Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P3044 - Racial Disparities in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Among People Living With HIV in the United States
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Neha Nanditha Adepu, MBBS (she/her/hers)
Osmania General Hospital and Medical College
Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian, MD1, Anusha Endreddy, MBBS2, Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar, MBBS3, Heer Pareshbhai Shah, MBBS4, Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula, MBBS5, Uzer Abdulaziz Memon, MBBS6, Dency Dineshbhai Mavani, MBBS7, Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad, MBBS4, Karthik Basumani, MBBS8, Mathangi Murali, MBBS9, Neha Nanditha Adepu, MBBS10, Jay Patel, MBBS11, Swetha Areti, MD12, Naveen Yellappa, MD13, Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, FIDSA14, Rutul Dalal, MD15
1Northeast Georgia Medical Center, Gainesville, GA; 2Alluri Sitarama Raju Academy of Medical Sciences, Eluru, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3ESIC Medical College and Postgraduate Institute of Medical Science and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 4Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Government General Hospital Kakinada, Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh, India; 6Smt NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 7Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 9Government Erode Medical College and Hospital, Perundurai, Tamil Nadu, India; 10Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 11B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 12WellSpan Health, Chambersburg, PA; 13Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA; 14Keystone Health, Chambersburg, PA; 15Penn State Health St. Joseph Medical Center, Reading, PA
Introduction: In the United States, African Americans (AA) accounted for approximately 40% of newly diagnosed HIV cases and had higher mortality than American Whites (AW) (20.1 vs 3.1 per 100,000). Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), though relatively rare with a prevalence of 1–14%, remains a significant concern. A gap exists in the impact of racial differences in HIV with UGIB. We aimed to study racial disparities in mortality in people living with HIV (PLWH) with UGIB.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis using the National Inpatient Sample (2016–2021) to identify PLWH adults (≥18 years) with UGIB. ICU-level care was identified by the presence of shock or the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and/or renal replacement therapy. We performed multivariate regression by adjusting for sociodemographic factors and comorbidities, and reported it as adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and adjusted mean differences (aMD). A p≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Among 6,923 PLWH with UGIB requiring ICU-level care, mortality was higher in AA than AW (37.1% vs 29.9%). AA had a higher mortality risk than AW (aOR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; p< 0.05). AA were associated with no difference in hospital charges (aMD -$19,347.5; 95% CI, -84,293.1 to 45,598.1; p >0.05), or length of stay (aMD 2.0 days; 95% CI, -2.1 to 6.0; p >0.05) than AW. In those with variceal bleeding, AA had increased mortality risk than AW (aOR 1.6, 95% CI 1.1-2.3, p=0.01). In AA who underwent endoscopy, the mortality risk remained higher compared to AW (aOR 1.6, 95% CI 0.8-3.1, p=0.1). In AA patients who underwent early endoscopy ( < 24 hours from admission), unadjusted mortality was lower than in AW patients (41.7% vs 45.8%, p< 0.05), but the difference was not significant after adjustment (p >0.05). The mortality between the two cohorts did not vary with radical embolization and variceal ligation (p >0.05). On analyzing the predictors of mortality in AA, variceal GI bleed, solid malignancy, acute coronary syndrome, acute kidney injury, sepsis, pancytopenia, and invasive ventilation were associated with higher mortality (p≤0.05).
Discussion: In PLWH with upper gastrointestinal bleeding, African American patients had higher mortality than American White patients. In this population, interventions to manage gastrointestinal bleeding should be validated through prospective studies. Targeted strategies to improve healthcare access and a multidisciplinary approach may help enhance outcomes.
