Monday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P3000 - Reassessing Gastric Biopsies in Normal-Appearing Mucosa: A Retrospective Study Evaluating the Impact of Discontinuing Immunohistochemical Staining
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Muhammad Saad Faisal, MD (he/him/his)
Henry Ford Health
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Saad Faisal, MD1, Neil Garg, BSc2, Bradley Karmo, MD3, Razan Aburumman, MD1, Anju Pradeep, MD4, Minahil Fatima, MD1, Muhammad Shahzil, MD5, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Muhammad Salman Faisal, MD4, Anas Kutait, MD1
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI; 3Henry Ford Health, West Bloomfield, MI; 4Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Helicobacter pylori can be diagnosed using both invasive and non-invasive methods. Among invasive techniques, histological analysis of gastric biopsies is the gold standard. These are typically examined with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, and Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining is often added to enhance diagnostic accuracy. However, this approach is resource-intensive, costly, and has prolonged turnaround times. As clinical practice shifts toward reducing invasive testing, especially in the setting of endoscopically normal gastric mucosa, the utility of routine biopsies and IHC staining in such cases warrants reevaluation. This study aimed to assess biopsy rates and diagnostic yield in patients with normal-appearing gastric mucosa before and after our institution discontinued IHC staining in these biopsies.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study across a multicenter health system. After IRB approval, we reviewed all EGDs performed in two time periods: Sep 1–Oct 31, 2023 (control group, when IHC was performed) and Jan 1–Feb 28, 2024 (case group, after IHC was discontinued). Patients with findings of normal gastric mucosa on EGD were included. The primary outcome was biopsy rate; the secondary outcome was histologic yield for H. pylori.
Results: A total of 217 patients met inclusion criteria, 102 (47%) in the control group and 115 (53%) in the case group. There were no significant differences in age, gender, race, or PPI use. Common EGD indications included anemia, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, heartburn, melena, and reflux, with similar distribution between groups. Gastric biopsies were taken in 72/102 (70.6%) patients in the control group vs. 74/115 (64.3%) in the case group (p=0.33). IHC staining was performed in 72 (70.6%) control patients compared to 25 (21.7%) in the case group (p< 0.01). Histology was positive for H. pylori in 15 (14.7%) control patients vs. 13 (11.3%) case patients (p=0.67).
Discussion: Reducing the use of IHC staining in biopsies from normal-appearing gastric mucosa did not affect the rate of biopsy nor the diagnostic yield for H. pylori. Despite a significant decrease in IHC utilization, detection rates remained unchanged. These findings suggest that routine biopsy and IHC staining of endoscopically normal gastric mucosa may have limited clinical value. Larger studies are warranted to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of invasive histologic evaluation compared to non-invasive diagnostic methods.
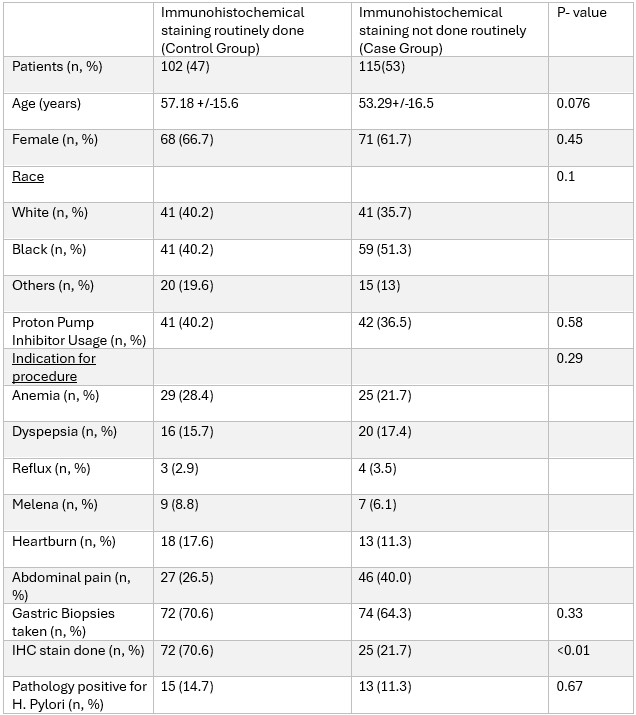
Figure: Table 1. Comparison of patient demographics, indications, and outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1. Comparison of Outcomes between the two groups.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad Faisal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bradley Karmo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Razan Aburumman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anju Pradeep indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shahzil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Salman Faisal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Kutait indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad Faisal, MD1, Neil Garg, BSc2, Bradley Karmo, MD3, Razan Aburumman, MD1, Anju Pradeep, MD4, Minahil Fatima, MD1, Muhammad