critically ill UGIB patients with anxiety disorders had lower inpatient and short-term mortality compared to published literature. This may be attributed to the higher prevalence of anxiety disorders among younger patients and their lower burden of chronic conditions. Rebleeding rates did not differ significantly between groups. Differences in comorbidities, organ dysfunction, and treatment utilization suggest that UGIB patients with anxiety disorders may represent a distinct clinical phenotype with a potentially better prognosis compared to those without anxiety disorders.
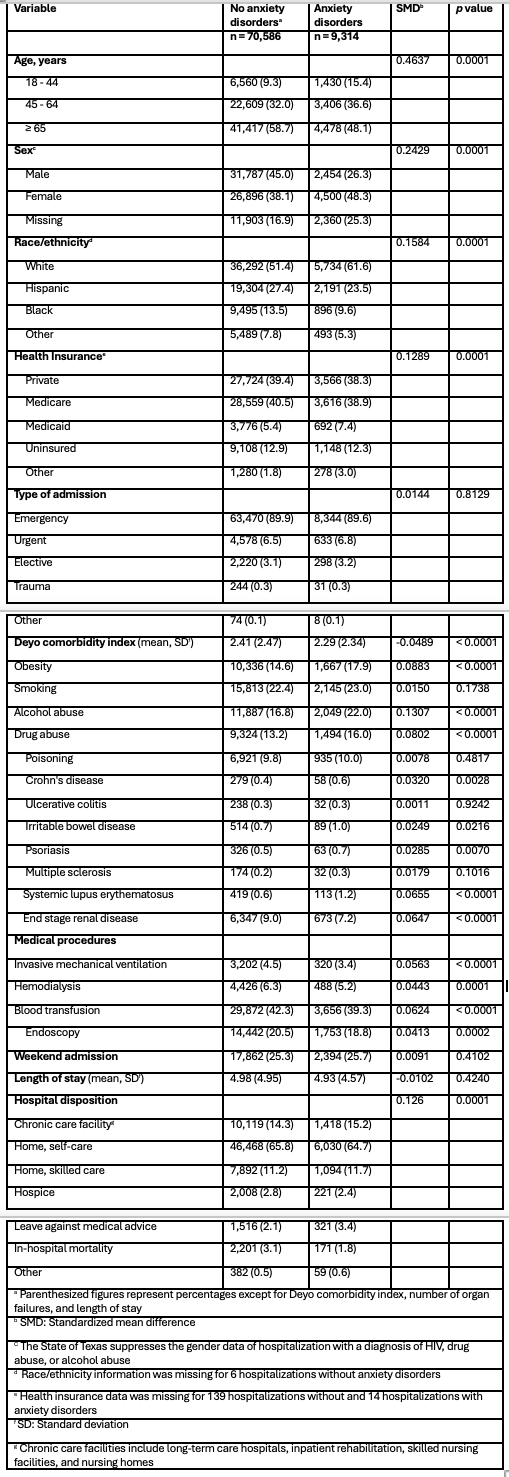
Figure: The characteristics and outcomes of critically ill upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding patients with and without anxiety disorders
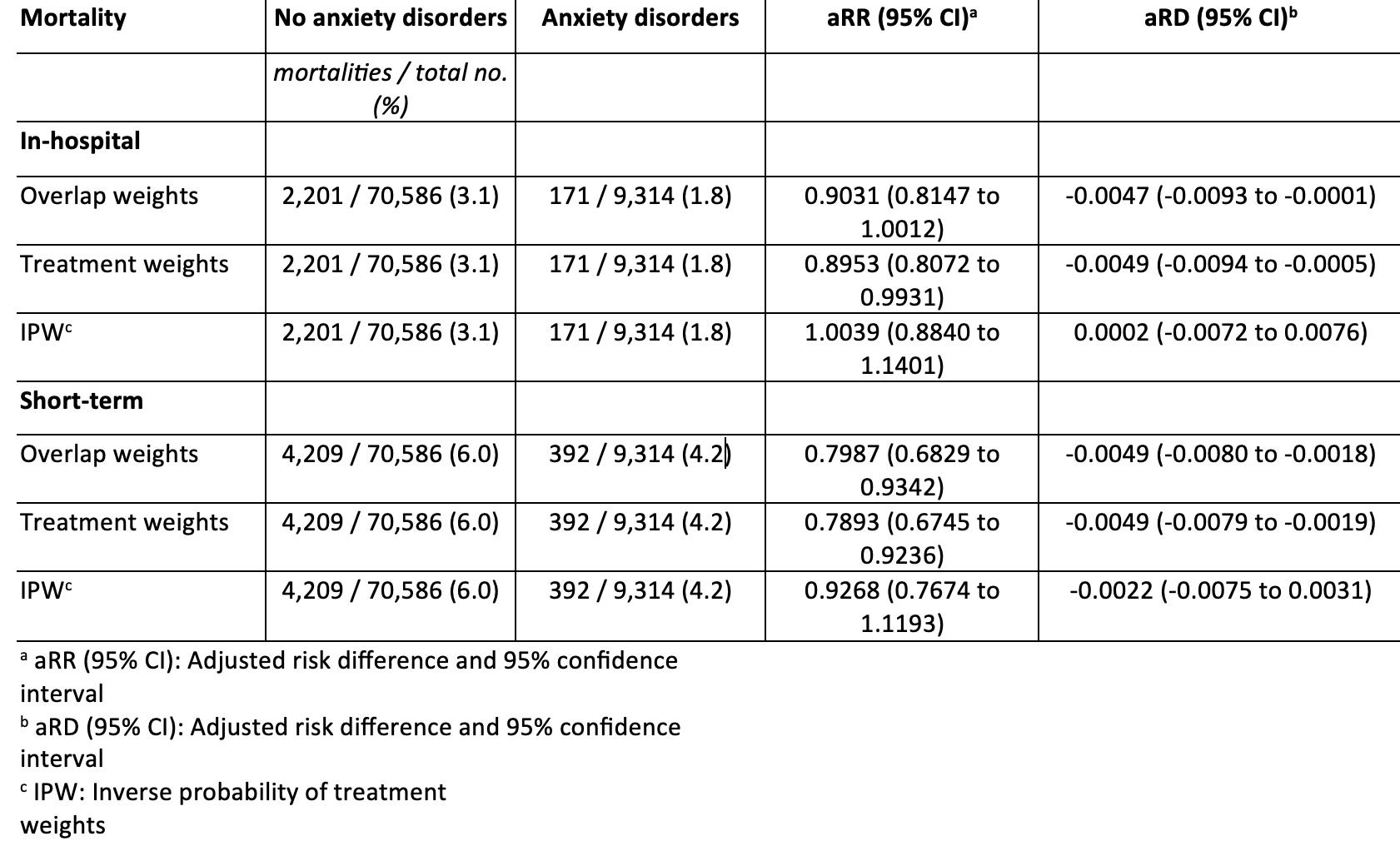
Figure: The relative risk of death among critically ill upper GI tract bleeding hospitalizations with and without anxiety disorders
Disclosures:
Anjul Verma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gloria Erazo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ooreoluwa Fasola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bibek Saha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karan Sachdeva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanya Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Garza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalyan Chakrala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjul Verma, MD1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS2, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Gloria Erazo, MD1, Ooreoluwa Fasola, MD1, Bibek Saha, MD3, Rohit Goyal, MD4, Sameer Rao, MBBS5, Karan Sachdeva, MD6, Muhammad Saad, MD7, Vanya Rai, MBBS3, John Garza, PhD8, Kalyan Chakrala, DO1. P3070 - Association of Anxiety Disorders and Mortality Among Critically Ill Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 2SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 4Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 5Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 6LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Midland, TX; 8Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center - Permian Basin, Odessa, TX
Introduction: Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) is a common and potentially life-threatening condition, with an annual incidence of 80 to 150 cases per 100,000 population and mortality rate of 2% to 10%. Anxiety disorders are prevalent, affecting up to 34% of individuals over their lifetime. Despite their high prevalence, the impact of anxiety disorders on critically ill patients hospitalized with UGIB remains unclear. Our study aims to explore the association between anxiety disorders and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients admitted with UGIB.