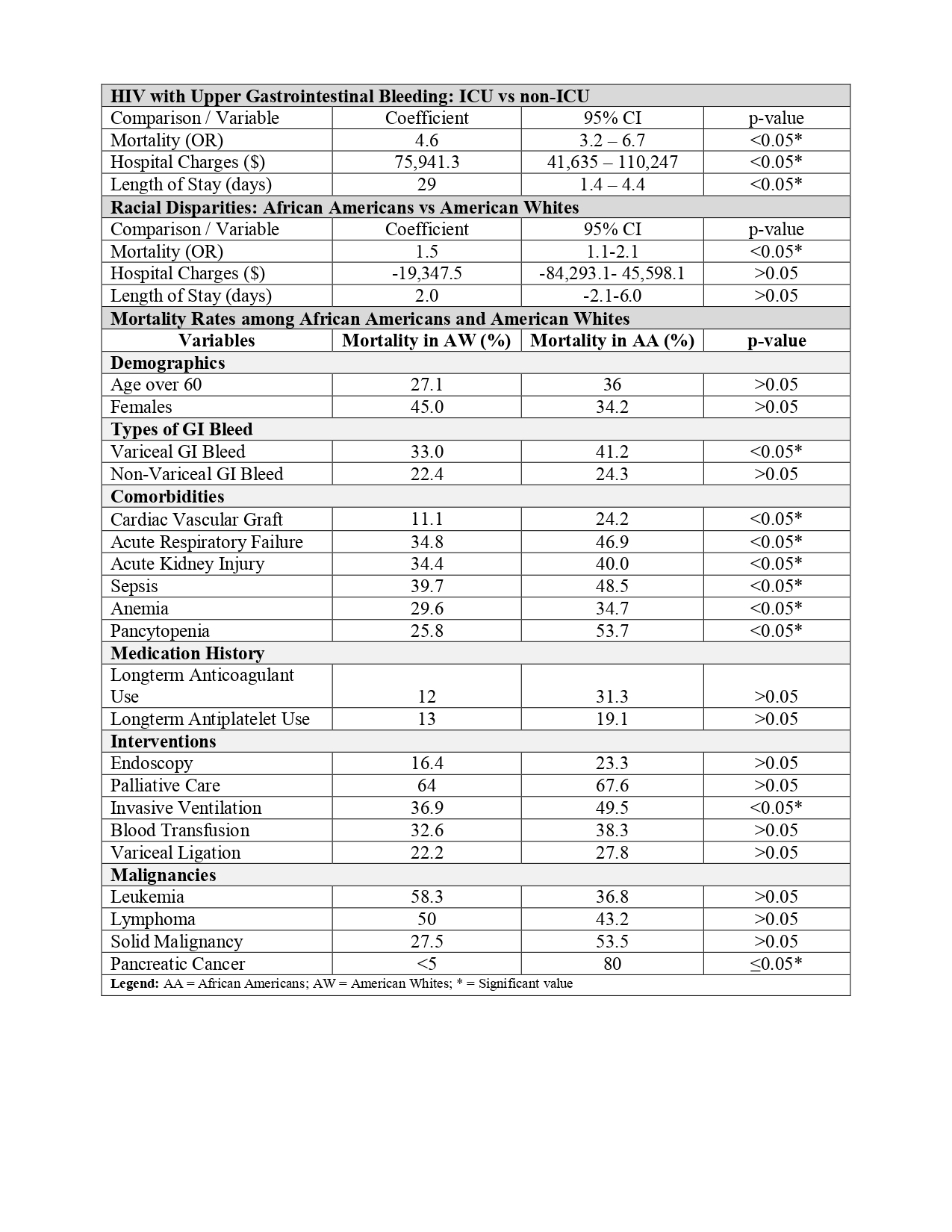
Figure: Racial Disparities in Mortality of HIV Patients with UGIB
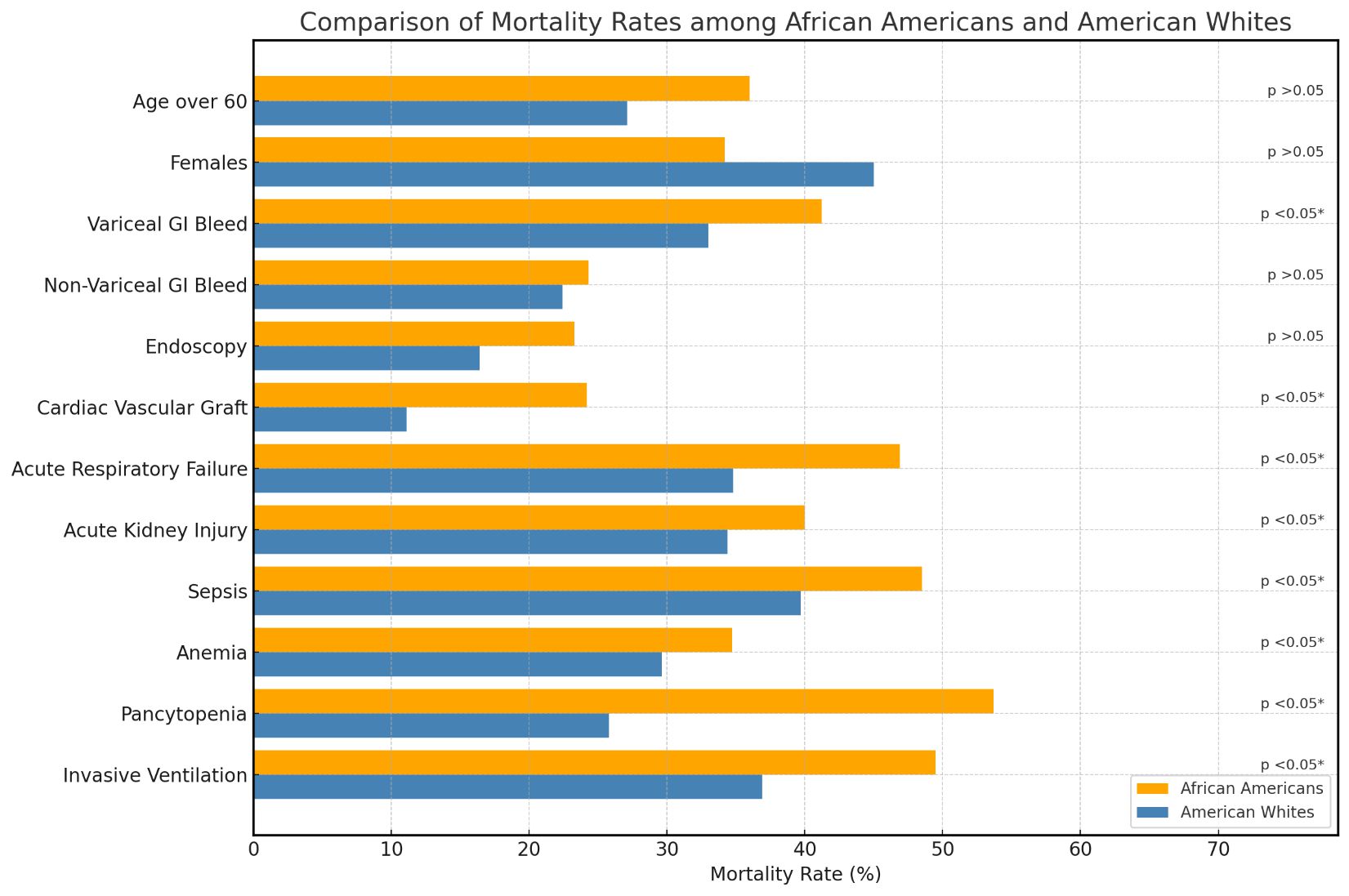
Figure: Comparison of Mortality Rates among African Americans and American Whites
Disclosures:
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Endreddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heer Pareshbhai Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Uzer Abdulaziz Memon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dency Dineshbhai Mavani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Basumani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mathangi Murali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Nanditha Adepu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jay Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swetha Areti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naveen Yellappa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raghavendra Tirupathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rutul Dalal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian, MD1, Anusha Endreddy, MBBS2, Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar, MBBS3, Heer Pareshbhai Shah, MBBS4, Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula, MBBS5, Uzer Abdulaziz Memon, MBBS6, Dency Dineshbhai Mavani, MBBS7, Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad, MBBS4, Karthik Basumani, MBBS8, Mathangi Murali, MBBS9, Neha Nanditha Adepu, MBBS10, Jay Patel, MBBS11, Swetha Areti, MD12, Naveen Yellappa, MD13, Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, FIDSA14, Rutul Dalal, MD15. P3044 - Racial Disparities in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Among People Living With HIV in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian, MD1, Anusha Endreddy, MBBS2, Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar, MBBS3, Heer Pareshbhai Shah, MBBS4, Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula, MBBS5, Uzer Abdulaziz Memon, MBBS6, Dency Dineshbhai Mavani, MBBS7, Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad, MBBS4, Karthik Basumani, MBBS8, Mathangi Murali, MBBS9, Neha Nanditha Adepu, MBBS10, Jay Patel, MBBS11, Swetha Areti, MD12, Naveen Yellappa, MD13, Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, FIDSA14, Rutul Dalal, MD15