Shahzil, MD5, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Muhammad Salman Faisal, MD4, Anas Kutait, MD1. P3000 - Reassessing Gastric Biopsies in Normal-Appearing Mucosa: A Retrospective Study Evaluating the Impact of Discontinuing Immunohistochemical Staining, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI; 3Henry Ford Health, West Bloomfield, MI; 4Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI; 5Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Helicobacter pylori can be diagnosed using both invasive and non-invasive methods. Among invasive techniques, histological analysis of gastric biopsies is the gold standard. These are typically examined with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, and Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining is often added to enhance diagnostic accuracy. However, this approach is resource-intensive, costly, and has prolonged turnaround times. As clinical practice shifts toward reducing invasive testing, especially in the setting of endoscopically normal gastric mucosa, the utility of routine biopsies and IHC staining in such cases warrants reevaluation. This study aimed to assess biopsy rates and diagnostic yield in patients with normal-appearing gastric mucosa before and after our institution discontinued IHC staining in these biopsies.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study across a multicenter health system. After IRB approval, we reviewed all EGDs performed in two time periods: Sep 1–Oct 31, 2023 (control group, when IHC was performed) and Jan 1–Feb 28, 2024 (case group, after IHC was discontinued). Patients with findings of normal gastric mucosa on EGD were included. The primary outcome was biopsy rate; the secondary outcome was histologic yield for H. pylori.
Results: A total of 217 patients met inclusion criteria, 102 (47%) in the control group and 115 (53%) in the case group. There were no significant differences in age, gender, race, or PPI use. Common EGD indications included anemia, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, heartburn, melena, and reflux, with similar distribution between groups. Gastric biopsies were taken in 72/102 (70.6%) patients in the control group vs. 74/115 (64.3%) in the case group (p=0.33). IHC staining was performed in 72 (70.6%) control patients compared to 25 (21.7%) in the case group (p< 0.01). Histology was positive for H. pylori in 15 (14.7%) control patients vs. 13 (11.3%) case patients (p=0.67).
Discussion: Reducing the use of IHC staining in biopsies from normal-appearing gastric mucosa did not affect the rate of biopsy nor the diagnostic yield for H. pylori. Despite a significant decrease in IHC utilization, detection rates remained unchanged. These findings suggest that routine biopsy and IHC staining of endoscopically normal gastric mucosa may have limited clinical value. Larger studies are warranted to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of invasive histologic evaluation compared to non-invasive diagnostic methods.

Figure: Table 1. Comparison of patient demographics, indications, and outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1. Comparison of Outcomes between the two groups.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad Faisal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bradley Karmo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Razan Aburumman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anju Pradeep indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shahzil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Salman Faisal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Kutait indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad Faisal, MD1, Neil Garg, BSc2, Bradley Karmo, MD3, Razan Aburumman, MD1, Anju Pradeep, MD4, Minahil Fatima, MD1, Muhammad Shahzil, MD5, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD1, Muhammad Salman Faisal, MD4, Anas Kutait, MD1. P3000 - Reassessing Gastric Biopsies in Normal-Appearing Mucosa: A Retrospective Study Evaluating the Impact of Discontinuing Immunohistochemical Staining, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