Methods: We conducted a population-based cohort study using deidentified, publicly available data on adults admitted to Texas acute care ICU units from 2016–2023 with a principal diagnosis of UGIB, identified using International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revisions, Clinical Modification codes selected from Clinical Classification Software Refined (CCSR) category DIG021: Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage. The primary exposure was anxiety disorders identified using CCSR category MBD005: Anxiety and fear-related disorders. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality, short-term mortality, and length of stay. Overlap propensity score weighting was applied with results expressed as adjusted risk ratio and 95% confidence interval.
Results: Among 79,900 hospitalizations for UGIB, 11.7% had anxiety disorders. These patients were younger (48.1% vs 58.7% aged ≥ 65 years, p < 0.0001) and and with lower Deyo comorbidity index (p < 0.0001). Anxiety disorders was associated with lower in-hospital (1.8% vs 3.1%) and short-term mortality (4.2% vs 6.0%). Adjusted analysis showed no association with in-hospital mortality (aRR 0.90, 95% CI 0.81–1.00), but remained associated with short-term mortality (aRR 0.80, 95% CI 0.68–0.93). Although mean length of stay was similar, anxiety disorders was associated with slightly longer adjusted length of stay (aRR 1.03, 95% CI 1.05–1.07).
Discussion: Critically ill UGIB patients with anxiety disorders had lower inpatient and short-term mortality compared to published literature. This may be attributed to the higher prevalence of anxiety disorders among younger patients and their lower burden of chronic conditions. Rebleeding rates did not differ significantly between groups. Differences in comorbidities, organ dysfunction, and treatment utilization suggest that UGIB patients with anxiety disorders may represent a distinct clinical phenotype with a potentially better prognosis compared to those without anxiety disorders.

Figure: The characteristics and outcomes of critically ill upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding patients with and without anxiety disorders

Figure: The relative risk of death among critically ill upper GI tract bleeding hospitalizations with and without anxiety disorders
Disclosures:
Anjul Verma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avneet Kaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gloria Erazo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ooreoluwa Fasola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bibek Saha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karan Sachdeva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanya Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Garza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kalyan Chakrala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjul Verma, MD1, Avneet Kaur, MBBS2, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD1, Gloria Erazo, MD1, Ooreoluwa Fasola, MD1, Bibek Saha, MD3, Rohit Goyal, MD4, Sameer Rao, MBBS5, Karan Sachdeva, MD6, Muhammad Saad, MD7, Vanya Rai, MBBS3, John Garza, PhD8, Kalyan Chakrala, DO1. P3070 - Association of Anxiety Disorders and Mortality Among Critically Ill Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