1Northeast Georgia Medical Center, Gainesville, GA; 2Alluri Sitarama Raju Academy of Medical Sciences, Eluru, Andhra Pradesh, India; 3ESIC Medical College and Postgraduate Institute of Medical Science and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 4Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Government General Hospital Kakinada, Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh, India; 6Smt NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 7Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India; 9Government Erode Medical College and Hospital, Perundurai, Tamil Nadu, India; 10Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 11B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 12WellSpan Health, Chambersburg, PA; 13Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA; 14Keystone Health, Chambersburg, PA; 15Penn State Health St. Joseph Medical Center, Reading, PA
Introduction: In the United States, African Americans (AA) accounted for approximately 40% of newly diagnosed HIV cases and had higher mortality than American Whites (AW) (20.1 vs 3.1 per 100,000). Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), though relatively rare with a prevalence of 1–14%, remains a significant concern. A gap exists in the impact of racial differences in HIV with UGIB. We aimed to study racial disparities in mortality in people living with HIV (PLWH) with UGIB.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis using the National Inpatient Sample (2016–2021) to identify PLWH adults (≥18 years) with UGIB. ICU-level care was identified by the presence of shock or the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and/or renal replacement therapy. We performed multivariate regression by adjusting for sociodemographic factors and comorbidities, and reported it as adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and adjusted mean differences (aMD). A p≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Among 6,923 PLWH with UGIB requiring ICU-level care, mortality was higher in AA than AW (37.1% vs 29.9%). AA had a higher mortality risk than AW (aOR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; p< 0.05). AA were associated with no difference in hospital charges (aMD -$19,347.5; 95% CI, -84,293.1 to 45,598.1; p >0.05), or length of stay (aMD 2.0 days; 95% CI, -2.1 to 6.0; p >0.05) than AW. In those with variceal bleeding, AA had increased mortality risk than AW (aOR 1.6, 95% CI 1.1-2.3, p=0.01). In AA who underwent endoscopy, the mortality risk remained higher compared to AW (aOR 1.6, 95% CI 0.8-3.1, p=0.1). In AA patients who underwent early endoscopy ( < 24 hours from