Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2843 - EoE Triggered by Roundup Herbicide Ingestion
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- FB
Flavio Bonilla, MD
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Flavio Bonilla, MD1, Adam Spandorfer, MD1, Megan Q. Chan, MD2, David J. Westrich, MD3
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2The Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 3The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic disorder driven by an environmental antigen immune-mediated response leading to activation of eosinophils and subsequent esophageal inflammation. Diagnosis is by combination of clinical, laboratory, endoscopic and histologic (≥ 15 eosinophils/HPF) findings.
Case Description/
Methods: A 24-year-old male with history of eczema and asthma presented to clinic for dysphagia. At age 13, he was pranked and unknowingly drank mountain dew mixed with glyphosate herbicide (Roundup). One week later he developed significant dysphagia to solids and liquids. He denied any issues with dysphagia prior to this incident. At that time, EGD showed severe acute esophagitis with ulceration without eosinophils on biopsies. Follow up EGD one month later showed improved esophagitis, but biopsies revealed up to 80 eosinophils. The patient had ongoing dysphagia and reflux symptoms over subsequent years despite use of Omeprazole 40 mg daily, requiring intermittent dilations with limited benefit. EGD at our institution demonstrated a narrow caliber esophagus with a predominant stricture at the gastroesophageal junction and subtle strictures proximally. EoE Endoscopic Reference Score was 4 (Figure A). Esophageal biopsies showed greater than 150 eosinophils distally and 100 proximally. His symptoms improved after esophageal dilation (Figure B) and initiation of dupilumab 300mg subQ weekly.
Discussion: The mechanism of EoE pathogenesis remains unknown but is hypothesized to be due to complex interplay of environmental and genetic factors leading to disruptions in the esophageal epithelial barrier triggering an immune Th2 response. Though limited, human case reports and animal models have shown development of EoE after large allergen exposure. Currently, there remains limited data exploring the role of chemicals such as herbicides in the development of EoE. A study using mice exposed to glyphosate, the active ingredient in Roundup, showed esophageal eosinophil levels similar to those in mice who underwent protocols to induce EoE. A large cross-sectional, case control study found higher odds of EoE with decreasing population density, which may indicate that herbicide exposure in rural environments could contribute to EoE pathogenesis. This case demonstrates a novel presentation of EoE after accidental Roundup ingestion where glyphosate is the suspected trigger for EoE development. More studies are needed to establish a clearer link between herbicide exposure and EoE development.
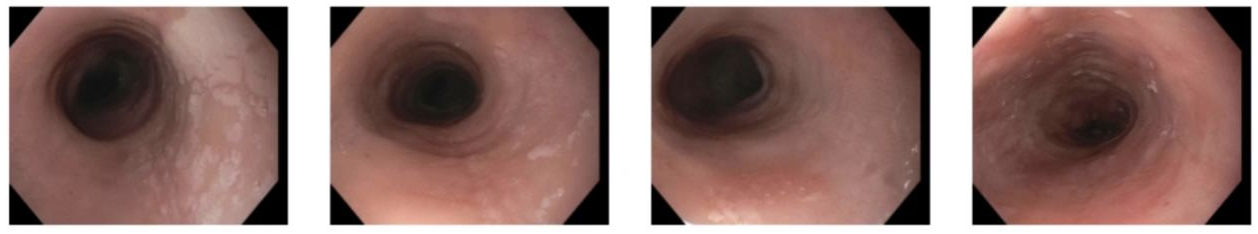
Figure: Figure A before dilation
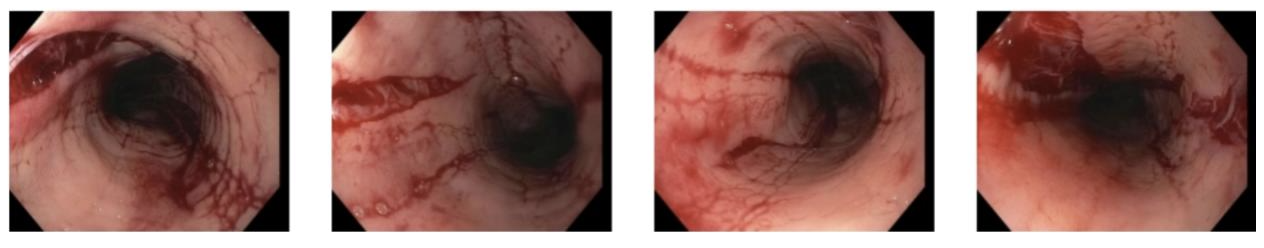
Figure: Figure B after dilation
Disclosures:
Flavio Bonilla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adam Spandorfer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Megan Chan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Westrich indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Flavio Bonilla, MD1, Adam Spandorfer, MD1, Megan Q. Chan, MD2, David J. Westrich, MD3. P2843 - EoE Triggered by Roundup Herbicide Ingestion, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2The Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 3The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic disorder driven by an environmental antigen immune-mediated response leading to activation of eosinophils and subsequent esophageal inflammation. Diagnosis is by combination of clinical, laboratory, endoscopic and histologic (≥ 15 eosinophils/HPF) findings.
Case Description/
Methods: A 24-year-old male with history of eczema and asthma presented to clinic for dysphagia. At age 13, he was pranked and unknowingly drank mountain dew mixed with glyphosate herbicide (Roundup). One week later he developed significant dysphagia to solids and liquids. He denied any issues with dysphagia prior to this incident. At that time, EGD showed severe acute esophagitis with ulceration without eosinophils on biopsies. Follow up EGD one month later showed improved esophagitis, but biopsies revealed up to 80 eosinophils. The patient had ongoing dysphagia and reflux symptoms over subsequent years despite use of Omeprazole 40 mg daily, requiring intermittent dilations with limited benefit. EGD at our institution demonstrated a narrow caliber esophagus with a predominant stricture at the gastroesophageal junction and subtle strictures proximally. EoE Endoscopic Reference Score was 4 (Figure A). Esophageal biopsies showed greater than 150 eosinophils distally and 100 proximally. His symptoms improved after esophageal dilation (Figure B) and initiation of dupilumab 300mg subQ weekly.
Discussion: The mechanism of EoE pathogenesis remains unknown but is hypothesized to be due to complex interplay of environmental and genetic factors leading to disruptions in the esophageal epithelial barrier triggering an immune Th2 response. Though limited, human case reports and animal models have shown development of EoE after large allergen exposure. Currently, there remains limited data exploring the role of chemicals such as herbicides in the development of EoE. A study using mice exposed to glyphosate, the active ingredient in Roundup, showed esophageal eosinophil levels similar to those in mice who underwent protocols to induce EoE. A large cross-sectional, case control study found higher odds of EoE with decreasing population density, which may indicate that herbicide exposure in rural environments could contribute to EoE pathogenesis. This case demonstrates a novel presentation of EoE after accidental Roundup ingestion where glyphosate is the suspected trigger for EoE development. More studies are needed to establish a clearer link between herbicide exposure and EoE development.

Figure: Figure A before dilation

Figure: Figure B after dilation
Disclosures:
Flavio Bonilla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adam Spandorfer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Megan Chan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Westrich indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Flavio Bonilla, MD1, Adam Spandorfer, MD1, Megan Q. Chan, MD2, David J. Westrich, MD3. P2843 - EoE Triggered by Roundup Herbicide Ingestion, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