admission), unadjusted mortality was lower than in AW patients (41.7% vs 45.8%, p< 0.05), but the difference was not significant after adjustment (p >0.05). The mortality between the two cohorts did not vary with radical embolization and variceal ligation (p >0.05). On analyzing the predictors of mortality in AA, variceal GI bleed, solid malignancy, acute coronary syndrome, acute kidney injury, sepsis, pancytopenia, and invasive ventilation were associated with higher mortality (p≤0.05).
Discussion: In PLWH with upper gastrointestinal bleeding, African American patients had higher mortality than American White patients. In this population, interventions to manage gastrointestinal bleeding should be validated through prospective studies. Targeted strategies to improve healthcare access and a multidisciplinary approach may help enhance outcomes.

Figure: Racial Disparities in Mortality of HIV Patients with UGIB

Figure: Comparison of Mortality Rates among African Americans and American Whites
Disclosures:
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Endreddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heer Pareshbhai Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Uzer Abdulaziz Memon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dency Dineshbhai Mavani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karthik Basumani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mathangi Murali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Nanditha Adepu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jay Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swetha Areti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naveen Yellappa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raghavendra Tirupathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rutul Dalal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barath Prashanth Sivasubramanian, MD1, Anusha Endreddy, MBBS2, Diviya Bharathi Ravikumar, MBBS3, Heer Pareshbhai Shah, MBBS4, Krishna Sai Kiran Sakalabaktula, MBBS5, Uzer Abdulaziz Memon, MBBS6, Dency Dineshbhai Mavani, MBBS7, Falaknaaz Mubassirhusen Saiyad, MBBS4, Karthik Basumani, MBBS8, Mathangi Murali, MBBS9, Neha Nanditha Adepu, MBBS10, Jay Patel, MBBS11, Swetha Areti, MD12, Naveen Yellappa, MD13, Raghavendra Tirupathi, MD, FIDSA14, Rutul Dalal, MD15. P3044 - Racial Disparities in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Among People Living With HIV in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.



